Scientific Development in China:Key Problem Tackling for Poverty Alleviation I
GENERAL PREFACE
Wang Chen
Minister of the State Council Information Office of the People's
Republic of China
Development is an eternal theme of human society. All the peoples of the world have struggled to find their own distinctive ways to explore a development road suited to their national conditions. Mong this road of development, they have accumulated valuable experience. The road a country takes towards development decides the future direction of that country's social and economic development. The series of books published under the commontitle Scientific Development in China show that China has, under the guidance of the Conceptof Scientific Outlook, made great achievements over the past decade since 2002 in such fieldsas the economy, justice, education, environmental protection, transportation, housing, ethnicpolicies, and poverty reduction. China has succeeded in enhancing its national strength and improving the quality of life for its people. Full of revealing facts and data, the series of books show how China has adhered to the Concept of Scientific Outlook in national economic andsocial development, an outlook which best suits the realities of China. The Concept of Scientific Outlook keeps up with the prevailing trends of the times, and it will lead China towards a great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
China's scientific development takes economic construction as the main focus of its work and it lays great emphasis on the need for coordinated development. According to theprinciple of scientific development, upholding development is the top priority, and efforts must be made to continuously emancipate and develop the productive forces of the nation,so as to promote sound and rapid economic development and meet the growing needs of the people and economic development. In the meantime, efforts must be made to focus on the work of coordinated development in five fields such as urban and rural development, regionaldevelopment, economic and social development, harmonious development between Man and Nature, and domestic development and the program of reform and opening up to the outsideworld. While pressing ahead with economic development, efforts will be made to take intoaccount all aspects of development requirements, so as to bring into full play various socio-economic sectors to bring about all-round social and economic development.
China takes scientific development as the means of transforming the development modeand stresses the need for sustainable development. Now, China is making efforts to optimize itseconomic structure, improve its overall quality and efficiency, and to accelerate the constructionof a resource-saving, environmentally friendly society, so as to enhance the sustainability of social and economic development.
Chinas scientific development takes the interests of the people as its starting point. It emphasizes the strength and role of the people, and works towards allowing the people to share common benefits. By fully mobilizing the enthusiasm, initiative and creativity of the broadmasses of the people, efforts are made to mobilize and organize hundreds of millions of people to devote themselves to the practice of scientific development, so that the fruits of development could be shared by the broad masses of the people. In the meantime, efforts are made toimprove the people's ideological and moral qualities and scientific and cultural qualities,continuously improve the quality of life and health of the people, and work to ensure all of the Chinese people enjoy all aspects of economic, political, cultural, and social rights and interests.The development road that China is following will be enormously beneficial to the Chinese people. What is more, it will make a significant contribution to human developmentand progress!
PREFACE
Poverty is the common challenge facing the international community. It isthe essential requirement of socialism, the major task of the reform and opening upand socialist modernization as well as the unswerving goal of the Chinese people to eradicate poverty, improve people's livelihood and achieve common prosperity.As the world's most populous developing country, China has a weak foundation for economic development and a large poor population and the phenomenon of imbalances is prominent. Poor people in China are mainly concentrated in rural areas and China's poverty reduction, to a large extent, is tosolve the problem of rural poverty.
Always taking poverty alleviation as an important development goal andtask, the Chinese government strives to make the outcome of economic and social development benefit all the people. Since the reform and opening up, China hasofficially launched the organized, planned, large-scale development-orientedpoverty alleviation, successively developed the "Seven-year Priority Poverty Alleviation Program (1994-2000)" and the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of China's Rural Areas (2001-2010)", clarified the guiding ideology,objectives and tasks as well as the policies for poverty alleviation and development,took it as an important part of the national modernization strategy to promotepoverty reduction, constantly increased investment, made innovations to the poverty alleviation and development mechanism, steadily promoted the povertyalleviation and development and made remarkable achievements. Since the 16thNational Congress of the CPC, China has made new progress in poverty alleviationand development, basically solved the livelihood, food and clothing problemof rural residents, significantly changed the appearance of impoverished areas,gradually improved the national pro-poor policy system, innovated the institutional system and achieved the millennium development goal of halving povertyahead of schedule, making a great contribution to the global poverty reductionand embarking on a path of poverty alleviation and development with Chinese characteristics.
Meanwhile, the industrialization, informatization, urbanization, marketizationand internationalization have been continuously deepened, the transformation ofthe mode of economic development has been accelerated, the national economymaintains steady and rapid growth, the overall national strength has been markedly enhanced and the social security system has been gradually improved,creating a favorable environment and good conditions for poverty alleviation and development. However, China is still and will be at the primary stage of socialism for a long time. The overall level of economic and social development is not high,the problem of unbalanced regional development is prominent and the deep-seated contradictions restricting the development of poverty-stricken areas still exist. There are still a large number of objects of poverty reduction, the problem ofrelative poverty is prominent, the phenomenon of returning to poverty happensoccasionally, the development of poverty-stricken areas, especially contiguous poor areas still lags behind and poverty alleviation and development is still an arduous task. The poverty alleviation and development in China has entered anew stage of consolidating the achievements in solving the problem of food andclothing, accelerating poverty reduction, improving the ecological environment,strengthening the capacity for development and narrowing the development gapfrom the stage of focusing on solving the problem of food and clothing.
Further promotion of poverty alleviation and development is a major initiative to coordinate urban and rural development, protect and improve people's livelihood, narrow development gap and help all people share the reformand development achievements, and an urgent need for building a moderately prosperous society and a harmonious socialist society. In 2011, the Chinese government developed the new outline for poverty alleviation and development to unify the idea and mobilize public participation, aiming at building a moderately prosperous society in all aspects by 2020. The Chinese government will do a good job in the new round of poverty alleviation and development with a greater determination, more efforts and more effective initiatives.
Charpter I History of China’s poverty Alleviation and Development
I. Institutional Reforms Promoted Poverty Alleviation (1978-1985)
In accordance with the poverty line set by the Chinese government, there were 250 million poverty-stricken people in China in 1978, accounting for 30.7% of the total ruralresidents. Many reasons led to large-scale poverty at this stage and the main reason was that theagricultural management system could not meet the needs of the development of productiveforces, resulting in low enthusiasm of poor farmers for production. Institutional reform,therefore, became a main approach to poverty alleviation.
The reforms launched by the Chinese government since 1978 first included the land management system reform: using the household contract management system to replace the collective operation system of the people's communes. The land system reform greatly stimulated the enthusiasm of farmers for labor service, thus greatly liberated the productive forces and improved the land productivity. At the same time, the gradual liberalization of the prices of agricultural products in rural areas and the development of township enterprises also contributed to rural poverty reduction. These reforms promoted the rapid economic development, benefited the poor through the enhancement of the prices of agricultural products, the agricultural transformation to higher value-added industries and rural labor employment in non-agricultural areas, and lifted poor farmers out of poverty, greatly alleviating rural poverty. From 1978 to 1985, according to statistics, the per capita output of grain in rural areas increased by 14%, the per capita output of cotton rose by 73.9%, that of oil plants grewby 176.4% and that of meat increased by 87.8%; the per capita net income of farmers increased by 2.6 times, the number of the poor whose food and clothing problem was not solved declined from 250 million to 125 million , the proportion of these people in rural residents dropped to14.8% and the number of poverty-stricken people declined by 17.86 million on average per year.
II Special Programs Promoted Poverty Alleviation (1986-2007)
Since 1986, the Chinese government has launched the large-scale planned, organized development-oriented poverty alleviation, which can be divided into three stages :
1986 - 1993, the stage of exploration
In the mid-1980s, driven by the reform and opening up policy, many rural areas in China witnessed rapid economic growth with development advantages, but the development of some regions lagged behind due to the restrictions of economic, social, historical, natural and geological conditions. The development gap between poverty-stricken regions and other areas, especially the eastern developed coastal regions in economy, society and culture was gradually widened. The problem of unbalanced development in rural China became prominent and the economic income of many low-income people could not meet the basic needs of their livelihoods.
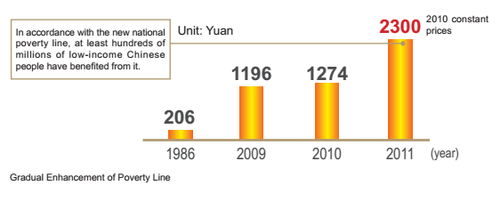
In order to further increase efforts on poverty alleviation, the Chinese government has adopted a series of major initiatives since 1986: It set up special poverty alleviation institutions, set the national poverty line (rural per capita net income below 206 Yuan that year), arranged special funds for key counties, developed special preferential policies, reformed the traditional model of relief-oriented poverty alleviation and determined the guideline of development-oriented poverty alleviation. After that, the Chinese government launched the large-scale planned, organized development-oriented poverty alleviation across the country and China’s poverty alleviation entered a new historic period. After eight years' unremitting efforts, the rural per capita net income of key impoverished counties increased from 206 Yuan in 1986 to 483.7 Yuan in 1993, the number of rural poor residents was reduced from 125 million to 80 million, with an annual decline of 6.4 million or 6.2% on average; and the incidence of poverty in rural areas dropped from 14.8% to 8.7%.
1994 - 2000, the stage of key problem tackling for poverty alleviation
In 1994, the "Seven-year Priority Poverty Alleviation Program" clearly put forward that we should concentrate the human, material and financial resources and mobilize all circles of society to basically solve the food and clothing problem of the rural poor in seven years by the end of 2000. This is the first poverty alleviation and development program with clear objective, clear targets, clear measures and clear deadline in the history of New China.
During the three years from 1997 to 1999, China solved the food and clothing problem of 8 million poor people every year, reaching the highest level since the 1990s. By the end of 2000, China basically achieved the goal of the "Seven-year Priority Poverty Alleviation Program".
During the period of the implementation of the "Seven-year Priority Poverty Alleviation Program", in the key counties for national poverty alleviation, the agricultural value added and industrial value added respectively increased by 54% and 99.3%, with an average annual growth of 7.5% and 12.2%; local fiscal revenue almost doubled, with an average annual growth of 12.9%; the food output rose by 12.3%, with an average annual growth of 1.9%, and rural per capita net income increased from 648 Yuan to 1337 Yuan, with an average annual growth of 12.8%. The food and clothing problem of the masses in the old revolutionary base areas of Yimeng Mountain area, Jingang Mountain area, Dabie Mountain area and the southwest areas of Fujian Province was basically solved and great changes took place to the appearance of some remote mountain areas and minority areas. After years of development and construction, the infrastructure and basic production conditions in Xingxi of Gansu and Xihaigu of Ningxia, the poorest regions in the history, were significantly improved and the poverty situation was alleviated.
2001 - 2007, the stage of deepening poverty alleviation
In 2001, the government formulated and issued the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of Chinas Rural Areas (2001-2010)”, continued to adhere to development-oriented poverty alleviation, identified 592 key counties in the central and western regions for national poverty alleviation and development, made the low-income poor the objectives of poverty reduction, identified 150,000 impoverished villages nationwide, adopted participatory poverty alleviation model, developed bottom-up poverty alleviation programs and strengthened the effective policies and measures. As of the end of 2007, the number of rural residents in absolute poverty was reduced from 32.09 million to 14.79 million and the number of low-income poor people declined from 62.13 million to 28.41 million, respectively with an average annual decline of 2.4714 million and 4.8171 million, and the per capital net income of farmers in the key counties amounted to 2278 Yuan.
III. Two-wheel Drive Promoted Poverty Alleviation (2008-2010)
Since the 16th National Congress of the CPC, a large-scale poverty alleviation pattern integrating special poverty alleviation, industrial poverty alleviation and social poverty alleviation has been gradually established based on the promotion by economic growth and special poverty alleviation programs in the past. The government clearly put forward that we should focus on entire village advancement, labor transfer training and industrialization poverty reduction in the poverty alleviation and development work and should reform the capital management method and improve the working mechanism. In October 2008, the Third Plenary
Session of the 17th CPC Central Committee proposed that we should insist on the guideline of development-oriented poverty alleviation and achieve effective convergence of the rural minimum living security system and pro-poor policies. In 2010, the per capita net income of Farmers in key counties reached 3273 Yuan, the number of rural low-income people dropped to 26.88 million, the number of rural residents in absolute poverty maintained below 10 million and the livelihood, food and clothing problem of rural residents was basically solved.
IV. New Stage of Poverty Alleviation and Development (since 2011 )
On May 27,2011, the Central Government and the State Council issued and implemented the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of Chinas Rural Areas (2011-2020)" (Zhong Fa No. [2011] 10, hereinafter referred to as the "New Outline") and pointed out that Chinas poverty alleviation development entered a new stage of consolidating the results achieved in solving the food and clothing problem, accelerating the pace of poverty reduction, improving the ecological environment, enhancing development capacity and narrowing development gap from the stage of solving the problem of food and clothing. The Central Work Conference on poverty alleviation and development held in November 2011 set the new national poverty line of 2300 Yuan of rural per capita net income (2010 constant price),92% up over the poverty line of 1196 Yuan in 2009, and 122 million people were the objects of rural poverty reduction, accounting for 12.7% of the total rural residents. At the end of 2011, the average minimum living allowance of the counties nationwide was 1718.4 Yuan and a total of 53.13 million people were covered by the rural minimum living security system. Taking contiguous regions with special difficulties as the main battlefield for key problem tackling in poverty alleviation, Chinas poverty alleviation and development cause has entered a new historic stage.
Charpter II Organization System for China’s Poverty Alleviation and Development
I. China's Government Poverty Alleviation Agencies at All Levels
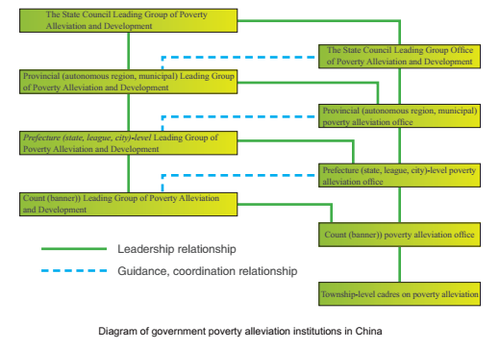
As the State Council's deliberation and coordination agency, the State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development was founded on May 16,1986 under the name of the State Council Leading Group for Economic Development of Poverty-stricken Areas and adopted the current name on December 28,1993. Vice Premier or State Councillor of the State Council in charge of rural work acts as the head of the Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development and the member units include the General Office of the State Council, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development, the General Political Department, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Agriculture, the People's Bank, Ministry of Civil Affairs, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Science and Technology, the State Ethnic Affairs Commission, Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, Ministry of Land and Resources, Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, Ministry of Transport, Ministry of Water Resources, Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Health, Population and Family Planning Commission, State- owned
Column 1: Member Units of the State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development The State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development has 33 member units, namely the General Office of the State Council, the General Political Department, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Agriculture, the People's Bank, Ministry of Civil Affairs, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Science and Technology, the State Ethnic Affairs Commission, Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, Ministry of Land and Resources, Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, Ministry of Transport, Ministry of Water Resources, Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Health, Population and Family Planning Commission, State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC), the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television (SARFT), the Statistics Bureau, Forestry Bureau, Tourism Bureau, the Agricultural Bank, All-China Federation of Supply and Marketing Cooperatives, All-China Federation of Trade Union, the CYL Central Committee, All-China Women's Federation, China Disabled Persons' Federation and All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce.
Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council (SASAC), the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television (SARFT), the Statistics Bureau, Forestry Bureau, Tourism Bureau, the Agricultural Bank, All China Federation of Supply and Marketing Cooperatives, All-China Federation of Trade Union, the CYL Central Committee, All-China Women's Federation, China Disabled Persons' Federation, All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce, etc.
The basic tasks of the Leading Group are: To organize investigations and researches;develop poverty alleviation and development guidelines, policies and programs; examine and approve plans for the allocation of central anti-poverty funds; help solve major problems in poverty alleviation and development; and check the work of provincial and municipal leading groups of poverty alleviation and development, etc.
Under the Leading Group for Poverty Alleviation and Development, it has set up an office, i.e. the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development (LGOP) to be responsible for routine work, including: Research and formulation of poverty alleviation and development policies and planning and the organization of implementation; Coordination of the poverty alleviation work of all circles of society, coordination and organization of fixed-point poverty alleviation of central organs and the anti-poverty work of eastern developed regions to support western poverty-stricken areas; Determination of poverty lines for rural areas and key counties for national poverty alleviation and development, research of the proposals on key county identifying and cancelling; Organization of statistics and dynamic monitoring on poverty alleviation and development work, giving instructions to the statistical and monitoring work of poverty alleviation system; Coordination and development of the allocation plan for central government's anti-poverty funds, instruction, inspection and supervision of the use of anti-poverty funds, instruction of inter-provincial key poverty-relief projects; Organization of poverty alleviation and development advocacy work; Responsible for relevant international exchanges and cooperation in the field of poverty alleviation; organizing poverty alleviation and development trainings for cadres of poverty-stricken areas in the country; Undertaking other tasks assigned by the State Council leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development.
Governments of relevant provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities, prefectures (cities) and counties have also established corresponding organizations to be responsible for local anti-poverty work. China practices the level-by-level responsibility system with the provincial authority as the main player in its administrative leadership of anti-poverty work. The provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities, especially provinces and autonomous regions with a large number of poverty-stricken areas, have put poverty alleviation and development high on their agendas, and formulated concrete local implementation plans in line with the state's poverty relief program.
II. Public Institutions and Social Organizations Directly under the LGOP
(I) Public institutions directly under the LGOP
1. Foreign Capital Project Management Center of the LGOP
Founded in February 1995, Foreign Capital Project Management Center (FCPMC) of the LGOP is a central project management agency engaged in foreign-funded poverty alleviation and development in the field of poverty reduction. According to the anti-poverty strategies and poverty alleviation and development policies developed by the Chinese government, targeting at impoverished regions and people, FCPMC makes use of domestic and foreign capital, information, technologies and management experience to enhance the income level of the poor and promote the sustainable development of economy, society and environment in poverty-stricken areas and the enhancement of self-development capabilities of the poor masses.
2. International Poverty Reduction Center in China
Founded in May 2005, the International Poverty Reduction Center in China (IPRCC) is a public institution directly under the LGOP and is also an international poverty alleviation agency jointly launched by the Chinese government and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). As a result, IPRCC is not only an important channel for the Chinese government to conduct South-South Cooperation, but also the exclusive international platform in the world engaged in the research, training, exchanges, cooperation and knowledge-sharing in the field of poverty reduction. In September 2005, Chinese President Hu Jintao noted at the UN Anniversary Summit that: "The International Poverty Reduction Center in China was established in Beijing with a mandate to contribute to worldwide poverty reduction."
3. Cadres Training Centre for Poverty-Stricken Areas of China
Founded in 1990, the Cadres Training Centre for Poverty-Stricken Areas of China is a professional agency engaged in cadre training for poverty alleviation system, farmer training management, information technology development, statistical work and monitoring in the field of poverty alleviation. Since its inception, to achieve the main objectives and tasks of poverty alleviation and development of the country, the Center has carried out a number of large-scale trainings for nearly 20,000 county-level party and government leaders in poverty-stricken areas to help them raise awareness, learn policies and update their concepts.
4. Poverty Alleviation and Development Center of China
Founded in 1998, the Poverty Alleviation and Development Center of China is the oldest public institution launched by the LGOP. Under the guidance of LGOP and the relevant ministries, to promote industrialization-based poverty alleviation and help rural households increase income and become rich, it provides comprehensive development services for the economic development of poverty-stricken areas. Its specific work includes: To provide information on labor services, talents, technologies, products and capital as well as consulting service for impoverished areas; to organize labor trainings and output; to help poor areas to establish economic ties with the external world, to organize commodity circulation, to develop internal and external trade; to promote agricultural applicable technologies suitable for poverty-stricken areas, etc.
(II) Social organizations directly under the LGOP
1. China Foundation for Poverty Alleviation
Founded in March 1989, China Foundation for Poverty Alleviation (CFPA) is a national non-government non-profit social organization engaged in poverty alleviation. It is committed to building a platform for interactions between the rich and the poor, advocating charity, making innovations to the mode of poverty alleviation, promoting the development of public welfare policies and promoting the development of civil society. It has organized the "Poverty Alleviation China - Visiting One Thousand Villages and Ten Thousand Households for Building a Harmonious Society", advocacy projects such as China Poverty Eradication Award Appraisal, Action 120: Maternal and Infant Health Project, Microfinance Project, New Great Wall Project - Self-improvement of Poverty-stricken College Students, Emergency Relief, Love Package, Love and Family - Orphan Support and other assistance projects, mobilized domestic and foreign organizations, institutions, enterprises and the public to donate money and materials to help vulnerable groups.
2. China Association of Poverty Alleviation and Development
Founded in June 1993, China Association of Poverty Alleviation and Development is a national non-profit social organization under the guidance of the LGOP The Association's tenet is to mobilize social forces, guide economic organizations in diverse forms of ownership to carry out industrial poverty alleviation work and safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of members to achieve the win-win situation of social benefits and returns on investment in poverty alleviation and development. In recent years, it has successively organized the industrial poverty alleviation to solve the drinking water problem of 820,000 people, education-based poverty alleviation of donating 70 million Yuan for poor students, "green computer" donations, rural poverty reduction by information technology, cultural poverty alleviation such as "Jointly Enriching Our Home" and donation of paintings and calligraphy works, and poverty-relief projects such as a series of activities to praise typical characters in the field of poverty reduction in China, poverty alleviation by special brands and donations for snow disasters and earthquake.
3. China Council for the Promotion of Construction in the Old Revolutionary Base Areas
Founded in 1990, China Council for the Promotion of Construction in the Old Revolutionary Base Areas is a national non-profit united social organization consisting of the old cadres, old generals, old experts and community leaders enthusiastic in the construction of old revolutionary base areas and the enterprises and institutions committed to the construction of old revolutionary base areas. Its tenet is to serve the people in the old revolutionary base areas wholeheartedly, adhere to the nature of non-profit societies and the spirit of selfless dedication, follow the principle of doing tangible things and seek practical benefits for the people in the old revolutionary base areas; fully implement the scientific concept of development and assist the party and government to promote the economic development, policy and cultural construction, social development and ecological civilization in the old revolutionary base areas.
4. The China Social Entrepreneur Foundation
Founded in 2007, the China Social Entrepreneur Foundation (hereinafter YouChange) is a new non-profit social welfare organization established with approval of the State Council of the People's Republic of China and registered in the Ministry of Civil Affairs with independent legal entity qualification. It is the first domestic innovative private foundation jointly launched by the well-known entrepreneurs of Mainland China, HK China and Taiwan China. With the tenet of building a people-oriented harmonious society and the main operating model of participatory funding.
Charpter III China’s Achievements in Poverty and Development Since the Sisteenth National Congress of the CPC
Since the 16th National Congress of the CPC, the number of the rural poor in China has been significantly reduced, poverty-stricken areas have witnessed comprehensive economic development, significant improvement in infrastructure and constant progress in social undertakings, the trend of ecological deterioration has been initially curbed, and livelihood, food and clothing problem of rural residents has been basically solved and China has become the first developing country in the world to achieve the UN Millennium Development Goal of halving poverty ahead of schedule.
I. A substantial decline in rural poverty
The Chinese government started to set national poverty line in 1986. Meanwhile, in order to conduct international cooperation and exchanges in the field of poverty reduction, it has also conducted comparative study on the international poverty line. No matter which poverty line is used, the number of poverty-stricken people in rural China has been significantly reduced. China has achieved the UN Millennium Development Goal of halving poverty by 2015 ahead of schedule and basically solved the livelihood, food and clothing problem of rural residents.
In accordance with China's poverty line in 1986
This standard used the Engel coefficient method, also called food poverty method. At that time, all those with per capita net income below 206 Yuan were regarded as poverty-stricken people. After that, the poverty line was adjusted year by year according to the price index. Based on this poverty line, China had 250 million poor people in 1978 and 125 million poverty-stricken people in 1986. From 2001 to 2008, the number of poor people based on this standard was reduced from 29.27 million to 10.04 million. After that, poverty monitoring reports no longer release the number of poor people under this poverty line as the figure was too small. According to the development trend, the number of poverty-stricken people under this standard will not exceed one million, accounting for less than 0.1% of the rural residents.
In accordance with China's poverty line in 2008
In order to meet the needs of building a moderately prosperous society, in 2001, the state included the low-income people whose food and clothing problem had been basically solved into the minimum living security system. In other words, all the low-income rural residents with per capita net income of less than 865 Yuan at the end of 2000 were identified as objects of poverty reduction. The low-income standard and poverty line were used at the same time and adjusted year by year according to the price index. In 2008, in accordance with the requirements of enhancing the poverty line of the 17th National Congress of the CPC, the government indentified all the rural residents living below the low-income standard as objects of poverty reduction and comprehensively implemented pro-poor policies. This is the first time for China to enhance the poverty standard. In 2001,90.29 million people lived below this standard. In 2010, this figure dropped to 26.88 million. After that, with the significant enhancement of Chinas poverty line, the government no longer released the number of the people living below this poverty line. According to the development trend, the number of poverty-stricken people under this standard has been reduced to less than 20 million.
In accordance with WB's poverty line of $1.25
"The World Bank conducted an international comparison of poverty situation with the purchasing power parity theory and proposed the use of the poverty line of $1.25 per person per day in the lowest-income countries. According to the estimates of the World Bank, in 2002, 363 million Chinese people lived below this poverty line. In 2008, this figure was reduced to 131 million.
In 2011, China again significantly enhanced the poverty standard and set the new national poverty line of 2300 Yuan (2010 constant price) of rural per capita net income,92% up over the previous poverty line. At the end of 2011,122 million rural residents lived below this poverty line.
II. Comprehensive Economic Development in Impoverished Areas
Firstly, the comprehensive economic capabilities of counties have been constantly strengthened and the industrial structure of impoverished regions has been further optimized. From 2002 to 2010, the regional GDP per capita in the 592 key counties for national poverty alleviation and development increased from 2842.6 Yuan to 11170 Yuan, with an average annual growth of 16.4%. In the same period, the value added of the primary, secondary and tertiary industry was respectively adjusted from 35%,33.1% and 32% to 22.4%,46% and 31.6%, and the employment rate of labor force respectively changed from 85.2%,6.9% and 7.9% to 76.3%,13.8% and 9.9%. From 2002 to 2011, the proportion of migrant workers among the labors in counties rose from 14.5% to 24.2%.
Secondly, local financial capability has been further enhanced. From 2002 to 2010, local general budget revenue of key counties increased from 28.33 billion Yuan to 135.5 billion Yuan, and expenditure on agriculture in the fiscal expenditure increased from 3.23 billion Yuan to 110.56 billion Yuan. In the same period, per capita local general budget revenue increased from 123 Yuan to 559 Yuan, with an average annual growth of 18.3%.
Thirdly, the level of consumption of farmers has been constantly enhanced. The rural per capita net income of key counties rose from 1305 Yuan in 2002 to 3985 Yuan in 20L1, with an average annual growth of 11.8%. In the same period, the per capita consumption expenditure increased from 1131 Yuan to 3453 Yuan, with an average annual growth of 11.8% (Price factor not considered). In this period, the proportion of farmers' expenditures on household equipment, transportation and housing in the key counties gradually increased and the Engel coefficient dropped from 0.574 to 0.477.
III. Significant Improvement of Infrastructure
From 2002 to 2010, in the 592 key counties for national poverty alleviation and development,52.456 million mu of additional basic farmland was developed,952,000 kilometers of highroads were newly built or rebuilt,35.061 million square meters of education and health buildings were set up and the drinking water problem of 56.757 million people and 49.993 million heads of livestock was solved. From 2002 to 2011, in the key counties, the proportion of rural households drinking tap water and deep well water rose from 51.7% to 63.5%, the proportion of the natural villages with access to highroads, electricity, telephone line and radio and television program respectively increased from 72.2%,92.9%,52.4% and 83.7% to 89.9%,98.5%,96.3% and 95.4%. Farmers' per capita living space increased from 20.1 square meters to 27.7 square meters and the proportion of the rural households using flush toilets rose from 1.8% to 10.2%.
IV. Constant Progress in Social Undertakings
Rural compulsory education has been strengthened and positive progress has been made in eliminating illiteracy among the young and adults. As of the end of 2011, the enrollment rate of school-age children of 7-15 in the key counties reached 97.4%; and the adult illiteracy/ semi-illiteracy rate was 9.5%, down 5.5% compared to 2002. The new rural cooperative medical system has covered all farmers and the primary health care service system has been constantly improved. As of the end of 2011, healthy people in the national key counties accounted for 92.6% of the total,94% of the sick could receive time medical services, all towns were equipped with hospitals and 83% of the villages got clinics. The construction of public cultural service system in poor areas was continuously strengthened.
V. The Trend of Ecological Deterioration of Poverty-stricken Areas Has Been Initially Curbed
From 2002 to 2010, the key counties returned farmland of 149.235 million mu to forests or grassland and increased forest area of 226.434 million mu. The proportion of rural households whose source of drinking water was contaminated in the key counties dropped from 15.5% to 5.1% and the proportion of rural households for whom it was difficult to get fuels declined from 45% in 2002 to 28.9% in 2011.
Charpter IV China’s Poverty Alleviation and Development Policices and the Policy Implemeentation
Since the beginning of the new century, Chinas national economy has witnessed steady and rapid growth and Chinas comprehensive national strength has been constantly enhanced. Economic growth has not only created material premise for the alleviation and eradication of poverty, but also provided development opportunities for the poor and created conditions for livelihood policies and investment in poverty alleviation. From 2003 to 2011, China's average annual economic growth rate was 10.7%, while the average growth rate of the world economy over the same period was only 3.9%. The proportion of Chinas GDP in the world's total economic output increased from 4.4% in 2002 to 10% in 2011, and the rank of Chinas GDP in the world rose from No.6 in 2002 to No.2 in 2010 and 2011. Always adhering to the theme of scientific development and the mainline of speeding up the transformation of economic development mode, the Chinese government constantly enhanced the development conditions of poverty-stricken areas, improved the scientific and cultural qualities of the masses, made full use of local natural conditions and labor resources and gave play to the comparative advantages to promote the economic and social development in poverty-stricken areas. In the process of poverty alleviation and development, the state included poverty alleviation and development in the overall planning for national economic and social development, formulated and implemented relevant policies to promote the development of poor rural areas, gave priority to investment in poverty alleviation in allocating public financial budget and poverty-stricken areas in providing public financial support and constantly increased support for impoverished areas.
I. "Three Rural" Development Policies
"Three rural issues" refer to the key issues concerning farmers, countryside and agriculture. Since the 16th National Congress of the CPC, China has implemented the strategy to balance urban and rural economic and social development, the policy for industry to support agriculture and for cities to promote rural development and the policy of "giving more, taking less and loosening control", and vigorously implemented relevant policies to support agricultural development and benefit and enrich farmers, which comprehensively promoted the economic and social development in rural areas and benefited poverty-stricken areas and the rural poor.
"Giving more" means that we should increase investment in agriculture, create conditions for income growth of farmers, improve and implement the agricultural subsidy policy, agricultural product price policy and poverty alleviation and development policies, and strive to provide necessary public products and social welfare for rural areas. "Taking less" means to reduce the burden on farmers and vigorously promote rural tax reform. Zhrough step-by-step reform of the urban-rural dual investment system, the state intends to significantly increase investment in rural education, culture and medical services in order to effectively reduce the burden on farmers. "Loosening control" means to liberate rural operation systems, get rid of institutional restrictions and policy obstacles, give farmers more decision-making power and mobilize the enthusiasm of farmers and herdsmen for production through system innovation and policy development to promote rural economic development.
(I) Promote rural tax reform
In 2000, China launched a far-reaching reform of rural taxes. First, cancel the agricultural tax. The government first cut the agricultural tax rate to reduce farmers' burdens. By 2006, the Agriculture Ordinance had been abolished, the agricultural taxes had been canceled nationwide and farmers were no longer required to pay agricultural taxes according to relevant law. Second, abolish taxes on special agricultural products. Since 2004, China has canceled the taxes on special agricultural products except tobacco. Third, cancel livestock slaughter tax. Slaughter tax was first canceled in pilot areas for tax reform. In 2006, the State Council officially abolished the "Provisional Regulations on Animal Slaughter Tax". Fourth, cancel the animal husbandry tax. In 2005, the state comprehensively canceled the livestock tax. The abolition of agricultural tax, animal husbandry tax, taxes on special agricultural products and slaughter tax can reduce the burden on farmers by 133.5 billion Yuan per year.
(II) Implement agricultural subsidy policy
Learning from the international experience, China has started to explore the establishment of a system of agricultural subsidies in line with WTO rules and national conditions. The core of the system is "the Four Subsidies": The first is the direct subsidy for grain producers, which is given to farmers according to the grain field size they farm, targeting at main grain producing regions. The second is the subsidy for production materials. This subsidy is calculated according to the price changes of essential farm inputs such as fertilizer, pesticide and diesel so as to offset the increase of grain production cost created by price rise of inputs. The third is the subsidy for using improved varieties. This is a subsidy provided by the central government to farmers who purchase and use improved crop varieties to encourage the use of improved varieties. The fourth is the subsidy for the purchase of farm tools and machines. It aims to encourage farmers to purchase state-of-art tools and machines to promote mechanization and physical backup for production. As of 2011, a total of 143.9 billion Yuan of"the Four Subsidies" had been issued.
(III) Increase investment in"three rural issues"
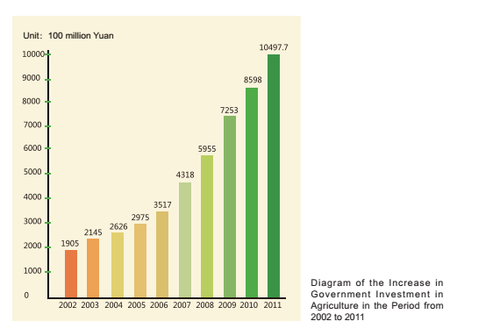
Taking the increase of investment as the fundamental measure to promote agricultural development, the government has clearly pointed out that we must improve the security system for agricultural inputs, adjust the financial support, investment in fixed assets and the credit investment structure to ensure the growth rate of financial investments in agriculture is higher than that of regular income, significantly increase government investment in rural infrastructure and social undertakings, significantly increase investment in agriculture with additional revenue from government land transfer and farmland use tax, and significantly increase investment in rural public construction projects in central and western regions. According to statistics, from 2004 to 2011, the central government's investment in the "three rural issues" increased from 262.6 billion Yuan to more than 1.04977 trillion Yuan, with an average annual growth of more than 20%.
(IV) Improve the rural basic management systems
In 2002, China formulated the "Rural Land Contract Law" to empower farmers the long-term rural land contract management right protected by the law. The "Property Law'promulgated in 2007 further confirmed that the land contract and management rights are usufructuary rights. In 2008, the "Decision of the CPC Central Committee concerning Several Major Issues on Promoting Rural Reform and Development" of the Third Plenary Session of the 17th CPC Central Committee pointed out that the existing land contract relationships should remain stable and unchanged for a long time. On the basis of maintaining existing land contract relations stable and unchanged for a long time, according to relevant laws and the principle of voluntariness and paid service, the government allows farmers to transfer the land contract and management rights in various forms and encourages the development of professional large family operation, family farms and farmers' professional cooperatives in the regions where conditions permit. The government has launched the reform of collective forest right system so that farmers will really have forest land contract and management rights and ownership of trees. It also implemented various preferential policies to develop forest economy and forest tourism and increase farmers' income.
(V) Implement farmer-benefiting policies in poverty-stricken areas
The state implemented pilot program of exemption from agricultural tax and the "two exemptions and one subsidy" policy for rural compulsory education (rural compulsory education students from poor families are exempted from textbook fees and miscellaneous fees, living expense subsidies are issued for boarding students) and reduced or canceled matching projects of county level or below for the basic public welfare projects newly arranged by the government in the key counties for national poverty alleviation and development, and gave priority to poor regions and poverty-stricken people in implementing policies to support agriculture and benefit farmers. So far, these policies have been implemented nationwide.
(Vl) Comprehensively establish the rural social security system
It is the most basic means for steadily solving the food and clothing problems of the poor to provide the poor with basic social security. The "Decision of the CPC Central Committee concerning Several Major Issues on Building A Socialist Harmonious Society" launched by the 6th Plenary Session of the 16th CPC Central Committee clearly pointed out that the "basic establishment of a social security system covering both urban and rural residents"" is one of the objectives and main tasks of building a socialist harmonious society.
In the arrangement of the new rural cooperative medical system, rural minimum living security system and the new rural social endowment insurance system, the central government has given priority to central and western regions. As of 2011,2637 counties (cities, districts) had implemented the new rural cooperative medical system and the participation rate reached 97.5%; the total new rural cooperative medical fund expenditures amounted to 171.02 billion Yuan, benefiting 832 million people.
In 2007, the state decided to comprehensively establish the minimum living security system in rural areas nationwide and included all the rural residents whose annual household per capita net income was below the poverty line into the system in order to steadily, permanently and effectively address the food and clothing problems of the rural poor. Rural minimum living standard was determined by local government of county level or above based on the annual costs for local rural residents to maintain basic life, including the costs for food, clothing, water and electricity, etc. As of the end of 2011, the rural minimum living security system had coveted 26.626 million households and 53.135 million people. In 2011, a total of 60.69 billion Yuan of subsistence allowance was issued to the rural poor, the average subsistence allowance in rural China was 143.2 Yuan per person per month and the average monthly subsidy is 96.4 Yuan per person.
For the dependent elderly, weak, orphaned, widowed and disabled who have lost the ability to work, China implemented the five-guarantee system to support them and provide them with material assistance in food, clothing, housing, medical care and funeral services. As of the end of 2011, the five-guarantee system had covered a total of 5.313 million rural households and 5.52 million rural residents, almost covering all eligible objects.
In 2009, China launched the pilot program of the new rural social endowment insurance. As of July 2011, the program had covered 60% of the rural areas and a total of 493 key counties for national poverty alleviation and development were identified as pilot areas, accounting for 83% of the total. A total of 326 million people were insured in the pilot areas. The sources of funding of the new rural social endowment insurance system include individual contributions, collective allowances and government subsidies. The payments include the basic pension and individual account pension payments. The central government gives the central and western regions the basic pension in full and a 50% subsidy to the eastern regions. As of the end of 2012, the new rural endowment insurance system is expected to cover all rural areas.
II. Regional Development Policies
(I) Western development strategy
Since the end of the last century, the Chinese government has started to implement the western development strategy. China's western regions have relatively poor natural conditions and backward infrastructure, concentrated with poor people. The western development covered 12 provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities), namely Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Sichuan, Chongqin8, Yunnan, Guizhou, Tibet Autonomous Region, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and three minority autonomous prefectures, covering a land area of 6.85 million square kilometers, accounting for 71.4% of the total land area of the country.
Over the past decade, the western regions constructed ten major projects, namely the construction of Ningxia Railway, Yuhuai Railway, western highroads, western airports, Chongqing Light Railway, Sebei- Xining- Lanzhou Gas Transmission Pipelines, Qinghai's 300,000-ton potash fertilizer project, western returning farmland to forests and grassland, infrastructure construction for western universities and Zipingpu hydro-junction project of Sichuan; implemented the project of Qinghai-Tibet Railway, West Gas to East and West Electric Power to East; launched large-scale airport, railway and highroad construction and carried out pilot projects of large area of returning farmland to forests and grassland, etc.
The sound development of western regions promoted poverty alleviation and development to develop towards a deeper degree and a more extensive range. In the construction of the irrigation works, returning farmland to forests and resources development in the western development, priority was given to the poor regions in the west with relatively vulnerable ecological environment, backward economy and a deeper degree of poverty such as the southern area of Xinjiang, eastern border areas of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Wuling Mountain area, Wumeng Mountain area, border mountain areas in the western areas of Yunnan and Qinba Mountain - Liupan Mountain area. The highroad building was further extended to impoverished areas to connect the counties in poor areas with national and provincial roads. In infrastructure construction, the government mainly used the labor force of impoverished regions in order to increase cash income of the poor.
(II) Strategy to promote the rise of Central China
After the development of the east coastal regions and the occurrence of Huangbohai Region, Yangtse River Delta and Pearl River Delta, the central government put forward the strategy of "Western Development" and the central regions were almost forgotten by the people with economic development seriously lagging behind the east coastal areas. To this end, in 2004, the government put forward the major strategy of the "Rise of Central China". Central regions refer to Shanxi, Henan, Anhui, Hunan, Jiangxi and Hubei Province of China.The state supports the central regions to play geological and economic advantages, accelerate the pace of reform and opening up and development, strengthen the construction of modern agricultural bases and major commercial grain bases, strengthen infrastructure construction, develop competitive manufacturing industry and high-tech industries and enhance the level of industrialization and urbanization.
It is an important content of the strategy to promote the rise of central China to increase support for impoverished areas. Since the implementation of the "Some Opinions on Promoting the Rise of Central China" (Zhong Fa (2006) No.10) in 2006, the government conducted concentrated contiguous development of the central regions concentrated with poor people, old revolutionary base areas and minority areas, increased financial investment in underdeveloped areas and the
work-relief fund, conducted poverty alleviation, provided credit loans, arranged construction projects and developed education and health undertakings according to the Western Development policy. Meanwhile, it increased support for the regions with special difficulties such as arid areas with little water, the areas with serious problem of soil erosion and flood diversion and storage areas, and promoted the implementation of village-reaching telephone line projects to enhance the level of communications of underdeveloped regions.
(III) Strategy to revitalize the old industrial bases in northeast China
The strategy to revitalize the industrial bases in northeast China is the objective requirement of the national strategy to coordinate regional development. Since the implementation of the strategy to revitalize the industrial bases in northeast China in 2004, the economy with different types of ownership has been booming, the economic structure has been further optimized, the independent innovation capability has been significantly enhanced, the level of opening up has been obviously raised, the infrastructure conditions have been improved, key livelihood problems have been gradually solved and great changes have taken place to urban and rural areas. To further bring the agricultural advantage of northeast regions into play, the state increased support for main grain producing areas, strengthened the construction of farmland and water conservancy projects, improved the agricultural production conditions and significantly increased the income of farmers.
In addition, the state has successively issued a series of regional development policies to promote the economic and social development in Tibet, the Tibetan areas of Sichuan,Yunnan, Gansu and Qinghai, as well as Xinjiang, Guangxi, Chongqing, Ningxia, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, Yunnan, etc, and promoted rural poverty alleviation and development, taking it as a policy priority.
III. Poverty Alleviation and Development Policies
(I) Steadily increase investment in poverty alleviation
The sources of funding for the Chinese government's anti-poverty actions mainly include the anti-poverty funds from the central government and the matching funds from local governments. The anti-poverty funds from the central government are mainly issued through transfer payment of the central government. Special anti-poverty funds for poor areas mainly include development funds, work-relief funds, subsidies for agricultural development in the "Three West Areas", development funds for minority areas, anti-poverty funds for state-owned impoverished farms, anti-poverty funds for national poor forestry centers and poverty-relief loan interest fund.
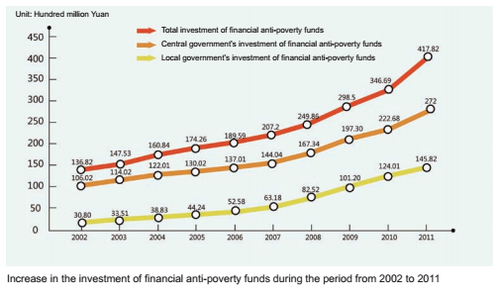
Over the years, the central and local governments at all levels have continuously adjusted the structure of financial expenditure and gradually increased the financial investment in poverty alleviation. The anti-poverty funds allocated by the central government increased from 10.602 billion Yuan in 2002 to 27.2 billion Yuan in 2011, with an average annual growth of 10.5%. A total of 161.235 billion Yuan was invested in the decade. Local governments at all levels also continued to increase investment in poverty alleviation. The financial anti-poverty funds were mainly put in contiguous impoverished regions identified by the state and the key counties and poor villages for poverty alleviation and development, with priority given to western regions, poor minority areas, poor border areas and impoverished old revolutionary base areas.
(II) Poor area targeting mechanism
In the past three decades, the key areas for China's poverty alleviation experienced a process of transition from impoverished counties, key counties and poor villages to contiguous poor areas, key counties and poor villages. In 2001, according to the principle of concentrating contiguous poor areas, the state gave priority to the central and west minority areas, old revolutionary base areas, border areas and the regions in special difficulties concentrated with poor people in the poverty, alleviation and development, and identified 592 key counties for poverty .alleviation and development in the above four types of areas. It is the main method of regional targeting of Chings poverty alleviation work and an important starting point for the government to promote the anti-poverty work to identify key counties for national poverty alleviation and development and provide support, aiming at further improving the targeting mechanism of anti-poverty work and make more poor people in the poorest regions receive policy support from the government. In addition, the government also identified 148,000 impoverished villages. Focusing on infrastructure construction, development of social undertakings, industrial development and the construction of spiritual civilization and grassroots organization, the government developed specific poverty alleviation planning for various villages using participatory approach and organized the implementation step by step every year to comprehensively improve the production, living and development conditions of poor areas. Key counties and poor villages are the key areas for the poverty alleviation and development in the first decade of the new century.
In 2011, in accordance with the principle of "focusing on contiguods areas, highlighting priorities, national coordination and complete division", taking poverty degree-related indexes as the standards, including 2007-2009 GDP per capita at county level, financial general budget revenue per capita at county level and rural per capita net income at county level (these three indexes were all below the western average in the same period), the state divided the connected counties with similar weather, same traditional industries, similar culture and customs and similar causes of poverty as contiguous impoverished regions. In the process of dividing these regions, the state gave priority to minority counties, old revolutionary base districts and counties and border counties through increasing weight and divided the country into 11 contiguous poor regions, namely Liupan Mountain area, Qinba Mountain area, Wuling Mountain area, Wumeng mountain area, the rocky desertified areas of Yunnan, Guangxi and Guizhou, the western border mountain areas of Yunnan Province, the southern foot of Daxing'anling Mountain, Yanshan - Taihang Mountain area, Lvliang Mountain area, Dabie Mountain area and Luoxiao Mountain area, covering a total of 505 counties.Plus Tibet, the Tibetan area of Sichuan and the south area of Xinjiang where special policies were implemented, these areas are regarded as the main battlefield for poverty alleviation and the government increased investment and support for them. With 680 counties, these 14 contiguous poor areas have a land area of 3.917 million square kilometers and a population of 240 million. Among the 680 counties,440 are key counties for poverty alleviation, accounting for 64.7% of the total; and 371 are minority counties, accounting for 54.6%. Meanwhile, the government made it clear that we must continue to do a good job in poverty alleviation in the key counties and impoverished villages except the contiguous poverty-stricken areas and not change the original policy to support the key counties.
(III) Establish a large-scale pattern of poverty alleviation
With the economic development and social progress as well as the gradual development of national pro-poor strategies, to meet the requirements of not only guaranteeing people's survival but also promoting the development for anti-poverty work, China has gradually established the large-scale pattern of poverty alleviation integrating special poverty alleviation, industrial poverty alleviation and social poverty alleviation which support one another in the practice process of poverty alleviation. It is an important innovation in Chinas poverty alleviation and development and has built a platform and created conditions for the integration of resources and the formation of joint force under the new situation.
The causes of poverty are complex and comprehensive, so we need to implement many strategies simultaneously to solve the problem of poverty. Taking the improvement of the production and living conditions of the masses in impoverished areas and the infrastructure construction as pilot projects of poverty alleviation and development, the government needs to vigorously strengthen the construction of basic farmland and water conservancy projects, solve the safe drinking water problem of humans and animals, continuously improve the ability to withstand natural disasters, strengthen the road network construction in poor areas, improve the trunk roads, eliminate dead-end roads, focus on solving the problem of rural roads, accelerate rural electrification and the upgrading of rural power grid and increase efforts on renovating dilapidated houses in rural areas to solve the problem of basic housing security of poor households. With resources advantages, we should study the laws of the market, know clearly the market demand and develop competitive products to form unique regional leading industries, vigorously cultivate leading enterprises and promote the adjustment of industrial structure to increase farmers' income, develop various types of specialized cooperative organizations to improve the degree of organization of farmers and the ability of farmers to participate in market competition, and strengthen the construction of ecological environment in poor areas, which is related to the overall ecological security of the country. We insist on the conservation of priorities and natural recovery to reverse the trend of ecological deterioration in poverty-stricken areas from the source, consolidate the results achieved in returning farmland to forest or grassland and natural forest protection, promote the control of desertification and rocky desertiflcation and protect grassland and wetland resources. We have established and improved the ecological compensation mechanism to effectively improve the ecological environment of poverty-stricken areas and achieve a virtuous circle of population, resources and environment. We have always stressed that we should tackle key problems jointly with social forces, vigorously carry out fixed-point poverty alleviation and east-west cooperation in poverty alleviation, actively organize and mobilize the democratic parties, enterprises, institutions, colleges, the army and armed police to participate in poverty alleviation and development, and conduct positive publicity to make the whole society understand and pay attention to poverty and participate in poverty alleviation.
(IV) Improve the self-development capability of the objects of poverty reduction
Since the beginning of 2001, we've implemented the entire village advancement project, carried out the overall transformation and upgrading of water, electricity, roads, gas, housing system combined with the new rural construction, developed specialized pillar industries and strengthened the economic capability. We continued to implement ex situ poverty-relief relocation to improve the living environment and conditions for development and eliminate the basis for Intergenerational Transmission of Poverty. On a voluntary basis, -we combined the poverty-relief relocation, ecological immigration and the post- geological disasters immigration organically, giving full consideration to the resource conditions and carrying capacity of the resettlement areas, and implemented relevant measures for orderly relocation according to local conditions. At the same time, attaching importance to the nurturing and development of follow-up industries in the resettlement areas, we created jobs and improved the employability of labor forces to ensure the poor are relocated and resettled steadily and have opportunities to develop and get rich. We organized comprehensive quality education, further enhanced the gross enrollment rate of three-year pre-school education in poor areas, consolidated and improved the level of compulsory education, continued to improve the enrollment rate of high school and gradually eliminate illiteracy among young and middle-aged people. Focusing on promoting stable employment of the objects of poverty alleviation, the government provided living subsidies for the junior and senior middle school graduates from rural needy families to participate in work preparation training and strengthened the practical technical training of poor labors.
Charpter V China’s Poverty Alleviation and Development Models
I. Special Poverty Alleviation
Special poverty alleviation refers to the state's anti-poverty work supported by financial poverty-relief funds of the central government and organized by local governments at all levels and the relevant departments, including ex-situ poverty alleviation relocation, entire village advancement, work-relief program, poverty alleviation by industrialization, employment promotion and the construction of pilot poverty-relief projects and old revolutionary base areas according to the requirements of "provinces assuming the overall responsibility, counties taking charge of the implementation and poverty alleviation conducted for specific villages and households".
(I) Entire village advancement
In 2001, to adapt to the characteristics of large dispersion and small concentration of rural poverty situation, in accordance with the requirements of focusing on the work for specific villages and households, the State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development took entire village advancement as the top priority of 2001-2010 poverty alleviation and development work. Entire village advancement refers to the poverty alleviation and development measure targeting at the poor based on village-level anti-poverty planning with the coordinated development of village economy, society, ecological environment and cultural industry as the goal and the improvement of the basic conditions, the promotion of industrial development, strengthening of capacity building, standardization of democratic management, establishment of civilized customs, enhancement of village appearance and stable solution to food and clothing problem as the main content. This program is implemented to improve the production and living conditions, enhance the capabilities of poor households and impoverished villages for sustainable development, steadily solve the food and clothing problem of the poor, promote the economic and social development of impoverished villages and lay a solid foundation for building a harmonious society and building a moderately prosperous society.
Column 2:"Empowering" Entire Village Advancement in Qianzhongjun Village, Hunan Province
Located in Yuanling County of Hunan Province, Qianzhongjun Village has 570 households and 2283 people and covers a forest area of 4680 mu, paddy field area of 1505 mu and dry land of 745 mu, with per capita farmland area of 0.3 mu that ensures stable yields despite drought or excessive rain. Due to inaccessibility to highroads and electricity, coupled with the small area of land, the masses live in difficulties and the village's per capita net income in 2003 was less than 800 Yuan. Since the launching of the New Village Poverty Reduction Project in 2004, targeting at the poor, with the improvement of the production and living conditions as the premise and the increase in income as the core, the village adhered to self-reliance in building home, embarked on the path of development-oriented povertyreduction for a better life and achieved remarkable results in the Entire Village Advancement. First, comprehensively improved the production conditions and solved the road, drinking water and electricity problems of the residents; Second, made obvious progress in social undertakings, rebuilt village primary school and newly built the village clinics; Third, backbone industries achieved outstanding benefits and the pig-raising-based industry developed basically in the village; Fourth, the income of farmers increased significantly. In 2008, the rural per capita net income was more than 4800 Yuan.
The poverty alleviation by entire village advancement in Qianzhongjun was reflected primarily through empowering. The main practices included: First, through economic empowerment, it allowed the villagers to benefit from the industrial development, and introduced foreign capital for technical innovation of the original traditional industries; Second, through psychological empowerment, it strengthened the knowledge education and skills training; giving top priority to the improvement of farmers' overall quality, it strengthened education and training work; Third, through social empowerment, it cultivated village social organizations and village elites; Fourth, through political empowerment, it built a platform for people to speak so that the farmers could have the decision-making power and participation rights in handling the village's affairs.
Source: Li Juan,"Reflections and Improvement of Poverty Alleviation by Entire Village Advancement" "Research on Rural Finance", September 2009
Entire village advancement is the platform, starting point and form for building a new socialist countryside in poor areas. From 2001 to 2010, according to statistics, entire village advancement project was launched in 126,000 poor villages in China, including all the impoverished villages in old revolutionary base areas, border areas and minority areas, which greatly promoted the new rural construction in impoverished regions. During the "12th Five-Year Plan" period, China will also identify 30,000 poverty-stricken villages of key counties outside the contiguous poor areas for the implementation of entire village advancement by stages and in groups.
(II) Labor training
Launched in 2004, the Rain Plan is a main platform for Chinas poverty alleviation system to engage in the development of human resources. Characterized by government leadership and public participation, taking the improvement of quality and the enhancement of employment and entrepreneurship capabilities as the tenet and vocational education, entrepreneurship training and agricultural practical technical training as the means, through promoting transfer of employment and voluntary entrepreneurship, "Rain Plan" is designed to help the young and middle-aged farmers in impoverished regions solve practical the practical difficulties encountered in the employment and entrepreneurship, promote the development of production, increase income and ultimately promote the economic development in impoverished regions.
The Rain Plan has three types of objects: First, young and middle-aged farmers (16-45 years old) whose records have been filed for poverty alleviation work; Second, demobilized soldiers in poor households (including technical sergeants); Third, cadres of key villages for poverty alleviation and development and the backbones who can help the poor shake off poverty and become rich. Four projects of Rain Plan: Vocational education and training project of the new labor force of poor families, labor transfer and employment training project for the young and middle-aged labors from needy families, poverty alleviation skills enhancement project for the labors of needy families and the training program of leaders for the development of poverty alleviation industry.
In many years of practice, local governments created and developed a variety of effective training models, including "sustainable development combining long-term programs and middle-term programs", "order output through school-enterprise cooperation", "fixed-point employment financed by enterprises", "work-study program combining working and study", "nearest training through school-enterprise docking", "local transfer, nearest settlement", "highlighting characteristics and creating brands" and "training with loans and repaying loans after obtaining employments". From the end of 2006 to the end of 2011, according to incomplete statistics, in order to implement the Rain Plan, the central and local governments put in a total of 6.1 billion Yuan of training funds, of which 4.46 billion Yuan was for labor transfer trainings of 7.51 million people and 890 million Yuan was for agricultural practical technical trainings of more than 8.4 million people.
Practice has proved that through investing training fees of 600-1500 Yuan for each poor labor, the Rain Plan supported vocational skills training, entrepreneurial and rural practical technology training. Through participating in the trainings, the trainee can find a job for himself in one or two years and lift the whole family out of poverty, effectively blocking the occurrence of Intergenerational Transmission of Poverty. After returning home villages, some trainees used the technologies they learned, the information they collected and the capital they obtained in entrepreneurship and the development of efficient featured agriculture and tertiary industry. While increasing the income the family, they also greatly promoted local economic development.
In view of the new situation of the Rain Plan, in 2010, on the basis of summarizing the experience in implementing the Rain Plan during the 11th Five-Year Plan" period, the LGOP reformed the implementation model of vocational education of new labor force, selected nine key counties for national poverty alleviation and development in the central and western areas as pilot areas for the reform of the implementation modalities and launched the pilot project. The pilot project was designed to guide and encourage the children from poor families to complete the nine-year compulsory education and ordinary high school education and continue secondary and senior vocational education and preparation skills trainings for more than one year through issuing subsidies for labors to receive education and trainings, aiming to further improve the overall quality of new labors from poor families and enhance their capability for getting stable jobs and more income. Subsidies were mainly issued to the students from registered needy families in the pilot counties who received 2010-2011 senior vocational (Grade One, Two and Three), secondary vocational (Grade One and Two) education and skills training for more than one year (except interns on relevant positions). As for the subsidy standard, based on other subsidy policy,1000 Yuan shall be issued for each person per year (500 Yuan per person per semester). The subsidies shall be issued through 'Till in One Card (Bankbook)". In the academic year 2011-2012, the government made further adjustments to the pilot program and raised the subsidy standard to 1500 Yuan per person. The coverage of pilot areas was expanded to 100 counties of 21 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). According to the data of National Bureau of Statistics, it is estimated that the annual program will subsidize a total of more than 210,000 and the subsidies will amount to 320 million Yuan.
(Ill) Poverty alleviation by industrialization
Industrial poverty alleviation is a form of industrialization of agriculture to encourage poor farmers to adjust structure and increase income through the establishment of agricultural product bases in poor areas or through order agriculture, lhe main means of industrial poverty alleviation include: Help impoverished regions and poor rural households to select leading enterprises based on local situation, provide financial and technical services and construction production bases; support poverty alleviation leading enterprises and develop processing industry; and organize marketing and develop new markets through farmers' cooperative organizations.
Column 3: Effectiveness of "Industrial Poverty Alleviation" in Laifeng County
Orange flower exuded a faint fragrance and tens of thousands of chickens crowed. On May 18, we paid a visit to Yufeng Farming Cooperatives of Jiusi Town, Laifeng County and were greeted by a scene of thriving vitality. "The Cooperatives was founded ten years ago. Currently, its annual production capacity of eggs is 375 tons and annual production value is more than 3 million Yuan", said Chen Yaqiong, the principal of the Cooperatives. "Last year, the Cooperatives encouraged more than ten rural households to develop farms at home.The county poverty alleviation and development office provided 25,000 Yuan for each household and per household profit amounted to 21,000 Yuan. This year, l'm going to mobilize more farmers to shake off poverty and become rich in this way." In recent years, adhering to the guiding line of "supporting industrial development through poverty alleviation and agricultural development" Laifeng County strived to support the development of leading enterprises for processing of agricultural products and encouraged the development of the model of"company + base + farmers + association", which not only steadily promoted the development of industries in the county, but also ensured that farmers have sustained sources of income in the process of industrial development. Through industrial development and the construction of industrial bases, in 2011, the poverty-stricken households involved in industrial development in Laifeng County accounted for more than 60% of the total poor.
"We'll conduct the industrial poverty alleviation-based anti-poverty work and highlight the principle of'regional development through planting and community construction through the development of animal husbandry' to promote industrial development based on the development of animal husbandry, specialty vegetables, forest and fruit industry, tung oil tree, tea and genuine medicinal materials" said Ni Yong, the Director-General of the County Poverty Alleviation and Development Office. "We'll also actively guide enterprises to participate in fixed-point poverty alleviation through village-enterprise cooperation and encourage enterprises to launch bases and develop industries in impoverished villages to increase the collective economic income and the income of poor farmers" In 2011, a total of 12 enterprises in the county were involved in the construction of key poverty-stricken villages and the investment amounted to 10 million Yuan.
Since 2011, according to statistics, the county has newly developed industrial bases of 17,000 mu and livestock breeding bases of 15,000 square meters, directly increasing the income of more than 10,000 households; newly built and rebuilt village roads of 220 kilometers to improve or solve the travel problem of nearly 30,000 people; newly built nearly 50 pools (water cellars) to solve the drinking water p problem of nearly 5000 people; organized technical trainings for 2300 person-times and Rain Plan trainings for 900 person-times, and there was a reduction of 7855 in the number of the poor in the county that year.
Source: Enshi Daily, May 24,2012
The key link in industrial poverty alleviation is the development of leading enterprises. On November 29,2004, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development issued the "Circular on the Declaration of National Poverty Alleviation Leading Enterprises" and launched the declaration and examination work for national poverty alleviation leading enterprises. By 2009, a total of 1298 national poverty alleviation leading enterprises had been identified in China, of which 625 were identified by the central government and 673 by provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities). These poverty alleviation leading enterprises have contributed to the income growth of more than 8 million rural households in impoverished regions and promoted the industrial structure adjustment in poverty-stricken areas
(IV) Work-relief program
As a special policy measure to support disadvantageous groups, work-relief program is a supporting policy for the relief recipients to participate in the construction of the infrastructure projects funded by government to gain labor remuneration instead of direct relief. Work-relief program is mainly implemented for the infrastructure construction in impoverished regions, including basic farmland, small water conservancy projects, village roads, drinking water projects for mankind and livestock and comprehensive management of small watershed to improve the production and living conditions as well as development environment. Meanwhile, local farmers shall be paid for project construction participation in impoverished regions so that they'll be able to increase the income of their families.
From 2001 to 2010, the central government allocated a total of more than 54.5 billion Yuan of work-relief funds, of which 24.7 billion Yuan was issued during the "Eleventh Five-Year Plan" period. Plus the local government investment, the total work-relief funds amounted to 32.5 billion Yuan, and a total of 3.33 billion Yuan of remuneration for personal services was provided for the masses involved in the project construction. The government newly built and rebuilt basic farmland of more than 4 million mu in rural poor areas, increased and improved irrigation area of more than 50 million mu and constructed rural highroads of more than 100,000 kilometers and independent bridges and culverts of 17,000 linear meters. Through the implementation of rural water resources projects, it solved the drinking water problems of 9.08 million people and 5.49 million heads of livestock. Through adopting engineering and biological measures, it initially improved basin area of 12,000 square kilometers and constructed grassland of more than 12 million mu. The traffic conditions, irrigation and water conservancy facilities and ecological environment in poor rural areas have been significantly improved.
(V) Ex-situ poverty alleviation relocation
The program of ex-situ poverty alleviation relocation refers to the policy to help the rural poor living in the regions with harsh conditions to relocate and shake off poverty on a voluntary basis. The govermnent provides subsidies for the construction of housing and other basic production and living facilities for the relocated masses. It is a complex livelihood project with a large amount of investment and remarkable results, mainly including infrastructure and production conditions, living facilities, social undertakings, economic development and ecological construction, etc.
Principles of ex-situ poverty alleviation relocation: Adhere to the wishes of the masses and give full play to the main role of the masses; adhere to the guidance and develop scientific plans; insist on targeting at the objects to benefit the real poor; adhere to the integration of resources and strive to improve the infrastructure; adhere to the industrial development and earnestly carry out follow-up supporting work and relevant projects to increase income; adhere to standardized management and continuously improve the effectiveness of relocation-based poverty alleviation.
As of 2011, this program had relocated a total of 8.48 million rural poor residents. It has improved the capabilities of the poor for resisting natural disasters, alleviated the ecological pressure on impoverished areas, improved the production and living conditions of impoverished people and accelerated the pace of poverty reduction in the poor.
Column 4: Ecological relocation for poverty alleviation lifted 12,000 Wushan people out of poverty
Moving forward along a spacious flat concrete main road, we saw rows of clean and beautiful farmers' houses on both sides of the road. When we went into one of the houses, we were attracted by the design of one bottom for one building and found it was a brick house equipped with living room, kitchen, bathroom and other facilities. That is what the reporter saw recently in the resettlement points for immigrants involved in the ecological relocation for poverty alleviation in Chayuan Village, Luoping Town of Wushan County.
"Compared to the original houses, our new homes are much more beautiful" said Xie Yanxiu, a 72-year-old elderly person in the settlement point of Chayuan Village for immigrants from mountain areas.
Xie told the reporter that her former home was in the mountain areas of 1800 meters above sea level in Yihe Village, Luoping Town and she lived in the old houses with cob walls. She used to worry about landslide in rainy days and had to carry things by herself as there were no highroads in the mountain areas.
"Harsh natural conditions and poor infrastructure have been the 'roots of poverty' that hinder the development of the local masses," said Zhu Qin, the Director-General of the Poverty Alleviation Office. Due to the disadvantageous location, despite the efforts made by the local masses, it is still hard for them to shake off poverty. Even if the food and clothing problem is solved, it can only maintain simple re-production. The phenomenon of "returning to hunger and still feeling cold after the food and clothing problem is solved"occasionally happens'.
In order to cut off the "roots of poverty", a new way needed to opened up. In 2006, taking ecological relocation for poverty alleviation as the starting point of lifting the poor in remote alpine areas out of poverty, Wushan decided to implement the projects of"entire town relocation" and "entire village advancement" through rural concentrated settlement, scattered settlement and relocation to the city, aiming to cut off the "roots of poverty" of the masses.
After that, since 2009, the county has invested a total of 50 million Yuan for the ecological relocation of 12,000 people and set up three rural concentrated settlement points respectively in Chayuan Village of Luoping Town, Xianqiao Village of Liangping Town and Wulong Village of Shuanglong Town.
At present, in the main settlement areas, the county has developed land of more than 5000 mu, built highroads of 30 kilometers and newly constructed drinking water projects for man and livestock, biogas digesters, high/low-voltage circuits, schools and village clinics, basically solve the electricity, drinking water,schooling and medical service problems of the immigrants.
"The government not only provided new houses for us, but also help us develop industries to increase income and become rich;' said the villager Li Zongtian, who did not move to the settlement point of Chayuan Village from Dahong Vilage of Jinping Town until this Spring Festival. Currently, the county has developed tobacco planting area of 30,000 mu, orange bases of 2000 mu and traditional Chinese medicine area of 5000 mu in the main settlement points, forming two farming communities. It has now got more than 50 large farming households and per household annual income growth of the masses in the settlement points exceeded 3000 Yuan.
Huang Yulong, a cadre of Chayuan Village told the reporter that this county has selected 30 rural households for the first time this year in the settlement points of Chayuan Village for the development of tourism industry and opened 30 clean comfortable family hotels which can receive more than 200 tourists. "If it succeeds in operating the first batch of family hotels, the county will expand the scale of rural tourism. In such a way, poor villagers will not only be willing to move out but also have the opportunity to increase income and become rich through the development of industry", said Huang.
In the next few years, Zhu Qinwan introduced, this county will move 15,000 households and 55,000 residents in remote mountain areas and alpine regions out of mountains through ecological relocation to cut off the "roots of poverty".
(Reporter: Liu Jiyi)
Source:"Chongqing Daily"for rural areas, November 15,2011
(Vl) Financial poverty alleviation
Soft loan. Since 2001, the LGOE the People's Bank and China Banking Regulatory Commission successively launched the pilot reform of "home loan" and "projeCt loan" and the pilot project of microfinance for households driven by "awards and subsidies", and continued to increase investment in discount loans for poverty alleviation. In 2008, in order to further establish and improve thet poverty reduction credit loan management system and operation mechanism meeting the requirements of market economy, in accordance with the guideline of "two decentralizations and two reforms", the central government decentralized the power of direct management of poverty-relief discount loans and discount funds to provincial government and the power of management of household loans and subsidies on interest payment to county government. Meanwhile, the government changed the "exclusive dealing" of poverty-relief loans of the Agricultural Bank to the market operation and changed fixed interest rate to fixed subsidies. The central government allocates subsidies for interests based on the discount period of one year. During that period, the subsidies for interest are provided for household loans according to the standard of annual interest rate of 5% and the subsidies for interests of project loans are given based on annual interest rate of 3%. The reform and improvement of the management system for subsidies for interests played an important role in mobilizing the enthusiasm of financial agencies, improving the mechanism for virtuous cycle development of poverty-relief discount loans, improving the production and living conditions of the masses in impoverished regions and narrowing the development gap between regions.
Carry out reform of subsidies for interest of anti-poverty loans to guide and encourage financial institutions to increase discount loans. From 2002 to 2011, the central government issued a total of 5.445 billion Yuan of subsidies for interests of anti-poverty loans and issued nearly 230 billion Yuan of loans for poverty reduction.
Pilot program of mutual funds for poor villages. The state launched this program in 2006 and allocated 150,000 Yuan of financial anti-poverty funds for each pilot village. It supported the development of production according to the principle of being owned, used, managed and enjoyed by the people for turnover and rolling development and established a long-term mechanism for the use of financial anti-poverty funds according. As of 2011, pilot projects of mutual funds had been launched in 16300 villages of 1141 counties nationwide and the mutual funds amounted to 3.306 billion Yuan.
(VII) Construction of old revolutionary base areas
In order to implement the spirit of "increasing support for the development of old revolutionary base areas, minority areas, border areas and poverty-stricken areas" of the 17th CPC Central Committee, in 2008, LGOP put forward the work task of "three guarantees":By 2010, ensure to complete the implementation of Entire Village Advancement program in minority poor villages, border poor villages and the poor villages in old revolutionary base areas, covering 24,008 poor villages in old revolutionary base areas, accounting for 97% of the total.As of the end of 2010, the task of"three guarantees" had been completed.
Pilot projects for contiguous development: From 2007 to 2011, the pilot projects for the "contiguous development with county as the unit, integrating funds and entire village advancement" were launched in 91 key counties of 22 provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions in the central and western areas. Each county put in financial anti-poverty funds of 10-12 million Yuan and a total of 984 million Yuan was invested. In addition,financial anti-poverty funds of about 170 million Yuan were arranged for the pilot projects in15 counties of Shanxi, Guangxi and Shaanxi.
Central special lottery public welfare funds support the Entire Village Advancement in old revolutionary base areas. From 2008 to 2011, central special lottery public welfare funds of 1.035 billion Yuan were arranged for the implementation of Entire Village Advancementin 62 old revolutionary base areas of the key counties in 19 provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities). The project contents included infrastructure construction in impoverished villages, improvement of village appearance and industrial development, etc.
Pilot projects of comprehensive poverty alleviation and development in the old revolutionary base areas. Since 2009, the central government has arranged annual financial funds of 20 million Yuan for six consecutive years for the implementation of pilot projects for "comprehensive poverty alleviation and development in Kasite" of Xianning County,Guizhou Province, aiming to help the poor shake offpoverty and explore a way for the overall development of old revolutionary base areas in poverty-stricken regions.
Encourage and mobilize social forces to support the development of old revolutionary base areas. Taking full advantage of the institutional strengths, the government mobilized and organized the party and government organs and social forces to participate in the development and construction of the old revolutionary base areas and positive and significant results have been achieved. Now, a total of 154 central state organs, democratic parties, social organizations and large state-owned enterprises have built pairing relationship with the old revolutionary base areas in 232 key counties for national poverty alleviation and development, accounting for 76% of the total old revolutionary base counties. Besides, many non-public economies and social forces have tried their best to carry out poverty alleviation activities in various forms, creating an atmosphere of the whole society's participation in the poverty alleviation of old revolutionary base areas.
II. Industrial Poverty Alleviation
Poverty alleviation by industrial sectors refers to the poverty alleviation work conducted by various industries' authorities or comprehensive functional departments through developing pro-poor policies for impoverished regions and people. In the development and implementation of industrial development programs, they give priority to impoverished regions in a planned, organized manner to promote the work done for the development of the poor. qhese sectors include departments of water conservancy, electricity, transportation, environment, education, medical services, civil administration, human resources and social security, broadcasting and television, finance, agriculture and forestry, culture, etc. In addition to taking charge of industrial poverty alleviation, the competent departments are also involved in fixed-point poverty alleviation.
Industrial poverty alleviation is an important part of the national large-scale poverty alleviation strategy, marking the poverty alleviation and development theory and practice has developed towards a certain stage. The 16th National Congress of the Cr'C pointed out that in the first two decades of this century, we'll build a well-to-do society of a higher level to benefit more than one billion people and advocate the equalization of public services, and various industrial, regional and social policies must give priority to "Three Rural Issues" and impoverished regions. On the basis of the goal of building a moderately prosperous society set by the 16th National Congress of the CPC, the 17th National Congress put forward new and higher objectives for the economic and social development and, in particular, stressed that we must enhance the harmony in the development of urban and rural areas and establish a new structure integrating urban and rural economic and social development to enhance the level of poverty alleviation and development. In the poverty alleviation and development in a certain period of time in the future, the "New Outline" pointed out, the industrial sectors must take the improvement of development environment and conditions of poor areas as the important content of the industrial development program, give priority to poverty-stricken areas in allocating funds and projects and complete their poverty relief tasks assigned by the government.
(I) Carry out poverty alleviation by science and technology
Science and technology are primary productive forces. Technological progress is the driving force of the growth of China's agricultural production, and will also be the primary driving force of the growth of China's future agricultural production.
Agricultural development through science and technology has become the determining factor for Chinas agriculture and rural development in the future. For a long time, focusing on featured competitive industries in impoverished areas, the relevant departments, especially the agricultural sector strived to promote various advanced practical technologies to improve the production efficiency of the breeding industry through technology contracting, combining technology and material sources and typical demonstration. For example, they vigorously launched demonstration projects in poor areas to promote the technologies for high-yield, efficient production of main crops, reuse of low-cost high-quality organic soil, safe and efficient prevention and control of pest and efficient utilization of soil, fertilizer, water and ecological environment. Facility agriculture is an important manifestation of agricultural development through science and technology. Since 2000, Chinas facility agriculture has entered a stage of rapid development and a
number of featured industries and regional competitive products have been developed in poor areas. These featured industries have become important pillar industries in rural China to absorb poor labors and promote the income growth of farmers.
For a long time, China attaches great importance to the organization of colleges and research institutes as support units for the dispatch of experts with practical experience and young and middle-aged intellectuals to form Technology Development Groups. It also dispatches deputy technology magistrates to key counties for poverty alleviation and development to help study and develop planning for poverty alleviation by science and technology, screen technology development projects, introduce advanced practical technology, organize technical trainings and solve key technical problems in the industrial development to improve the technical level of industrial development in poor areas, be government attaches importance to the rural entrepreneurial activity of science and technology correspondents in impoverished areas, encourages scientific and technological personnel to form a community of interests with farmers, launch businesses and provide services, guide the concentration of modern science and technology, information, capital, management and other factors of production to the poverty-stricken areas to promote local economic and social development and help farmers obtain more income and become rich.
In 2009, eight departments, including the Ministry of Science and Technology launched the rural entrepreneurial activity of science and technology correspondents. By 2010, a total of 72,000 science and technology correspondents had been sent to the rural areas in central and western areas to support local agricultural development and more than 3,200 research institutes, universities, colleges and science and technology enterprises led the majority of poor farmers to shake off poverty as corporate science and technology correspondents. Through Spark Program, Special Technological Richness Project, agricultural technological fruit transfer fund, technological workers' services for enterprises' special projects, other technological plans and special technological projects for the basic level, the Ministry of Science & Technology executed some technological projects in impoverished areas. In addition, it carried out various technology training activities in view of the low technology quality and weak technology consciousness of the cadres and the masses in impoverished areas.
(II) Improve traffic conditions in poor areas
There is a popular proverb in poverty-stricken areas of China: "To get rich, first build roads". The construction of rural road network has become the necessary prerequisite for poor areas to shake off poverty and become rich. According to the overall deployment for the construction of new socialist countryside and the requirements of the national "Eleventh Five-Year Plan", the state continued to increase investment in rural road construction. Focusing on the implementation of rural road "accessible" and "smooth" projects, township bus terminal and rural road crossing reconstruction project, the state gave priority to the construction projects in minority areas, border areas and impoverished mountain areas in the allocation of central government funds to address the road problem of the masses in poverty-stricken areas as soon as possible.
Since the implementation of the "Outline", the construction of transport facilities in rural China has been very effective and the goals have been basically achieved. By the end of 2010, almost all the towns across the country and all the administrative villages with certain
conditions in eastern and central areas had access to asphalt (cement) roads and highroads were build in all the administrative villages in western areas with certain conditions. During the "11th Five-Year Plan" period, the central government allocated 197.8 billion Yuan for rural highroad construction, of which 35.5 billion Yuan was from central government budget and 162.3 billion Yuan was vehicle purchase tax fund. The central government investment greatly promoted local government investment in rural highroad building. In the five years, a total of 950 billion Yuan was invested for the repair and construction of rural highroads of about 1.868 million kilometers, of which 527,000 kilometers of roads were newly built and 1.341 million kilometers of highroads were repaired. The rural roadway depth, smooth degree, technical grade and the proportion of road surface paving have been constantly enhanced and the traffic conditions in rural areas have been significantly improved. As of the end of 2010, the total length of rural highroads reached 3.45 million kilometers,96% of the towns and 81% of the administrative villages were equipped with asphalt (cement) roads, and 98% of the towns and 90% of the administrative villages obtained access to regular bus.
In 2012, the government issued the "Outline of Poverty Mleviation Planning for Traffic Construction in Contiguous Areas with Special Difficulties (2011-2020)". By 2020, according to the planning, the highroads of national highway network in the contiguous areas shall be basically built, the counties where conditions permit shall be equipped with highroads of second grade or above, the towns and administrative villages where conditions permit shall be equipped with asphalt (cement) roads and have access to regular bus, the rural logistic service system shall be basically set up, the efficiency of urban and rural passenger transport services shall be significantly improved, the rural highroad service level and disaster prevention and resilience capabilities shall be obviously enhanced, and the traffic safety and emergency response capabilities shall be significantly enhanced. During the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, more than 510 billion Yuan is expected to be invested. This outline will become an important guarantee for the improvement of transportation infrastructure to inject vitality into the development of poor areas.
(III) Strengthen water conservancy construction in poor areas
Water conservancy construction and water disaster elimination have always been major events for administering state affairs well and ensuring national security. Water conservancy construction in poor areas mainly includes: Rural drinking water, irrigation and water conservancy, rural water and electricity, water and soil conservation, hydrological and science and technology education, etc. Relevant industry sectors strived to solve the drinking water problem of rural residents and livestock in impoverished areas to actively promote the construction of rural drinking water safety projects; promote the construction of matching projects and water-saving projects in irrigation districts, carry out the implementation of "five small water conservancy projects", namely small water cellar, small pond, small reservoir, small pumping station and small canal, and implement cross-regional water allocation projects in the places where conditions permit to solve the water problem of poor areas. Meanwhile, they strengthened the construction of flood control projects, speed up the dam reinforceraent, management of medium and small rivers and the recovery of water conservancy projects due to water disaster, and strengthened the protection of water sources and water pollution control.
The main approach is: To accelerate the construction of matching projects and water-saving transformation in large-scale irrigation districts, strengthened the construction of the end canal system, implement the control and management of the use of irrigation water,and expand the scope and scale of technical transformation of large-scale pumping stations.
In comprehensive agricultural development, we should increase investment in the water-saving transformation of medium irrigation districts, strengthen the construction of drought resisting water sources in hills and mountains, speed up the construction of small and medium-sized water projects in southwest region, increase special subsidies for the construction of small farmland and irrigation works, increase the dam reinforcement efforts, strengthen the management of medium and small rivers to improve rural water environment, guide farmers to construct farmland and water conservancy projects for direct benefits and promote the effective practices of water users in participating in irrigation management.
In the new stage, the state further strengthened the construction of water conservancy projects in impoverished areas. Since 2011, the state has allocated 10% of the land transfer income for the construction of farmland and irrigation works, including that in poor areas. By 2015, the total investment in water conservancy will amount to 1800 billion Yuan,20% of which will be allocated for the construction of farmland and irrigation works. At present, the "Planning for National Poverty Alleviation by Water Conservancy Construction (2011-2020)" for contiguous poor areas is being prepared.
(IV) Solve the electricity problem of people without electricity
As a important infrastructure in rural areas, rural power grid is related to the lives of farmers, agricultural production and rural prosperity. In order to achieve the goal of providing electric power for the vast majority of administrative villages by 2010, the state organized the implementation of Phase I and Phase II rural power grid improvement project, rural power grid improvement projects in central and western regions, household-reaching electricity projects, electric power projects in the areas without electricity, a new round of rural'power grid upgrading projects and new rural electrification construction projects to improve the reliability and power supply capacity of rural power grid.
Through hard work, we've achieved good results, reflected by: First, the power grid structure in poverty-stricken areas has been significantly improved, the power supply capacity and reliability have been significantly enhanced, and a management system for county power supply enterprises to directly manage households has been basically set up. Second, the prices of rural electricity have been significantly lowered, effectively reducing the electricity burden on farmers, and the regions covered by rural grid improvement have all achieved the goal of same price for daily electric power use in urban and rural areas. Third, it promoted electricity consumption in rural areas and accelerated rural economic development. Fourth, the electricity problem has been gradually solved, creating conditions for farmers and herdsmen to shake off poverty and improve the living conditions. Fifth, it effectively expanded domestic demand and stimulated the manufacturing of electrical equipment. In addition, it created a lot of jobs for rural areas and played an important role in expanding domestic demand.
In the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, the Chinese government will continue to improve the supply security of electricity in rural areas,
improve the rural power grids nationwide, guarantee residential electricity consumption in rural areas, basically solve the electricity problem of agricultural production and basically set up the new rural power grid characterized by safety, reliability, energy saving and environmental protection, new and advanced technology, as well as standardized management. The specific approaches: First, conduct a comprehensive transformatiofi of the rural power grids in the regions not covered by transformation in accordance with the new construction standards and requirements. Second, upgrade the rural power grids with insufficient power supply capability and low reliability despite of the transformation. Third, upgrade the power supply facilities for farmland irrigation, rural economic crops and agricultural product processing as well as livestock breeding in the main grain producing areas based on local conditions to meet the electricity needs of agricultural production. Fourth, in accordance with the requirements of balancing urban and rural development, on the basis of achieving same price for residential use of electricity in urban and rural areas, strive to achieve same price for various kinds of electricity use in urban and rural areas to further reduce the electricity burden on rural areas. Fifths, deepen rural electric system reform, comprehensively abolish the "representational administration system" of county power companies and establish the systems and mechanisms conductive to promoting the sound development of rural electricity industry. Sixth, increase financial support. The funds for the upgrading of rural power grids in middle and western regions are mainly allocated by the central government. Continue to implement the policy of charging additional 2 cents for per kilowatt-hour electricity, earmarked for repaying the capital and interests of the loans for rural power grid construction and upgrading.
In addition, the Chinese government has also introduced various preferential policies to encourage the development of a variety of energy in the light of local conditions. Since 2000,it has invested 3.4 billion Yuan for the implementation of the "Plan to Enrich People through Building Eco-homes". It mainly refers to the construction of a variety of energy-ecology model projects with rural households' biogas digesters as the link. Based on the actual needs, at the same time, it also implemented solar energy projects, firewood and coal-saving projects and small power source projects so that the land, solar energy and biomass resources can be used more effectively, forming a virtuous cycle of energy, and material flow in the basic production and lives of rural households, achieving the goal of warm and clean homes, efficient yard economy and harmless agricultural production. Energy-ecology model projects refer to the energy-ecology model of "pig-biogas digester-fruit" in the south, "four-in-one" in the north or the "five matching projects" in the northwest. Solar energy utilization projects refer to solar water heaters, solar cookers and solar houses; the firewood and coal-saving projects refer to rural firewood and coal-saving stoves or efficient prefabricated assembly aerial stoves; the small power projects refer to household solar photovohaic power projects and smaU wind power or micro-hydro projects.
(V) Conduct renovation of rural dilapidated houses
The renovation of rural dilapidated houses is a major implementation way housing assistance in rural China. The government helps the families with special housing difficulties build their houses through providing cash subsidies. Since 2008, in order to solve the basic housing safety problem of the rural masses with difficulties, China launched pilot projects of renovation of rural dilapidated houses, lhe "Guiding Opinions on Expanding Pilot Projects of the Renovation of Rural Dilapidated Houses in 2009" proposed to expand the coverage of subsidies for pilot projects of renovation of rural dilapidated houses, targeting at the scattered flve-guarantee households, the rural households living on subsistence allowances and other rural poor households living in dangerous houses. In 2009, the task of expanding the pilot projects was to complete the renovation of dangerous houses of 800,000 rural poor households.The central government allocated 4 billion Yuan of subsidies, averagely 5000 Yuan for each household.2010 No.1 Document of the Central Government proposed to take it as a major measure to expand domestic demand to support house building of farmers with the rapid growth of rural house building and sufficient supply of building materials, adopt effective measures to promote the marketing of construction materials in the countryside and encourage farmers to build houses for living according to laws and regulations. In September 2011, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development issued the "Technology Policy for Construction of Rural Housing (Trial)" to provide illustration and limitations for village and town planning, housing design, energy-saving construction, disaster prevention and reduction, construction materials and building construction, matching project implementation and environment protection as well as the establishment and improvement of the management system, etc.
In 2010, the central government allocated 7.5 billion Yuan to support the renovation of dilapidated houses of 1.2 million rural households in border counties of mainland, western counties, national key counties, the counties re-identified by the State Council for Western Development and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps. As of the end of May 2011,the dilapidated house renovation task for 2010 had been completed with a total investment of 43 billion Yuan. The situation of dilapidated houses in rural China, especially that of the rural poor has been significantly improved and the dilapidated house problem in border areas has been thoroughly solved.
(VI) Conduct poverty alleviation by education
Education-based poverty alleviation is mainly conducted through developing policies and strengthening the infrastructure construction in impoverished areas.
1. Implement free compulsory education policy
In the last century, China set the "two basic" goals of "basically making nine – year compulsory education universal and basically eliminating the illiteracy among young and middle-aged adults". Due to the huge gap between urban and rural areas, the government increased support for rural compulsory education and gradually implement the policy of "two exempt and one subsidy" - Students from needy families in rural poor areas are exempted from miscellaneous expenses and textbook fees and boarding students can get subsidies for cost-of-living. The pilot project of this policy was launched in 2001. "The students from needy families in rural primary and secondary schools of key counties were exempted from textbook fees. Since 2005, all the students at the stage of compulsory education from needy families in rural areas of the key counties have been exempted from textbook fees and tuition fees and the boarding students have got subsidies for living. Since 2007, the policy of "two exempt and one subsidy" has covered all the students at the stage of compulsory education from needy families in rural areas across the country.
2. Provide education aid to ensure that poor children will not drop out of school due to financial difficulty
The government, society and individuals provide assistance to solve the financial problem in the education of children at various stages from needy families through subsidizing them, fee exempting, awarding them, providing student loans and part-time jobs. In order to ensure that no children will drop out of school for financial reasons, in recent years, the central and local governments have successively adopted a series of major measures and established a complete education assistance policy system: In universities, the government has set up an aid policy system with government awards and grants as the core, supplemented with other subsidizing measures; In secondary vocational schools, it has set up an assistance policy system with student grant and fee exemption as the core, supplemented with other measures such as the combination of work and study of students and internship; In common high schools, it has set up the education assistance project supported by the central special lottery funds, which mainly provide financial aid for the students from rural needy families in the middle and west counties and towns; In the stage of compulsory education, all urban and rural students are exempted from tuition fees and textbook fees, and boarding students from needy families in rural areas receive living subsidies.
In 2010, the state issued four new subsidy policies: First, established the mechanism for dynamic adjustment of university student grants to effectively alleviate the adverse impact of rising prices on students from needy families; Second, established the subsidy system to provide financial aid for high school students from poor families, marking that China has basically improved the subsidy policy system for students of primary school to university from needy families. Third, further expanded the coverage of tuition-flee policy for secondary vocational education, included the students of secondary vocational schools from urban needy families in the coverage and absorbed more students and young people to receive vocational education. Fourth, raised the subsidy standards for boarding students at the stage of compulsory education from rural needy families, further reduced the economic burden on these boarding students and helped them improve the nutritional status. The continuous improvement and implementation of the subsidy policy system for students from poor families greatly promoted educational equality and social equity, promoted the popularization and consolidation of the nine-year compulsory education and the development of vocational education and higher education, and thus helped achieve the goal of poverty reduction.
At the end of 2011, the state launched the nutrition improvement program for rural students at the stage of compulsory education. The subsidy standard is three Yuan per person per day and the standard will be raised continuously.680 counties in the contiguous poor areas were the first to benefit from the program.
3. Rural education infrastructure construction has been constantly strengthened
Continue to allocate special funds for "national poverty-relief education projects" to support the construction of rural primary schools in national poor counties where education is extremely backward. Implement junior middle school renovation projects in rural areas of middle and west regions, continue to improve the conditions of rural junior middle schools,strengthen the protection of living facilities for students, basically eliminate the phenomenon of "big bed" and house-renting outside the school and enhance the retention rate of junior middle school students. This project is mainly implemented in the key counties for national poverty alleviation and development except those for key problem tackling in implementing the "two basic" policy in middle and western regions, minority counties, old revolutionary base areas, some counties concentrated with poor residents and some provincial poverty-stricken counties and border counties in the western regions.
In 2009, the primary and secondary school security project was launched nationwide. The overall objective was: To consolidate or rebuild the primary and secondary schools with hidden danger across the country and make these schools meet local standards for earthquake resistance and meet the safety requirements of resisting other geological disasters, floods, typhoon, fire and lightning, aiming at making the primary and secondary schools the safest, most reliable and most satisfying buildings.
In 2010, the state launched the pilot project of turnover dormitories for teachers of rural schools in remote areas with harsh conditions. The central government only supported the rural schools at the stage of compulsory education in remote areas with harsh conditions, mainly improved the living conditions of teachers at special posts, exchange teachers, teachers working in remote regions with poor conditions and teachers responsible for the management of boarding schools, and solved the accommodation problem of the poorest teachers whose living conditions need to be improved urgently. Local government mustn't expand the range of support at random.
(VII) Develop the medical and health services in impoverished areas
Medical and public health services are the foundation for people's health security. In recent years, the development of medical and public health services in impoverished regions mainly included the establishment of the medical health service.network, the implementation of medical assistance and the establishment of the rural new cooperative medical system in poverty-stricken rural areas.
Since the deepening of medical reform, through multi-channel funding, the central and local government increase the intensity of institution building and further improved the rural three-tier health service system and urban communities' health service system.
As a result, the medical conditions and environment of the masses have been significantly improved. The central government allocated a total of 40 billion Yuan of special funds for the construction of 1,877 county-level hospitals,5,169 central hospitals,11,250 village clinics and 2,382 community health service centers. At the same time, through the transformation and improvement of primary health care institutions and mobilize public participation, the urban communities' health service resources have been strengthened. The health service system has been continuously improved and the masses' access to services has been significantly enhanced. As of the end of April 2011, there were a total of 941,000 health care agencies nationwide.
The medical assistance system is the most basic medical support provided by the government and society for some low-income vulnerable groups in poverty to alleviate their difficulties in receiving medical services due to weak economic capability, prevent them from falling into or returning to poverty due to illness and strengthen their ability to protect themselves and survive. In 2009, the state further improved the urban and rural medical assistance system and included the seriously ill persons from urban and rural families receiving subsistence allowances, flve-guarantee households and low-income families in the system. In 2010, a total of 56.346 million poor farmers received medical assistance and 8.35 billion Yuan of financial funds for rural medical assistance were issued, up 29.2% over the previous year, of which: 1.4 billion Yuan was issued to subsidize farmers to participate in the new rural cooperative medical system, up 33.3%, and 6.7 million Yuan was direct relief funds, up 35.6%.
In order to solve the problems of falling into poverty due to illness and returning to poverty due to illness, etc, since 2003, the government selected two or three counties (cities) in each provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities) to carry out pilot projects of the new rural cooperative medical system. Later, four groups of pilot projects were launched. By 2010, the system almost covered all rural residents. At present, the new rural cooperative medical system has been set up in all rural areas, the system framework and operation mechanism have been basically established, medical burden on rural residents have been reduced, the utilization rate of health services has been enhanced and the situation of falling into or returning to poverty due to illness has been alleviated. As of the end of 2010, a total of 2678 counties (districts,cities) nationwide carried out the new rural cooperative medical services and 836 million people were involved. The participation rate was 96%. In 2010, a total of 130.83 billion Yuan was raised, averagely 156.6 Yuan for each person; the expenditure of the new rural cooperative medical system was 118.78 billion Yuan and the compensation expenditure benefited 1.087 billion person-times (hospitalization compensation for 66 million person-times and common outpatient service compensation for 989 million person-times).
(VIII) Implement the broadcasting and television coverage project
Radio and television are important channels for the poor to get information anti an important way to enrich the knowledge and upgrade the ideas of the objects of poverty reduction.
Based on the first round of village-reaching broadcasting and TV project, the government continued to implement this project in 2006. In accordance with the requirements of "consolidating the results, expanding the coverage, enhance the quality and improve the services", China established a public service system for broadcasting and TV program, gradually expanded the coverage of radio and TV program and constantly improved and level and quality of radio and TV programs of the central government for the rural masses.
As of the end of 2010, the state had invested a total of 7.679 billion Yuan of construction fund and 2.262 billion Yuan of maintenance fee for the village-reaching broadcasting and TV project, qhe implementation of this project effectively expanded the coverage of radio and TV programs in rural areas and enhanced the level and quality of the radio and TV programs for the rural masses. The population coverage rate of Chinas radio and TV programs respectively rose from 86.02% and 87.68% before the project implementation to 96.78% and 97.62% in 2010. The population coverage rate of Channel I of China National Radio and Channel I and Channel VII of the CCTV respectively increased by 85%,85% and 69%, and these three channels respectively covered 1.1 billion,1.1 billion and 900 million people.
(IX) Strengthen the ecological construction in poor areas
Environment is closely related to poverty. In China, poverty-stricken regions and ecologically weak regions overlap, indicating the interaction between environment problem and poverty. It is of great significance to promote the poverty reduction in poor areas to develop practical policy to protect the ecological environment.
Since the beginning of the new century, the state has continued to promote the implementation of the project of returning farmland to forestry (grassland), combined it with the strategy of western development and put forward the integrated initiative of "returning farmland to forestry (grassland), mountain closing and afforestation, food relief and individual contracting". In 2003, it comprehensively launched the project of returning grazing land to grassland. Through fence construction, resowing and improvement, grazing prohibition,moderate and rotational grazing and other measures, it restored steppe vegetation, improved the ecological environment of grassland, enhanced the productivity of grassland and promoted the coordinated development of ecological environment of grassland and animal husbandry. In 2007, the State Council further improved the policy for returning farmland to forestry,continued to provide appropriate subsidies for the rural households involved in returning farmland to forestry and established special funds for consolidating the results of returning farmland to forestry to solve the long-term livelihood problem of the involved rural households.The people with special difficulties who lived in the regions without living conditions were relocated to other areas. The government gave priority to the poverty-stricken areas with backward economy, a large number of minority people and an important ecological location in the allocation of the special funds for consolidating the results of returning farmland to forestry. In 2011, the state issued the "Opinions on Improving the Policy for Returning Grazing Land to Grassland". During the "12th Five-Year Plan" period, according to the "Opinions", thegovernment will continue to arrange the construction of 500 million mu of fences for returning grazing land to grassland, implement resowing and improvement of deteriorated grassland of 150 million mu, further improve the subsidy policy system and raise the standards.
Returning farmland to forestry and returning grazing land to grassland are major projects launched by the Chinese government to protect the ecological environment. The implementation of the policies for returning farmland to forestry and returning grazing land to grassland has accelerated the process of land afforestation, increased vegetation cover, reduced soil erosion and sand wind damage, promoted the rural ecological construction, improved rural ecological environment, increased the income of farmers and promoted the adjustment of agricultural industrial structure.
The new rural environment construction is an important part of Chinas community construction. The Chinese government has developed special planning and assigned the task.During the "11th Five-Year Plan" period, it initially solved the problem of being "dirty, chaotic and poor" of rural environment, achieved periodical results in preventing and controlling industrial pollution in rural areas, improved the drinking water environment or rural areas, basically controlled the pollution of scaled livestock breeding, increased a number of organic food production bases, comprehensively implemented the construction of demonstrative ecological zones, strengthened the rural environment supervision capability and further enhanced the public consciousness of environmental protection. The rural environment has been initially improved.
III. Social Poverty Alleviation
(I) Fixed-point poverty alleviation
Fixed-point poverty alleviation conducted by party and government organizations, enterprises and institutions is an important part of the poverty alleviation and development work with Chinese characteristics. Fixed-point poverty alleviation refers to the program for the central and national organs at all levels, enterprises and institutions, central government of democratic parties, All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce, social groups, army and armed police to provide financial, material, technical, talent, project and information support for the twinned key counties. It is a major measure to increase support for the development of old revolutionary base areas, minority areas, border areas and impoverished regions and an important way for the poverty alleviation units to understand the situation of grassroots organizations and the conditions of the people, train cadres, change work styles and establish good relationship between the CPC and the masses and between cadres and the masses. It is of great significance to ensuring the completion of the poverty alleviation and development task and the achievement of building a moderately prosperous society.
In 2002, the central work conference on fixed-point poverty alleviation was convened to conduct mobilization and make deployments for fixed-point poverty alleviation. The State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development, the Organization Department of the CPC Central Committee, the Work Committee for Offices Directly under the CCCPC,the Work Committee of Central Government Departments, the Financial Work Committee of the CPC Central Committee and Central Work Committee for Large Enterprises jointly issued the "Opinions on Further Promote the Fixed-point Poverty Alleviation of Central and State Organs and Relevant Units" (Guo Kai Fa No. [2002]3) and 272 central ministries, enterprises and institutions were appointed to support 481 key counties for national poverty alleviation and development.
In May 2010, the General Office of the Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council issued the "Notice on Further Promote Fixed-point Poverty Alleviation" (Ting Zi No. [2010]2), again made deployments for the fixed-point poverty alleviation work and put forward the overall task and requirements of fixed-point poverty alleviation to further strengthen and promote the fixed-point poverty alleviation.
Taking it as a glorious task assigned by the Party Central Committee and the State Council, the central and state organs, the Central Committees of the democratic parties,All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce, the army and armed forces and relevant enterprises and institutions seriously carried out fixed-point poverty alleviation and made an important contribution to the economic and social development of impoverished regions and the poverty reduction among the poor. According to statistics, from 2002 to 2011, the central organs dispatched 3963 cadres and 51000 persons to conduct field survey in the twinned counties, directly put in cash and materials of 10.63 billion Yuan, helped the introduction of various kinds of funds of 38.96 billion Yuan, held 15,000 trainings, trained 1.833 million cadres, technicians and rural labors and subsidized 335,000 poor students.
The fixed-point poverty alleviation conducted by the central and state organs have three distinctive characteristics:
First, give play to the industrial advantages to help the twinned counties improve infrastructure and develop competitive featured industries. The Ministry of Water Resources,for example, insisted on the main contents of "five water projects + science and education" and,through planning for the rapid development of water conservancy in the twinned counties,promoted local economic and social development. The Ministry of Transport adjusted the twinned region to Aba Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Sichuan after Wenchuan Earthquake and comprehensively undertook the highroad building task for a few disaster-hit counties in Aba Prefecture. It not only dispatched three comrades to form the first liaison group for poverty alleviation in Aba Prefecture, but also selected 26 professional technicians to support the post-disaster reconstruction and traffic poverty alleviation in Aba Prefecture. CITIC invested to construct a one million-mu guava base in Honghe Prefecture of Yunnan for industrialization poverty alleviation, conducted industrialization poverty alleviation and combined business development with the development of poor areas and poverty-stricken people to form an interest community.
Second, give play to the advantages of various departments and introduce capital projects for the twinned counties through wide social contacts and various channels. Over the eight years for it to support Huaian County of Hebei Province, the General Office of the State Council has introduced more than 40 projects for the county. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs used various channels and selected honorary ambassadors for poverty alleviation to make propaganda for poverty reduction in foreign embassies in China, Chinese embassies in foreign countries, domestic and foreign big companies and non-government organizations, and actively raised anti-poverty funds. Since 2001, it has raised more than 150 million Yuan to support the poverty alleviation and development of Jinping County and Malipo County.
Third, pay attention to personnel and technology investment, select excellent cadres to carry out trainings and education-based poverty alleviation and provide intellectual support for the twinned counties. Over the past decade, for example, the Ministry of Science and Technology has dispatched ten science and technology poverty alleviation groups, involving 90 people, and developed the "Measures for the Management of Science and Technology Poverty Alleviation Groups" and the "Manuals for Science and Technology Poverty Alleviation Groups of the Ministry of Science and Technology). Trainings were organized before the poverty alleviation groups started their work and old and new poverty-relief groups often exchanged work experience. The Ministry of Agriculture not only dispatched cadres to support the poverty reduction in the twinned counties, but also selected grassroots cadres from the twinned counties to conduct exchanges with relevant stage organs, playing a role of dual intellectual support. With advantage in contacting the intellectuals in medical industry, the Central Committee of Chinese Peasants and Workers Democratic Party promoted the planting of traditional Chinese medicinal materials in the twinned counties, invited relevant experts to give site instruction, invited Tongjitang Chinese Medicines Company to participate in the work,practiced procurement at the lowest protective prices and guided local government to develop the "Development Planning for Chinese Herbal Medicine Industry (2009-2020)".
Driven by the fixed-point poverty alleviation of central organs, various provinces,cities and counties also conducted fixed-point poverty alleviation and played a positive role in contracting impoverished villages, targeting at the poor and directly promoting the development of the poor, with many highlights.
First, open the liaison office of leaders. Most of the provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities) have set up and insisted on the poverty alleviation liaison office system for contacting members of standing committee and vice governor (vice chairman, deputy mayor),which directly promoted the flxed-point poverty alleviation conducted by provincial organs and local party organs at all levels in counties for poor towns, impoverished villages and poverty-stricken households, establishing the working mechanism and a good atmosphere for provincial, municipal and county-level fixed-point alleviation.
Second, comprehensive support. Chongqing, for example, implemented the "group poverty alleviatioff'. Under the leadership of a comprehensive department, many departments and units jointly support a poor county to enhance the level of local economic and social development. Jiangsu Province practiced the "Five-party Linkage" poverty alleviation system,linking one provincial organ, one university (research institution), one large enterprise, one city in the south of Jiangsu and one county in the north of the province. To the village with rather weak economic foundation, it practiced the "five one" working mechanism - "one poverty alleviation instructor in the village, one twinned science and technology correspondent,one industrial and commercial enterprise for support, one rich village for twinning and one leading industry", bringing the love of CPC and government, science and technology results,market operation methods and advanced concepts to help get rich to impoverished areas simultaneously.
Third, village and household-reaching. In the fixed-point poverty alleviation in many provinces, the leaders are responsible for contacting the twinned counties, relevant units support the poverty alleviation in villages and party members contract the poor households.Guangdong Province, for example, has made overall deployment of "planning for households and responsibility to specific persons" for the work, assigned its anti-poverty task in 3409 impoverished villages to provincial units, the units in Guangdong and developed cities in the Pearl River Delta and determined June 30 as the "Anti-poverty Day of Guangdong". Shaanxi Province practiced "two linkage and one contract" system: provincial units are responsible for contracting the counties and towns and take charge of poverty alleviation in villages. Qinghai Province comprehensively carried out "household-for-household and one-for-one" anti-poverty activities in the poverty alleviation and development.
Fourth assessment and incentive. In many provinces, the fixed-point poverty alleviation work has entered the institutionalized stage and been included into the assessment and management by objectives. Liaoning Province has established poverty alleviation accountability and assessment and incentive mechanisms to strengthen the supervision, inspection, assessment and appraisal of the anti-poverty work of relevant units. It strengthened the "one-vote veto" system to ensure the year-beginning deployment making, mid-year check and inspection and year-end results for the provincial fixed-point poverty alleviation work. Yunnan Provincial Government issued the "Opinions on Improving the Fixed-point Poverty Alleviation Systems of the Provincial Organs, Enterprises and Institutions", the provincial leading group of poverty alleviation and development has signed target management responsibility document with the twinned units, made clear the investment standards and assessment requirements for the twinned units and conduct assessment, announcement and praise of relevant units based on their results in fixed-point poverty alleviation. Xinjiang Autonomous Region has implemented the "top leader" responsibility system and made clear that the organization department is responsible for personnel management while anti-poverty department takes charge of specific affairs, and linked the annual assessment of social poverty alleviation with the assessment of leaders' performance.
From 2002 to 2011, according to statistics, fruitful results were achieved in provincial (regional, municipal) fixed-point poverty alleviation. A total of 5,195 department units participated in the work and supported 12,161 impoverished towns and 59,547 poor villages,92,845 cadres were dispatched and 407,000 people visited the twinned counties. A total of 45.52 billion Yuan was invested in kind and cash and 46.84 billion Yuan of various kinds of funds were introduced; 87,000 seminars were held, and trainings of cadres, technicians and labors were organized for 7.05 million person-times.3.218 million labors were tralasferred and 840,000 poor students received subsidies.
(II) East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation
East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation is a major strategic plan developed by the CPC Central Committee and the State Council to achieve the great idea of common prosperity of Comrade Deng Xiaoping.
Since the implementation of East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation, in the practice of supporting the western regions to accelerate poverty reduction, helping eastern regions expand development space and jointly promoting coordinated regional development,the eastern and western provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities) closely cooperated and accumulated rich experience in leaders' exchange visits, twinning at various levels, joint meeting, cadre dispatching, industrial partnership and social participation, forming the basic working framework with government aid, enterprise cooperation, social support and personnel support as the core.
According to preliminary statistics, from 2003 to 2011, the eastern regions issued government aid of 5.28 billion Yuan and social contributions of 1.526 billion Yuan to the western regions; had 5879 cooperative enterprises, actually put in 254.49 billion Yuan; supported the construction of 3461 schools, subsidized 389,000 poor students, supported the construction of 1510 hospitals and highroads of 10,000 kilometers; dispatched 2733 cadres, held 8135 seminars, trained 1.383 million technicians and labors and organized labor export for 1.58 million person-times.
In June 2010, approved by the State Council, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development adjusted the cooperative relationship between some provinces and autonomous regions. See Column 5 for the new East-West cooperative relationship in the poverty alleviation.
Column 5: New East-West Cooperative Relationship in Poverty Alleviation after the Adjustment
Beijing - Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
Tianjin - Gansu
Liaoning - Qinghai
Shanghai - Yunnan
Jiangsu - Shaanxi
Zhejiang - Sichuan
Fujian - Nincjxia Hui Autonomous Region
Shandong - Chongqing
Guangdong - Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Dalian, Qingdao, Shenzhen, Ningbo - Guizhou
Xiamen - Linxia Hui Autonomous Region of Guans Province
Zhuhai- Liangshan Yi Autonomous Region of Sichuan Province
"Faking poverty alleviation and development as the central task, East-West regional collaboration as the implementation carrier, while accelerating the development of western impoverished areas, the East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation has also opened up broad space for development and created new opportunities for development.
(III) Army and armed police participate in poverty alleviation
As an important force for the cause of national construction, the army and armed police play an irreplaceable important role in promoting China's poverty alleviation and development work.
For a long time, in accordance with the national and regional planning for poverty alleviation and development, the army and armed police forces have given play to their advantages and taken initiatives to carry out anti-poverty activities in various forms, making a contribution to accelerating the pace of national poverty alleviation and elimination. At the new stage in the new century, the army and armed police forces have seriously implemented the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of Chinas Rural Areas (2001-2010)", made steady progress in the anti-poverty work based on the actual situation of local area and the army and actively helped the poor develop production and improve living conditions, greatly promoting' the economic arid social development of poor areas and the poverty reduction among the masses.
First, implement fixed-point poverty alleviation and entire village advancement projects. Adhering to the goal of promoting the construction of a new socialist countryside, troops above the regiment level are organized to support the development of impoverished villages through building partnership to lift the whole village out of poverty. Ilae army has successively built partnership with 47 poverty-stricken counties,215 poor towns and 1470 impoverished villages, set up more than 26,000 liaison offices for poverty alleviation, supported the construction of more than 2500 liaison offices for new rural construction and lifted more than 2.1 million people out of poverty. Hunan Military Region has supported three towns and seven administrative villages in the national key county Sangzhi for 23 consecutive years and lifted 57,000 people out of poverty. Chongqing Garrison coordinated 23 military and civilian units in Chongqing to provide support for the poverty alleviation of more than 20 poor villages of Fengjie County for 12 consecutive years and lifted more than 50,000 people out of poverty. The Pu'er military sub-district of Yunnan Province actively undertook the task of relocating Kucong people, newly built 14 immigrants' villages and helped Kucong people bid farewell to the original hole habitat and traditional backward mode of production.
Second, support the rural and agricultural infrastructure construction in poverty-stricken areas. Based on the actual situation of poor areas, combining local needs and the wishes of the masses with the capabilities of the army, various forces make full use of their arms, personnel and technological resources to conduct extensive anti-poverty activities. From 2001 to 2010, they successively supported the construction of more than 100,000 small engineering projects such as farmland irrigation works, rural road building, small watershed management and so on, dug 1119 wells for the masses, supported local area to develop more than 73,000 featured industries and helped train more than 600 million practical talents. Water supply engineering regiment of the Lanzhou Military Area Command has implemented the "Poverty Alleviation Project by Digging 100 Wells", the "Project to Support and Enrich Farmers by Digging 100 Wells", and dug 300 wells for arid regions of Ningxia, which is an effective solution to the resident's production and life water problem. After completing the task of national defense construction, PLA Second Artillery Corps insisted on supporting one poor area, rebuilt 7 roads in mountain areas for the poor of Gansu and Qinghai Province and built 17 convenient bridges to promote local poverty alleviation.
Third, donate money for education. Taking the support for the development of basic education in poor areas as a basic, strategic task for poverty alleviation and development, the troops actively support the "two basics" key problem tackling in poor areas and have conducted a
series of activities such as supporting the construction of "Bayi Aimin Schools", "l +1" donation for education and the "Spring Bud Program". From 2001 to 2010, the army had supported the construction of more than 1800 primary and secondary schools and subsidized more than 210,000 poor students. In 2006, to commemorate the 70th anniversary of victory of the Red Army, the army and armed forces supported the construction of 112 "Bayi Aimin Schools" along the Long March Routes and improved the schooling conditions of a number of primary and secondary schools in the poverty-stricken areas along the Long March Routes.The Air Force has implemented the "Blue Sky Spring Bud Program" for 17 consecutive years,opened 150 Blue Sky Spring Bud Girl Classes in 23 provinces (autonomous regions) such as Xinjiang and Tibet and helped more than 14,000 drop-out girls return to school.
Fourth, implement poverty alleviation by science and technology. Military academies,research institutes and the forces take full advantage of the personnel, equipment and technological resources to hold seminars, transfer science and technology results and conduct technological cooperation and joint key problem tackling, actively provide technology and information services for the poor to shake off poverty and become well-off. In the past five years, the army transferred more than 1200 scientific and technological achievements to local area, trained more than 400,000 persons for poor areas, providing powerful technological and personnel support tbr the economic development of impoverished regions. "The troops of PIA General Armament Department in Xinjiang transferred more than 20 high-tech achievements including nano, radiation and detection technology, creating more than 100 million Yuan of economic output for local area.
Fifth, organize poverty alleviation by health services. Strive to solve the medical treatment problem of the masses in impoverished areas and actively do a good job in poverty alleviation by health services. The military medical system has supported the construction of 130 county-level hospitals in western poor areas,1823 township (village) hospitals (clinics), trained more than 85,000 medical workers and donated more than 5900 sets of medical equipment. Medical institutions at all levels often make a round of visits and provide medical services and medicines for the masses. They've successively sent more than 12,000 medical teams to the plateau, the border and remote poor mountainous areas and provided free medical treatment for more than 61 million person-times. The PLA Fourth Hospital makes a round of visits to the masses on Tibetan Plateau, known as "the patron saint of lives on the plateau". People's Armed Police and Air Force General Hospital launched the "Heart Bud Project" and a large number of ethnic minority children with congenital heart disease received timely medical treatment.
Sixth, often organize activities to deliver warmth and offer love. Always being concerned about the food and clothing problem of the masses, the forces often organize officers and soldiers to donate money and materials to help the masses solve the pressing problems and deliver warmth to them. Forces' grassroots units established a long-term mechanism for helping the poor and often provide assistance for more than 40,000 needy families and more than 8,000 childless elderly people and persons with disabilities. They often visit the poor and send food, oil, clothing and medicines to them. Whenever a disaster occurred, while courageously participating in emergency rescue and disaster relief, the forces also donated money and materials. In the snow disasters occurred in some southern regions and Wenchuan Earthquake in 2008 as well as the Southwest Drought, Yushu Earthquake and Zhouqu mudslides occurred in 2010, the officers and soldiers donated more than 1 billion Yuan in cash and more than 3.52 million sets of clothing and quilts to help the people in the disaster areas tide over the difficulties, which was highly praised by the local party committees, governments and the masses of all ethnic groups.
The army and armed police have unique advantages and favorable conditions for participating in poverty alleviation and development. First, political advantage. In poverty alleviation and development, the forces can give full play to this unique advantage to help local government thoroughly publicize the scientific concept of development and other innovation theories, publicity the policy to enrich people and poverty alleviation and development achievements so that the masses in poor regions will be confident in shaking off poverty and building a moderately prosperous society. Second, advantages in strict organization and assault strength. As a highly centralized armed group with strict discipline, the army can be flexibly mobilized with rapid action. The officers and soldiers have the continuous fighting spirit and do not fear fatigue. They can act as the pioneers in emergency response in poverty alleviation and development and play a key role in critical moments. Third, the talent and technological advantages. Being rich in knowledge and strong in technology, military academies, scientific research and medical institutions can carry out technology and intellectual poverty alleviation, provide information services and help the poor develop planting and breeding industry and agricultural and sideline products processing to improve self-development ability to lay a solid foundation for the long-term development of the poor areas. Fourth, the equipment and technology advantages. Engineering, water supply, mapping, air force units, and water,electricity, transportation and other professional engineering forces are well equipped,have strong technical force and can directly participate in the construction of rural roads,hydroelectric stations and other infrastructure, anti-desertification, afforestation and other ecological environment construction and can undertake the task of key problem tackling in poverty alleviation and development to fundamentally improve the production and living conditions of the masses. In addition, the construction of defense facilities can also support poverty, alleviation and development. Through building the border defense highways, the army also solved the travel problem of the masses of surrounding impoverished villages. With these unique advantages and favorable conditions, the army and armed police are expected to make a great contribution to poverty alleviation and development.
(IV) All circles of society are involved in poverty alleviation
Corporate and public participation in poverty reduction: With the guidance and support of the government, businesses and all circles of society voluntarily use their own resources to participate in poverty alleviation and development work in various forms to contribute to economic and social development of poor areas and poverty reduction of the masses. It is an important way of poverty reduction and a priority of the current and future poverty alleviation and development work to effectively link all circles of society including the enterprises with the most promising enterprises with the poor masses with the most pressing needs.
In the poverty alleviation, enterprises and all circles of society took rural industrial development, infrastructure construction, the development of social undertakings and human resource development as key areas and created and accumulated many successful experiences and practices, which can be summarized in four modes: First, long-term counterpart support.One enterprise supported one or a few key counties for national poverty alleviation and development, introduced projects for local areas, dispatched cadres to give instruction,organized technical trainings, helped labors transfer employment and provided information services, etc. Second, villages-corporate cooperation in poverty alleviation. On the basis of the Glory Cause, since 2007, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development and All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce launched pilot projects of "village-corporate cooperation in poverty alleviation" in eight provinces and autonomous regions including Hubei and Ningxia and guided private enterprises and poor villages to find the joint point of interests in accordance with the principle of "complementary advantages,mutual benefit, the two-way interaction and common development" and jointly contribute to the development of poor villages. At present, a total of more than 69,000 private enterprises provide counterpart support for more than 61,000 administrative villages. Third, the industrialization of agriculture promoted poverty alleviation. They launched industrialization poverty-relief projects in poor areas and established the interest chains of enterprises and farmers and a long-term mechanism for income growth of farmers to help farmers and rural areas enter the market. Fourth, charitable donations for poverty alleviation. Through donating money and materials and providing volunteer services, businesses and individuals directly carry out anti-poverty activities or indirectly participate in poverty reduction through various kinds of foundations and other social organizations.
Column 6: Poverty alleviation projects launched and involved by all
circles of society
The Central Committee of the Communist Youth League--Action Program of Poverty Alleviation Volunteer
All-China Women's Federation --Water Cellar for Mothers, Spring Buds Program
China Youth Development Foundation-- Project Hope
China Population Welfare Foundation--Happiness Project
All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce--Glory Cause
China Foundation for Poverty Alleviation-- Microfinance, New Great Wall Self-improvement Project
China Association of Poverty Alleviation and Development——Changzhi Flood Control Project in Shanxi Province
Enterprises and all circles of society played a significant role in advancing the process of Chinas poverty alleviation a:ld development. First, they help stimulate the development vitality of poor areas fundamentally. As the main body of market activity, enterprises are more sensitive in market information and its changes, directly affecting the resources development,industrial nurture and structure adjustment of impoverished regions, and can stimulate the development vitality of poor areas fundamentally and increase the income of farmers. Secondly,they help change the concept of development of poverty-stricken areas. The participation of corporate and all circles of society in poverty alleviation can not only bring capital, technologies and other advanced productivity factors to poor areas, more importantly, it helps the poor directly accept advanced concepts and management knowledge and receive practical technical trainings to break the shackles of traditional concept and the closed state and effectively improve their ability of self-development. Thirdly, it is conducive to the expansion of the field of poverty alleviation and development. The participation of corporate and all circles of society in anti-poverty activities changed the single mode of government investment in poverty alleviation, broadened the channels and areas of poverty alleviation funding, enriched the poverty alleviation and development modes, promoted the innovation in poverty alleviation and development systems and mechanism and alleviated the financial pressure of inadequate input on the government of impoverished areas, providing strong for the economic and social development of poor areas.

扫描下载手机客户端
地址:北京朝阳区太阳宫北街1号 邮编100028 电话:+86-10-84419655 传真:+86-10-84419658(电子地图)
版权所有©中国国际扶贫中心 未经许可不得复制 京ICP备2020039194号-2