Scientific Development in China:Key Problem Tackling for Poverty Alleviation II
IV.International Exchangesandcooperation
(I).Use international experience to promote the process of poverty
reduction in China
Chinas poverty reduction cannot be separated from the support and participation of the international community. It is an important part of Chinas poverty alleviation and development work to strive for international development assistance and strengthen international exchange in the field of poverty reduction. Since the 16th National Congress of the CPC, in the face of the new situation in rural areas and new problems for poverty reduction cause, the Chinese government has actively carried out cooperation with relevant international organizations, bilateral agencies and non-government organizations for joint implementation of poverty alleviation projects and activities in various forms, learned with an open mind the new concepts and new methods of various countries and international organizations in the field of poverty reduction, explored new mechanisms, trained relevant working staffs and achieved remarkable restflts, which fiarther enriched our experience in poverty alleviation and development with Chinese characteristics. Zhe Chinese government is committed to solving the problem of poverty on their own and pay attention to learning the advanced poverty reduction ideas and achievements of the international community in the international exchanges and cooperation.
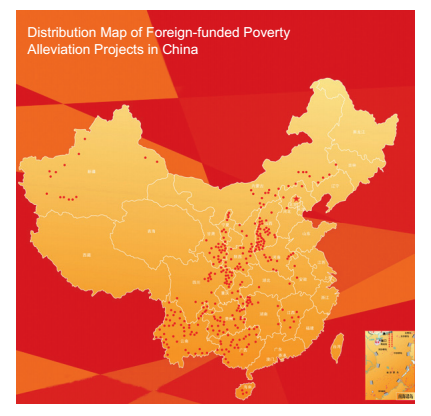
In early 1990s, China began to use foreign capital for poverty alleviation and successively conducted fruitful cooperation with the World Bank, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the Asian Development Bank and other international organizations, the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan and other countries as well as foreign non-governmental organizations in the area of poverty reduction. According to incomplete statistics, as of 2010, a total of $ 1.4 billion of foreign capital was put in the field of poverty reduction, plus domestic matching funds, the total investment amounted to 20 billion Yuan and a total of 110 foreign-funded poverty alleviation projects were implemented, covering more than 300 craunties of 20 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) in the middle and western regions,benefiting nearly 20 million poor people.
As an important part of China's poverty alleviation and development work, foreign-funded poverty alleviation gradually applied some advanced international poverty-reduction concepts and methods such as participatory poverty alleviation, microfinance, project evaluation and management, poverty monitoring and evaluation to the practice of China's poverty alleviation, which had a positive impact on the innovation of the mechanism for poverty alleviation and development, the improvement of the level of anti-poverty work and the development of human resources for poverty alleviation teams.
With the technical assistance of international organizations, China has continued to explore new ideas, new models and new methods for poverty alleviation and development. In the implementation of Community Driven Development (CDD) project, for the first time,it gave the capital control and decision-making power directly to the community, aiming at exploring a new mechanism for self-organization, self-management, self-development and self-monitoring of communities. The results achieved in the village-level development fund project launched in poor communities with the fifth technical aid project funds of the World Bank have been used by the Ministry of Finance and the LGOP to carry out large-scale community mutual fund projects in more than 10,000 impoverished villages nationwide, exploring a new path to financial services for the poor. In the face of the impact from environment change, the World Bank has introduced the design for sustainable land use and adapting to climate change in poverty reduction projects to deal with the negative impact of environment issues on the vulnerable poor areas and actively promoted green development.
In a nutshell, the international cooperation in the area of poverty alleviation has the following effects:
First, increase the total input in poverty alleviation and development. The investment of international organizations for poverty reduction in China is mainly put in the western regions with weak financial capacity, which has complemented the government investment of these areas to some extent and promoted the income growth and helped the food and clothing problem solving of the poor.
Second, alleviate the poverty in the project areas. The monitoring results of the Southwest Poverty Reduction Project of the Chinese government in cooperation with the World Bank show that the socio-economic indicators of the project areas have been significantly improved through project implementation.
Thirdly, promote the institutional innovation for China's poverty alleviation. With foreign-funded projects as the carrier, the rich development experience and anti-poverty methods of international institutions have been introduced to China and proved and promoted in the practice, having a positive impact on Chinas poverty alleviation and development theory, policy, method and system building.
Fourthly, promote the improvement of project management level. Before the project implementation, long-term serious preparation work has been done and clear plans and objectives have been developed. Establish scientific and strict management standards in the project implementation management to make the project's operation more transparent. Develop clear operational standards for the selection of target groups of the project and establish a systematic project monitoring and evaluation system.
Fifthly, lay a foundation for sustainable development of poor areas. Foreign-funded poverty alleviation projects not only provide a material foundation for the development of project areas, but also take into account the institutional arrangements and implementation forms f()r sustainable development of the project. In the implementation process, the project trained a number of project management teams. The project directly or indirectly conducted human resources development so that the target community got core competence for solving a dilemma. Through participating in the project construction, the poor strengthened their consciousness of main body and "ownership".
Sixthly, strengthen international exchanges and cooperation in the area of poverty reduction. The cooperation between the Chinese government and the international community not only made a contribution to China's poverty alleviation, but also provided experience for other developing countries to learn. On the Global Conference on Poverty Reduction held in Shanghai in May 2004, the experience of the Southwest Poverty Reduction Project of China in cooperation with the World Bank was exchanged as a typical successful case.
List of some international cooperation projects in the field of poverty alleviation
|
Partner |
Project Name |
|
|
The World Bank
|
Southwest Poverty Reduction Project in China |
|
|
Qinba Mountains Poverty Reduction Project in China |
||
|
Gansu and Inner Mongolia's Poverty Reduction Project in China |
||
|
Community Development Project of Poor Rural Areas in China |
||
|
Shanxi's Poverty Alleviation Project in China |
||
|
Strengthen Capacity Building of Poverty Alleviation Departments of Poor Areas TCC4) |
||
|
Community-Driven Development Project in China |
||
|
Community Development Rolling Fund Project (TCC5) |
||
|
Asian Development Bank
|
Research on the Way and Means to Support Rural Poverty Alleviation Projects in China |
|
|
Listen to the Voice of the Poor |
||
|
China's Reservoir Resettlement Policy Studies |
||
|
Village-level Participatory Poverty Alleviation Planning Study |
||
|
Research on China's Pro-poor Policies - Trends, Challenges and Future Direction |
||
|
NGO: Government's Partner for Village-level Poverty Alleviation |
||
|
United Nations Development Programme |
EAIDS and Poverty Research and Intervention Projects in China
|
|
|
United Nations Children's Fund |
Research on Children and Women's Poverty |
|
|
International Fund for Agriculture Development
|
Qinling Mountains' Poverty Reduction Project |
|
|
Western Guangxi's Poverty Alleviation Project |
||
|
Ningxia and Shanxi's Environmental Protection and Poverty Alleviation Projects |
||
|
Gannan's Poverty Reduction Project |
||
|
Poverty Alleviation Project in Xinjiang |
||
|
European Union |
Research on the Policy and Practice of Returning Farmland to Forest |
|
|
UK Department for nternational Development |
Community Development Project in Poor Rural Communities of China
|
|
|
Aus AID
|
Strengthen the Capacity Building of National Poverty Reduction System |
|
|
Sino-Australia Cooperation in Environmental Restoration and Poverty Alleviation in the Karst Areas |
||
|
GTZ |
SuPport the Implementation of the Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development in Rural China - Pilot Project of Poverty Monitoring in Jiangxi |
|
|
Japan Bank for International Cooperation |
Poverty Alleviation Project in Wuling Mountain, Hunan |
|
|
Guizhou’s Enviornment and Poverty Alleviation Projects |
||
|
International Plan |
Shaanxi’s Community-Driven Development Project. |
|
|
Dxfam Hong Kong
|
Pliot Project of Community Development and AIDS Control in Lixin County of Anhui |
|
|
Pilot Project of Development and Application of Leading Training Materials for Migrant Workers |
||
|
The Kadoorie Charitable Foundations |
Pilot Project of Integrated Poverty Alleviation and Development in Guyang County Of Inner Mongolia
|
|
|
Ford Foundation
|
Research onntheiExperience and Promotion Method of Community Development Funds |
|
|
American Resources Protection Committee |
Research on the Current Status of the Utilization of Life Energy in China's Tibetan Areas and the Application of Altermative Source |
|
|
The Nature Conservancy |
Study onathetPovertyiAlleviationlModeltofeNatureeReserve and Surrounding Areas & Pilot Projects |
|
![]()
(II) Build a platform for international exchanges in the field of poverty reduction
China actively participates in international poverty reduction and is committed to building a platform for international exchanges and cooperation in the field of poverty reduction so as to share experience in poverty reduction with the majority of developing countries for common development. In 2004 the Chinese government and the World Bank held in Shanghai the Global Conference on Poverty Reduction and set up the International Poverty Reduction Center in China (IPRCC) jointly with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and other international agencies.
The main contents of international exchanges and cooperation in poverty reduction include: To carry out joint research in the field of poverty reduction and development, sum up the experience of China and other developing countries in poverty reduction; promote international exchanges in poverty reduction through forums, seminars, exchange visits, etc;hold short-term trainings and give master lessons on poverty reduction and development for developing countries; provide policy advice and technical services for developing countries based on their needs; conduct poverty reduction project cooperation in developing countries;use information technology and the Internet to provide poverty reduction and development-related information, knowledge and technical services.
Beginning in 2007, the Chinese government and the United Nations in China jointly hold the "Poverty Reduction and Development Forum" every year on October 17 - the International Day for the Eradication of Poverty and invite relevant experts, scholars and officials to talk about the hot issues on international poverty reduction. Vice Premier Hui Liangyu attended the previous forums and delivered speeches on behalf of the Chinese government. The forum attracted a number of Nobel laureates, ministerial officials and representatives of developing countries, representatives of international agencies and non-governmental organizations,Chinas ministry leaders and experts on poverty reduction to deliver speech and it has become an important platform for international exchange in the field of poverty reduction. The "China- ASEAN Forum on Social Development and Poverty Reduction" jointly organized by the Chinese Government, the ASEAN Secretariat, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Asian Development Bank has been held for six times alternately in China and the ASEAN countries, mainly talking about hot issues on regional development. It has effectively promoted China-ASEAN cooperation and experience exchange in poverty reduction and become an important platform for China-ASEAN cooperation. Taking it as one of the contents of the cooperation with Africa, since 2010, the Chinese government has held the "China-Africa Poverty Reduction and Development Conference" jointly with relevant countries and international agencies. According to the needs of African countries, the theme of the three seminars was respectively "Development in Changes", "Chinas SEZ Development and Poverty Reduction" and "Agricultural Modernization and Poverty Reduction". The conference mainly shares the development paths and poverty reduction modes of China and African countries to constantly accelerate the process of achieving MDGs in Africa. In recent years, the Chinese government held more than one hundred high-level dialogues, seminars and forums and paid bilateral visits to exchange experience in the field of poverty reduction and signed poverty reduction agreements or set up poverty reduction cooperation centers with many developing countries such as Mexico, Argentina, Peru, Venezuela, Colombia, Tanzania and Mozambique to gradually deepen the exchanges in the area of poverty alleviation.
Charpter VI Poverty Alleviation and Development of Special Poverty-Stricken in China
I. Support the Development of Minorities
(I) Relax the standards for identification of minority objects of poverty reduction
In 1986, the State Council determined the standard of key poverty-stricken counties for national poverty alleviation: rural per capita net income of less than 150 Yuan in 1985 for the generally impoverished areas, but the standard was raised to 200 Yuan for old revolutionary base areas and autonomous Counties (300 Yuan for pasturing areas).62 poor ounties were listed among the key poverty-stricken counties after the relaxation of the standard, of which 51 were minority autonomous regions, accounting for 82%. The government gave priority to minority areas in identifying key areas for poverty alleviation and development. In 2001, in identifying the key counties, the state included the middle and western minority areas concentrated with poor people in the list of key regions for poverty alleviation and development and relaxed the standard for minority areas. Among the 592 key counties covered by the previous outline for poverty alleviation and development in rural China, minority counties accounted for 61%.
In 2011, the central government decided to take contiguous poor areas as the main battlefield of anti-poverty work and also gave priority to minority areas in dividing the contiguous poor areas
(II) Increase investment in minority areas
Give priority to poor minority areas in the size of bank loans and the allocation of fertilizer, diesel, agricultural film and other means of production. As for the increased national investment in agriculture, education funds, food for work, food and clothing project as well as other anti-poverty funds and materials, the distribution ratio of poverty-stricken minority areas is also significantly higher than that of other regions.
In the process of labor transfer training, each of the five ethnic minority autonomous regions and Yunnan, Guizhou and Qinghai province (referred to as the eight minority provinces) identified a national demonstration base of labor export training, arranged a certain amount of funds to develop ethnic handicrafts, actively carried out labor skills trainings and local labor transfer, and organized agricultural practical technical trainings of labor force left behind to improve their labor skills. In the implementation of the ex situ poverty alleviation relocation, in view of the poor living conditions of some minority people, the government vigorously constructed housing projects. As for poverty alleviation by science and technology,priority was also given to poor minority areas. In 2010,20 million Yuan of funds were issued for the poverty alleviation by science and technology in minority areas, accounting for 40% of the total. Meanwhile, the state issued anti-poverty loans to support poverty alleviation leading enterprises in minority areas. Driven by these enterprises, minority areas developed planting,breeding, specialty agricultural products processing industry and specialty tourism. In the East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation, the state arranged Beijing, Guangdong, Fujian,Shangdong and Qingdao, Shanghai, Liaoning and Dalian, Shenzhen and Ningbo to provide counterpart support for minority provinces and autonomous regions. In the arrangement for central state organs to participate in fixed-point poverty alleviation, it gave priority to the key counties in minority areas and a total of 204 key counties in minority areas were supported.In the international cooperation projects conducted jointly with international organizations, it also gives priority to minority areas.
From 2002 to 2011, after allocating 8.7848 billion Yuan of development funds for minority areas, the central government continued to increase investment in poverty alleviation in the eight minority provinces. The central government's special poverty relief funds increased from 3.8 billion Yuan in 2002 to 11.3 billion Yuan in 2011 and a total of 62 billion Yuan was invested in the decade, accounting for 415 of the total for all provinces. In 2008, all the 120 border counties including those in the western regions were covered by the "Action to Vitalize Border Areas and Enrich the People". Meanwhile, the provincial financial investment for poverty alleviation of the eight minority provinces is also increasing.
In the arrangement of the "food for work" funds, the state gave priority to the middle and western regions and poverty-stricken minority areas. As a result, the basic conditions of poor minority areas have been improved, creating a favorable external environment for the poverty reduction.
(III) Implement preferential policies
Release the marketing of agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry and mineral products beyond the national plan; allow poor minority areas to launch SMEs suited local resources advantage and allow local characteristics and advantages to supplement the national industrial policy after careful examination and approval; appropriately extend the repayment period and stop charging overdue penalty interest for the anti-poverty loans owed by poor households without the ability to repay, and allow the interest cease for unpaid debts; reduce the task of poverty-stricken counties to buy Treasuries and poor households are exempted from payment for treasury bills; determine the tax base of poverty-stricken counties and the overcharged are all reserved, continue to practice low interest rate and low tax rate on minority trading enterprises and provide price subsidies for the agricultural products of minority trading enterprises and the industrial products for the production of daily necessities of minority people. Poverty alleviation loan departments relax loan conditions in terms of repayment period and the proportion of self-owned capital for the agricultural, forest and pasturing development projects contributing to solving the food and clothing problem of the masses based on the production cycle and try to simplify loan procedures to ensure that the loans can be timely issued with the progress in the implementation of poverty alleviation projects.
(IV) Mobilize the whole society to participate in the poverty alleviation of minority areas
Since the reform, the state has given full play to the institutional strengths, mobilized and organized the eastern coastal provinces and municipalities, party and political organs at all levels and all circles of society to participate in the poverty alleviation and development of poor minority areas and achieved remarkable results. Over the years, relevant units conducted the fixed-point poverty alleviation through sending cadres, infrastructure construction, industrial poverty reduction, labor training and transfer, poverty alleviation by culture and education,poverty alleviation by science and technology, foreign-funded poverty reduction, poverty alleviation by ecological construction, poverty alleviation by health services, disaster relief and warmth delivery.
In the East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation, the government ontinued to arrange Beijing, Guangdong, Fujian, Shandong, Shanghai, Liaoning and Dalian, Qingdao, Shenzhen and Ningbo to provide counterpart support for seven minority provinces and autonomous regions. Based on the actual situation of poverty in Yunnan Province, Shanghai launched the food and clothing project, industrial development, education, health care and human resources development projects. In the arrangement for central state organs to participate in fixed-point poverty alleviation, it gave priority to the key counties in minority areas and a total of 204 key counties in minority areas were supported. In the international cooperation projects conducted jointly with international organizations, it also gives priority to minority areas. Xinjiang Autonomous Region, for example, has introduced and implemented the IFAD's comprehensive development projects for rural poor areas and UNDP's green poverty alleviation projects with total investment of $ 25.7 million, covering 1170 villages, benefiting 176,000 rural households.
In addition, the state has actively conducted cooperation with international organizations in the poverty alleviation and development in poor minority areas and got the support of anti-poverty funds from the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, a number of international non-governmental development agencies and organizations.
(V) Develop special policy measures to support the development of minorities
Beginning in 2002, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development has worked with the State Ethnic Affairs Commission in preparing the "Planning to Support the Development of Minorities (2005-2010)" and the "'11th Five-Year' Plan for the Action to Vitalize Border Areas and Enrich the People" and actively participated in the plan implementation. In 2005, the LGOP issued the "Circular on Some Regulations of the State Council on Conscientious Implementation of the 'Law of People's Republic of China on Regional Ethnic Autonomy'". Poverty alleviation departments at all levels were required to attach great importance to the poverty alleviation and development work in minority areas and include it into the planning for local economic and social development. Among the 267 key counties, the government selected the minority autonomous counties and all the Tibetan counties as the key areas for poverty alleviation and provided special support for these areas.The planning for poverty alleviation through entire village advancement covered 34,000 impoverished villages in seven minority provinces (autonomous regions), accounting for 22.9% of the total poor villages nationwide, and 200 poor towns in Tibet. The state organized the special action to vitalize border areas and enrich the people, supported border areas to boost the economic and social development and helped the masses in border areas increase income and become rich, covering all border counties in mainland China and border farms of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps. From 2002 to 2011, a total of 3.077 billion Yuan was invested in the action.
In order to implement the spirit of "increasing support for the development of old revolutionary base areas, ethnic minority areas, border areas and poverty-stricken areas" of the 17th National Congress of the CPC, the LGOP further increased efforts on entire village advancement and put forward that we must complete the implementation of the poverty alleviation planning of 209 minority villages,432 border poor village and 24008 poor villages in old revolutionary base areas of the key counties before the end of 2010. Among the "three guarantees" villages, one third are minority villages and many people are the minority poor. At present, we've completed the entire village advancement work.
Through these efforts, from 2001 to 2010, the number of low-income people in the eight minority provinces dropped from 30.768 million to 10.34 million and the rural per capita net income of the key counties in minority areas increased from 1219 Yuan in 2002 to 3131.3 Yuan in 2010. Poverty alleviation and development has improved the infrastructure of minority areas, enhanced the level of social services, increased the income of the poor,and changed the lives of the masses.
II. Support the Development of Poor Rural Women
The Chinese government has always been concerned about the poverty of rural women.In the development of pro-poor policies and planning, the government follows the principle of "women first" in allocating funds and projects. Over the decade, the state has included the development of women into the overall planning for national economy and social development, constantly improved the legal system to protect women's rights, strengthened the responsibility of government, increased investment and strengthened the social propaganda and mobilization. As of 2010, China had made significant progress in promoting the women's development and the equality between men and women. The degree of social security for women was generally enhanced and the situation of poor women was further improved; the level of political participation of women was constantly enhanced and women's consciousness of social participation was further strengthened. Women's education level continued to rise and the education gap between men and women was further narrowed; women's health status was significantly improved and the average life expectancy further extended; the legislation and law enforcement to protect women's rights was further strengthened and women's rights were further protected; the basic national policy of equality between men and women was deeply rooted among the people and the social environment for women's development was further improved.
The state mobilized social forces to concern about poor women and help women in poverty-stricken areas improve production and living conditions. Rural microfinance poverty alleviation project has been successively launched in the urban and rural areas of more than 20 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities through "microcredit, household poverty reduction and recycle". The project fund was 120 million Yuan and local matching fund was more than 70 million Yuan. It helped more than 300,000 women develop planting, breeding and processing industry and lifted more than 3 million people out of poverty. As of the end of October 2011, the "Happiness Project" to aid poor mothers had set up 463 project areas in 29 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) with a total investment of 829 million Yuan, helped 253,400 impoverished mothers and families, benefiting 1.138 million people. With unique objects of poverty alleviation, low cost and high efficiency poverty alleviation model, the "Happiness Project - Action of Helping Poor Mothers" achieved beneficial results in the practice of poverty alleviation and development. The "Spring Bud Program" designed to subsidize drop-out girls has raised more than 800 million Yuan of funds over the years, donated for the construction of more than 900 Spring Bud Schools, subsidized 1.8 million drop-out girls return to school, donated for the construction of nearly 5000 "Spring Bud Girl Classes" and organized practical technical trainings for more than 430,000 girls. From 2001 to 2010,the "Water Cellar for Mothers", which was designed to support the women in western water-deficient areas, invested more than 400 million Yuan for the construction of more than 120,000 water cells for mothers in 23 provinces, mainly in the west, and more than 1300 small projects for concentrated supply of water, and solved the drinking water difficulties of. more than 1.7 million people jointly with the CPC and the government.
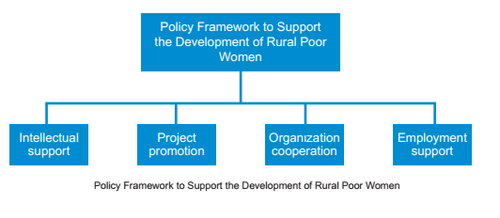
The state supports the implementation of the "Learning and Competing Campaign" and vigorously implemented the "Women's Action for Poverty Alleviation", "Community Service Project of Women" and "Motivational Project of Women". Through intellectual support,project implementation, cooperation between organizations, poverty reduction by providing jobs and regional cooperation, it strived to lift the women in poor areas out of poverty and increase their income, and achieved good results.
Through establishing contract offices and selecting contract households for poverty alleviation, All-China Women's Federation, the largest women's organization in China has carried out the cultural and technical trainings, provided microfinance service, organized the labor transfer of women in impoverished regions and launched women's poverty alleviation projects to lift poor women out of poverty. From 2001 to 2010, in order to give play to the role of female leaders in poor areas, it has successively held more than 40 trainings on the promotion of agricultural technology, cultivation of leaders in becoming wealthy by science and technology and female brokers, directly training nearly 10,000 women. The main contents of the trainings included: Marketing and modern management, financial knowledge, laws and regulations. Through training, it enhanced the self-development capabilities of backbone women in western regions and improved their ability to help rural women increase income and become rich. In addition, through the creation of 150,000 rural women schools, it organized trainings of practical skills, policies, laws and regulations, health care and environmental protection knowledge for rural women, especially the women in the middle and western poor areas. More than 8 million people received the trainings, nearly 5 million women mastered one or two practical technologies and nearly 750,000 women were titled as agricultural technicians and obtained green certificates.
Column 7: Anti-poverty loans for women saved and enriched my family
Lin Qiufeng, the "female champion" of pig breeding in Luxia town, Nanping City of Fujian Province has now more than 200 pigs in her farm. According to the latest market conditions, her net profit will exceed 50,000 Yuan. Eight years ago,however, Lin Qiufeng lived in extremely poverty."The anti-poverty loans for women saved and enriched my home", said Lin, with tears in eyes.
The loans mentioned by Lin refer to the microfinance policy implemented by Fujian Provincial Women's Federation in cooperation with the provincial financial department, provincial poverty alleviation office and financial department.
Eight years ago, Lin Qiufeng's husband suffered a car accident and became disabled. Lin spent more than 6,000 Yuan, which was saved for her family to buy citrus seedlings and piglets on medical treatment of her husband and the situation of the poor family was worse. At this moment, the "timely rain" of microfinance policy of Fujian Provincial Women's Federation occurred. Lin and other four impoverished women each applied for loans of 3000 Yuan as five-guarantee objects.
Lin used the loans to buy 7 sows and obtained benefit of 5700 Yuan that year. In the next year, she expanded the area of hog house and raised additional tens of piglets, By the end of that year, she earned more than 10,000 Yuan."The loans really help the poor", said Lin gratefully.
Fujian Provincial Women's Federation introduced that since it strived for anti- poverty funds of 3 million Yuan from the provincial government, it has issued small soft loans and carried out "Women's Business Loans" and other anti-poverty work to support rural poor women jointly with financial department. So far, it has issued a total of 1.059 billion Yuan of poverty-relief loans and helped more than 300,000 poor, low-income women to increase income by 1000-3000 Yuan per household.
In the recent two years, in order to maximize the efficiency of the limited amount of funds, the women's federations at all levels in Fujian Province created the microfinance model. You Cuiying, the principal of the Department for Women's Development of Fujian Provincial Women's Federation told the reporter that the model of"poverty alleviation by able women + credit household" achieved the best results. Last year, the businesswomen Wang Fenglan from Lixin Village, Lixin Town of Jianning County led 11 poor women of the village to engage in lotus seed purchase, processing and sales with small loans and helped them increase income by more than 5,000 Yuan per person.
Source: Xinhuanet, November 9,2008
III. Support the Development of Poor Rural Persons with Disabilities
People with disabilities are special social groups with difficulties. Poor disabled people account for a large proportion in the poor. According to the latest poverty line of 2300 Yuan of per capita net income, there are at least 20 million impoverished persons with disabilities in rural areas.
The poverty alleviation and development of rural people with disabilities is an important part of the poverty alleviation and development work. To further promote poverty alleviation and development of persons with disabilities, the state has developed the "Poverty Alleviation and Development Program for Rural Persons with Disabilities (2001-2010)" and the "Poverty Alleviation and Development Program for Rural Persons with Disabilities (2011-2020)". Since 2001, according to statistics, the food and clothing problem of nearly 13 million people with disabilities has been solved, the living conditions of the disabled have been improved'and their family income have witnessed a steady increase. The dilapidated houses of 546,000 families with disabled members have been renovated and the living conditions have been significantly improved.8.68 million persons with disabilities received agricultural production and practical skills trainings and master one or two production skills. Most of them have shaken off poverty through hard work and many became technical experts and leaders in becoming wealthy. More than 1.4 million people with disabilities have been directly supported by the discount loans for rehabilitation,2.17 million people with disabilities have shaken off poverty and become rich through working in the poverty alleviation base, and 118,000 units have built counterpart relationship with poverty-stricken families with disabled members.
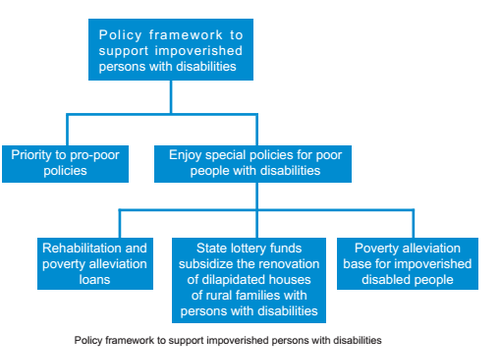
The experience of the Chinese government in poverty reduction for persons with disabilities: First, adhere to government leadership, include poverty reduction for persons with disabilities in the overall planning for poverty alleviation by governments at all levels, make overall arrangements and conduct synchronized implementation. Party committees and governments at all levels have included poverty reduction for persons with disabilities in the important agenda, developed a series of relevant policy measures, implemented the target assessment responsibility system and strengthened the supervision and inspection. Secondly, strengthen coordination among the departments, make concerted efforts to work together to promote the work. Based on their job responsibilities, the relevant government departments strived to improve the pro-poor policies, integrated relevant resources, increased financial investment and strengthened the implementation of various policies and measures. Thirdly, mobilize all social forces to participate in the work and support impoverished persons with disabilities in various forms. Local governments actively conducted the counterpart support activities of "one-for-one" and "many-for-one" and signed counterpart support agreements to ensure the poverty reduction. Fourthly, explore effective methods to reduce poverty among the disabled, support poor people with disabilities to develop production and increase income. According to the characteristics of persons with disabilities, local governments actively carried out various efficient sustainable development projects with little investment such as the project of "base + farmers", "five small businesses" and so on and achieved rapid income rowth of impoverished persons with disabilities. Fifthly, actively give play to the special role of disabled persons in the poverty alleviation for persons with disabilities and effectively implement the pro-poor policy measures for the disabled. Based on the vital interests and actual needs of persons with disabilities, the disabled persons' organizations at all levels gave full play to their own advantages, coordinated the implementation of policy measures of relevant departments,organized, guided and encouraged poor persons with disabilities to develop production and provided comprehensive and effective services. The good experience played an important role in promoting the poverty alleviation for the disabled and laid a solid foundation for future poverty alleviation for people with disabilities.
The "Outline of Poverty Alleviation and Development Program for Persons with Disabilities in Rural Areas (2011-2020)" points out that the government will continue to implement the state's rural social security systems, basic public service measures and poverty alleviation and development policies; include rural impoverished disabled people in the coverage of social security in rural areas and give them priority in protection and special support providing, and take the poor disabled with the ability to work as the key targets of poverty alleviation and development. By 2015, it will support 10 million rural poor families with disabled persons to increase income and improve living conditions; the social security systems will cover all persons with disabilities in rural areas; all rural eligible rural persons with disabilities will be covered by the minimum living security system and the disabled in rural areas will participate in the new rural social pension insurance system and the new rural cooperative medical system according to relevant regulations; the government will carry out community rehabilitation for the disabled in rural areas and provide rehabilitation assistance; and the poor disabled will be equipped with the basic aids when needed. By 2020, the impoverished disabled people in rural areas will generally obtain targeted support and their development capacity will be enhanced significantly; the level of social security and welfare for rural persons with disabilities will be further enhanced and the special social security and welfare system for the disabled will be gradually established and constantly improved; rural persons with disabilities in need of rehabilitation will generally obtain effective rehabilitation services, disability prevention knowledge will be popularized to effectively control the occurrence and development of disabilities. This program depicts a clear path for the poverty "alleviation and development for rural persons with disability in the future.
Column 8: "Renovation of Dilapidated Houses for Rural Persons with Disabilities"
In order to alleviate the housing difficulties of rural poor people with disabilities, the central government has arranged lottery welfare funds for the renovation of dilapidated houses for rural poor persons with disabilities and China Disabled Persons' Federation is responsible for the implementation and management. In 2009, according to the overall planning, the dilapidated houses of 69,000 poor rural households with disabled members would be renovated. The central government provided 102 million Yuan to support the middle and western provinces. The provinces and municipalities with better economic conditions such as Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangsu, Guangdong, Shandong and Liaoning strived to raise funds on their own and the central government no longer provided subsidy for these regions to conduct renovation of dangerous buildings.The central government subsidy for the renovation of dilapidated houses was 2500 Yuan per household, and the provincial, municipal and county financial departments provided the matching funds according to the ratio of 1:1. Regional governments can increase local tasks and subsidies based on the actual needs and financial resources.
Column 9: Rehabilitation and poverty alleviation loans
Rehabilitation and poverty alleviation loans are special credit funds issued by the state to solve the food and clothing problem of poor persons with disabilities, mainly used to support rural persons with disabilities to engage in farming, aquaculture, handicrafts and household sideline to solve their food and clothing problem. The loans are issued in form of microcredit directly to poverty-stricken households with disabled members and the central government issues interest subsidy.
Charpter VIIPilot Poverty Alleviation Projects in Special regions
In order to solve the problem of poverty of the regions and the masses with special difficulties, China has successively carried out a series of pilot poverty reduction projects. These various kinds of pilot projects at all levels in different scales conducted based on local conditions have explored a path, innovated the mechanisms and accumulated experience for the poverty alleviation and development in the new era.
I. Poverty Alleviation in Aheqi Border Area of Xinjiang
Located in the western part of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Aheqi County is mainly composed of mountains and deserts with soil area accounting for 0.3% of the total land area. It is always in winter and has no summer, with large evaporation capacity. It covers a large area but is sparsely populated and has inconvenient traffic. Meanwhile, it undertakes "the task of safeguarding 46 mountain passes and long border line of 371.4 kilometers. The per capita income of farmers and herdsmen in the county was only 42% of that in Xinjiang, the lowest in the whole region, and the incidence of poverty is 45% in rural areas.
Due to historical reasons, inadequate investment in border area and backward economic and social development, the front-line border residents live in extremely difficult conditions,there is a growing development gap between the border counties, the bases to support and serve border residents, and the inland cities, and the service functions of the border areas have been weakened. The number of the people living in border areas has been decreasing year by year and the quality of the border people is not high. The problems of outflow of talents, long-term poverty in front-line areas and weakened ability of border areas are prominent.
In March 2007, taking poverty alleviation and development as a platform, the state launched poverty alleviation pilot projects in border areas of Aheqi County. Through integrating the funds of Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Water Resources, State Administration of Radio, Film and TV and the Ethnic Affairs Commission and the grants of China Huaneng Group and Wuxi City, it has invested a total of 280 million Yuan for tile construction of 153 border poverty alleviation projects. In March 2007, Aheqi County was identified as a pilot area for border poverty reduction and developed the guideline of "one center" (developing industries, counties and border areas to promote the development of urban areas based on people's livelihood), "two targets" (targeting at the border line and rural areas) and "three changes" (changes in villages,families and the border line) for the pilot poverty alleviation work in border areas.
In the pilot poverty alleviation, Aheqi County successfully explored the new model of poverty reduction in border areas: Frontline is responsible for safeguarding the border line,second-tier regions are responsible for consolidating the border areas and third-tier regions mainly provide services. Remarkable achievements have been made in the work. It has invested a total of more than 280 million Yuan for the construction of 153 border poverty alleviation projects to solve the problems of food, schooling, medical treatment, travelling and industrial development most concerned by border residents, which promoted the integration of border areas and the mainland and promoted the integrated development of urban and rural areas in counties. As a result, the income levels of border residents have been significantly enhanced and the bearing capacity of the border defense staff.
Column 10: Main results of poverty alleviation in border areas of Aheqi, Xinjiang in 2010
1. Remarkable results in poverty reduction and development. In 2010, two key villages in Aheqi County passed the examination and acceptance for entire village advancement and 320 households and 1300 people steadily shook off poverty.
2. Rapid development of county economy. In 2010, with the implementation of a new round of poverty alleviation projects in border areas,Aheqi County witnessed rapid economic development and achieved GDP of 343 million Yuan, up 17% over the previous year; total fixed asset investment reached 920 million Yuan, up 99.5%; consumable retail revenue amounted to 62.45 million Yuan, up 12%; and the fiscal revenue reached 40.2 million Yuan, with an increase of 66.3%.
3. Constantly improved Infrastructure. First. launched housing projects for 300 households, established 5 residential areas equipped with plumbing facilities, electricity, heating equipment and highroads; Secondly, set up 650 Gobi facility agricultural sheds, developed forage base of 15,000 mu, strengthened the construction of water conservancy projects and newly built three diversion canals and water channels of 54 kilometers, which greatly improved the irrigation conditions of farming and pastoral areas; Thirdly, launched solar hot water projects. As of the end of 2010, a total of 487 solar water heaters had been installed.
4. Higher income level of farmers and herdsmen. As export of labor service and Gobi industries such as modern animal husbandry, facility agriculture and featured forestry and fruit industry have gradually become the leading industries,the farmers and herdsmen in Aheqi County have got stable channels for income growth. In 2010, the rural per capita net income reached 1697 Yuan,215 Yuan more than that of the previous year, up 15%.
5, Sound development of social undertakings. Further optimized the management mechanism with "primary schools built for all towns and junior middle schools for all counties", improved the county, town and village-level health care network and family planning service network, consolidated and improved the new rural cooperative medical system and medical assistance system and comprehensively launched the new rural social endowment insurance to ensure that all our people enjoy their rights to housing, employment, medical and old-age care.
6. A stronger sense of national identity of border residents. Based on the poverty reduction in border areas, a 44-member propaganda team was organized to conduct in-depth education activity themed "building a beautiful home with great love for the motherland". As a result, the border residents have a stronger sense of national identity and love for the motherland.
Source:"Yearbook of China Poverty Alleviation and Development (2011)", China Financial and Economic Publishing House,2011
II. Poverty Alleviation and Development and Integrated Control of Kashin-Beck Disease in Aba Prefecture of Sichuan Province
Kashin-Beck disease is an endemic, chronic, multiple and degenerative osteoarthropathy with unknown causes and it mainly occurs in children and adolescents. The international medical community calls it Kashin - Beck Disease.
In order to help 860,000 Tibetan and Qiang people of Aba Prefecture of Sicbuan get rid of the Kashin-Beck disease, since 2008, for five consecutive years, the central government has arranged 334 million Yuan for the poverty alleviation and development and integrated control of Kashin-Beck disease to help solve the disease problem plaguing the sick for a long time,change the situation of poverty and backwardness, accelerate the new rural construction in minority areas, consolidate national unity and promote social harmony. As of the end of June 2010, a total of 1.538 billion Yuan was paid, of which 1.002 billion Yuan was the anti-poverty funds provided by the central government,350 billion Yuan was from National Development and Reform Commission and 186 million Yuan was provincial matching funds. Working groups at all levels carried out the pilot work orderly through mobilizing the masses.
No one missing in relocation and education: All the 26,400 children above 5 in the Kaschin-Beck Disease Region have been transferred to the schools of non-disease areas.
The relocation gained unprecedented public approval: The relocation projects have been launched for 21200 people from 4514 households in 55 villages of nine counties.3208 households have already relocated and most of the farmers have moved into the new houses.
Adequate and timely supply of food. Grain of nearly 40 million kg has been supplied for 144,600 people (including 26400 school-age children in the disease areas) in the Kaschin-Beck Disease Region.
Full implementation of Entire Village Advancement: The Entire Village Advancement projects have been implemented in 255 villages. ]he program has built a total of 3,438 houses for the villages, constructed "five changes and two construction" household projects for 21,900 households, built village roads of 1,007 kilometers and village activity rooms of 14,800 square meters; supported the development of pillar industries of 9,401 farm households; improved power grids for 98,412 households; and trained 1,355 village-level cadres and 6,353 rural labors.
Basic safety of drinking water: Implemented 136 drinking water projects for poor villages,added effective irrigation area of 14,900 mu of farmland and basically solved the drinking water safety problem of 126,100 people in the disease areas.
Full coverage of social security: MI the 41,200 Kashin-Beck patients were included in the rural medical assistance and the new rural cooperative medical system; implemented medical treatment for 20,800 people; built 20 centralized support centers with 2,540 beds and a total of 935 III degree patients have checked in; provided rural subsistence allowances of 27.08 million Yuan for I and II degree patients.
Synchronization support for prosperity and industrial development: Implemented backbone industrial projects in 66 villages and launched eight aquaculture base construction projects. Newly built pollution-flee vegetables and potato base of 80,000 mu, featured fruit base of 36,800 mu, high-quality barley base of 47,800 mu and authentic Tibetan medicine base of 40,800 mu; cultivated 2.62 million bags of plateau middle/low-temperature type edible fungus, built four seedlings and standardization demonstration bases; purchased 61,500 heads of livestock, planed artificial grassland of 75,100 mu, built livestock pens of 601,500 square meters and 13 commercial livestock production bases; introduced 1010 improved varieties of male livestock, newly built 396 improvement bases and organized technical trainings for 5074 person-times.
Implemented technical services for 1,585 households, organized agricultural practical skills trainings for 20,700 people, improved basic farmland of 37,800 mu and newly built and improved tractor roads of 1,563 kilometers.
Meanwhile, the government has successfully constructed 14 high-quality tourist villages and built 454 "happiness of farmers (herdsmen) and happiness of Tibet (Qiang)" projects. In 2009, it received a total of 1.1763 million tourists with revenue of 46.1018 million Yuan.
Column 11: Remarkable results have been achieved in the poverty alleviation and development and integrated control of Kashin-Beck disease in Aba Prefecture
Through three years of hard work, Aba Prefecture achieved remarkable results in the poverty alleviation and development and integrated control of Kashin-Beck disease.
First, the incidence of Kashin-Beck disease has been effectively controlled. The medica service system in the disease area has been reproved steadily, remarkable results have been achieved in symptomatic treatment, the comprehensive disease prevention and control network integrating research,control and prevention has been established, the positive rate of X-Ray detection was reduced to 0.63% and new cases of Kashin-Beck disease have been effectively controlled.
Second, the educational conditions in the disease areas have been comprehensively improved. The school enrollment and consolidation rate of poor and sick children reached 100% and children are completely free from the risk of suffering from Kashin-Beck disease in the critica period of growth and development.
Third, the disease area has a new look. The living environment of more than 50,000 poor and sick people has been comprehensively improved, nearly 20,000 people moved away from the disease area, cutting off the chain of disease,and 126,000 people have got access to clean and safe tap water.
Fourth, the social security in the disease areas has been comprehensive enhanced. Through concentrated support, five-guarantee support and the rural minimum living security system, the government established an all-round security system in the disease area, achieving the goal of"security for everyone".
Fifth, the living standards of the poor and the sick have been significantly improved. A diversified income structure with "featured industry as the core supplemented by second and tertiary industry and migrant work" has been established and the trend of falling into or returning to poverty due to illness has been eased. In 2010, the rural per capita net income in 8 disease areas amounted to 3863 Yuan,122 Yuan above the prefectural average,1751 Yuan more than that in 2006, up 83%, and the growth rate was above the prefectural average.
The pilot projects really benefited the poor and the sick. As a'result, the poor and the sick begin to wholeheartedly support the construction of the party and the government's livelihood projects, the relationship between CPC and the masses and between cadres and the masses is better and the cohesion and combat effectiveness of the grass-roots party organizations have been further enhanced.
Source: Aba Government Network, China, April 3,2011
III. Overhead Cable Transformation
To solve the problem of difficulty in travelling of the people in remote areas, especially minority areas and help farmers and herdsmen improve the production and living conditions,in 2009, the central government launched the pilot projects of transforming overhead cables into footbridges in Sichuan, Yunnan and Tibet. Sichuan put in a total of 11.1847 million Yuan in the pilot project construction, of which,5 million Yuan was the financial anti-poverty funds from the central government,5 million Yuan was financial anti-poverty funds from the provincial government and 1.1847 million Yuan was the labor input of the masses. Yunnan invested a total of 9.7588 million Yuan, of which: 5 million Yuan was the financial anti-poverty funds from the central government,3 million Yuan was from departments and 1.7588 million Yuan was the labor input of the masses. Tibet invested a total of 23.09 million Yuan, including 23 million Yuan financial anti-poverty funds from the central government and 90,000 Yuan of other funds.
Through the joint efforts of various departments at all levels, initial results have been achieved in the pilot work. In Sichuan, the first batch of pilot projects were launched in seven counties including Ganzi and Liangshan, covering ten flexible cable suspension bridges of 980.17 meters, which has solved the problem of "difficulty in traveling, schooling, seeing a doctor and income growth" of 11376 local residents from 904 households in the project areas,and 35130 people from 6094 households in neighboring areas. In Yunnan, the government has completed five overhead cable transformation projects in five counties including Baoshan,Nujiang and Diqing, covering 20839 people and 4880 households. In Tibet, the pilot projects were launched in ten counties in Changdu, Shigatse and Linzhi, covering 18 simple bridges for human and animals. As of the end of 2009, six bridges had been built and relevant department was going to organize the examination and acceptance. The other 12 bridges are being built. After the project construction,8886 residents and 1568 households in the project areas will say goodbye to the cable era.
Column 12: Effectiveness of Tibet's overhead cable transformation in 2010
As of the end of 2010, Tibet had completed the design and expert inspection work for the remaining 66 overhead cable transformation projects. In September,it approved the construction of 45 overhead cable transformation projects with total investment of 160 million Yuan, of which 159 million Yuan from the state and 1.3791 million Yuan was labor service contribution of the masses. The state actually issued 120 million Yuan. Relevant experts have checked the design proposals of the remaining 21 projects and relevant department will then make further examination and inspection. Among the 45 overhead cable transformation projects,33 were constructed in Changdu with government investment of 88.5243 million Yuan; 10 were in Linzhi with government investment of 65.4212 million Yuan; and two are in Shigatse with state investment of 5.0252 million Yuan. The projects that have not been approved yet include ten in Changdu, ten in Naqu and one in Shigatse.
From 2009 to 2010,Tibet built 23 suspension bridges through overhead cable transformation, including 19 in Changdu,2 in Shigatse,2 in Naqu and one in Linzhi.The completion of these projects made 1800 households and 10205 people bid farewell to the "overhead cable era':
Source:"Yearbook of China Poverty Alleviation and Development (2011)",
China Financial and Economic Publishing House,2011
IV. Grass Growing and Livestock Breeding in Rocky Desertified Areas of Guizhou
Rocky desertification is a unique phenomenon of ecological desertitication in Karst region of South China. Similar to the northwest desertification, it is one of the extreme forms of land degradation and deterioration. These two phenomena are known as Chinffs two major ecological disasters in the 21st Century. Karst Areas of Southwest is one of the country's poorest regions and a key area for national poverty alleviation and development. It has more than 40 key counties for poverty alleviation, a population of 16 million and a land area of nearly 130,000 square kilometers with per capita GDP, per capita financial resources and farmers' per capita income far below the national average. This area has little arable land of poor quality.Due to the over-exploitation in the past, it is facing serious soil erosion and severe rocky desertification and is ecologically fragile. The agricultural production was once in a dilemma -farmers were poor without development, but the ecological environment would be destroyed again if development was conducted.
In 2001, Guizhou Province launched the pilot poverty alleviation project by developing Boer goat industry in Qinglong County. With technology poverty alleviation project as the carrier, it formed an industrialization poverty alleviation model characterized by government leadership, department cooperation, leading enterprises driving, cooperatives organization and enterprises' base building to benefit rural households and achieved good results, embarking on a path of poverty alleviation by grass growing and breeding, breaking the vicious cycle of economy and ecological environment of "grain growing - destruction of vegetation – soil erosion - decrease in grain production - expanding planting area - more serious problem of soil erosion and less arable land", and forming a vicious cycle of economy and ecological environment of "grass growing - soil protection - income growth by breeding - growing more grass" with obvious poverty reduction effect and ecological benefits. "[he average income of the farmers in project area is three to five times that of the farmers in non-project areas.
In June 2006, the LGOP and the Central Coordination Group for Intellectual Support for Border Areas held an on-the-spot meeting in Qinglong County and proposed the implementation of pilot project of industrialization poverty alleviation by grass growing and livestock breeding in the rocky desertified areas of eight southern provinces and autonomous regions. Guizhou Province put a lot of efforts on promoting the implementation of the pilot project. The provincial party committee and government leaders and department heads personally took charge of the pilot work, the livestock department actively cooperated to gradually address the difficulties encountered in the implementation of pilot project. As a result,the problems in the project construction were timely solved.
Since 2008, for three consecutive years, the central government has allocated financial anti-poverty funds for pilot projects of grass growing and livestock breeding in rocky desertified areas of Guizhou Province. From 2009 to 2010, a total of 1.125 billion Yuan was invested in the project construction, of which 40 million Yuan was issued for the pilot project of stony desertification control,95 million Yuan was industrial poverty alleviation funds from the central government,120 million Yuan was provincial anti-poverty funds for industrialization and 870 million Yuan was raised from Qianxinan Prefecture and Bijie. At present, the project construction has been basically completed with good poverty reduction effects.
V. Post-disaster Reconstruction after Wenchuan Earthquake in Sichuan
Wenchuan Earthquake occurred on May 12,2008 caused tremendous damage to the infrastructure, industrial and agricultural production, social services and people's lives and property in Sichuan, Gansu and Shaanxi Province, especially in rural areas and impoverished regions. In summary, the impact of the earthquake disaster to the poverty of planning areas included: (1) The poverty-stricken area in disaster-affected regions expanded rapidly. The poverty alleviation and development results were destroyed and the original poor became increasingly poor, even destitute. More people returned to poverty due to the disaster and the poverty-stricken area expanded. (2) The degree of poverty was further deepened. After the earthquake, the originally fragile infrastructure in the planning area was severely damaged,there was a significant reduction in public service capacity, the production means and the production and living conditions were seriously damaged, rural per capita net income dropped to less than 1000 Yuan (deducting subsidy income), more people had no houses to live, no sources of income and no production means, the masses were confronted with more difficulties in life and there was a serious decline in the level of economic and social development in the disaster-affected poor villages. (3) Resources and environment became more vulnerable. The planning area had inadequate resources of cultivated land and the quality of resources was rather poor. The load bearing of the land exceeded the carrying capacity by 2-5 times and many farmers maintained their livelihood relying on migrant work for a long time. qhe earthquake destroyed arable land and vegetation and caused landslides and soil erosion and the resources and environment became even more overwhelmed. In some poor villages and production teams, even all the villagers lived in absolute poverty. ]he production and living conditions in the regions where people once lived on natural resources became worse. (4) Poverty alleviation and development process was delayed. Since 2001, among the 4834 poor villages,2661 villages implemented entire village advancement, the production and living conditions were significantly improved, a large number of local featured industries were developed to increase the income of farmers and the poverty situation of rural areas was greatly improved. The earthquake almost destroyed the production and living facilities built with years of efforts, severely damaged the development foundation established through three decades of reform and opening up and two decades of poverty alleviation and development, increased the difficulty for the government to achieve the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of Chinas Rural Areas (2001-2010)" on schedule and delayed the process of poverty alleviation and development.
In order to support the post-disaster reconstruction in poor villages and make the economic and social development return to pre-disaster level to lay a foundation for sustainable development, explore mechanisms and models combining reconstruction and poverty alleviation and development, summarize relevant experience and enrich the poverty alleviation and development theories and practices with Chinese characteristics, the LGOP set up special agencies to carry out pilot work of post-disaster restoration and reconstruction in 100 impoverished villages in three batches. According to the requirements of basically completing the three-year reconstruction work within two years, it guided, coordinated, aided and pushed forward Sichuan, Gansu and Shaanxi's poverty alleviation departments to integrate resources and orderly and effectively promote the post-disaster restoration and reconstruction in 4834 poor villages in the planning area.
As of the end of 2009, the rural housing reconstruction in the Wenchuan earthquake-stricken area had been basically completed, the construction of public facilities had been accelerated, infrastructure restoration and reconstruction was conducted in an orderly manner,initial results were achieved in industrial reconstruction and structural adjustment, urban system construction was launched, the market service system was restored and smooth progress was made in ecological restoration, disaster prevention and mitigation and land use. The effectiveness of post-disaster restoration and reconstruction after Wenchuan Earthquake could be summarized as the following eight aspects: First, stimulated the internal dynamism of the poor villages for restoration and reconstruction and enhanced the confidence of the poor in reconstruction and development. Second, significantly improved the basic production and living conditions of poor villages, laying a foundation for sustainable development. "Third, improved the patterns of training and exchange activities and effectively enhanced the ability of poverty alleviation departments and village cadres to organize the restoration and reconstruction.Fourth, improved the management system for the development and implementation of the participatory post-disaster restoration and reconstruction planning for poor villages and showed the working characteristics and capacity of poverty alleviation departments. Fifth, explored the establishment of a mechanism for multi-sectoral participation in post-disaster reconstruction of poor villages and accumulated preliminary experience. First of all, the government paid attention to the coordination in the planning development process to promote the participation of various parties. Meanwhile, it made full use of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)-funded early recovery and disaster risk management projects after Wenchuan earthquake and, jointly with UNDP and relevant departments, explored the establishment of a mechanism for multi-sectoral participation in post-disaster reconstruction of poor villages.Sixth, conducted relevant topic summary and research work to promote the experience sharing and exchange. Seventh, advocated the ideology and awareness of combining disaster prevention and mitigation / post-disaster reconstruction with poverty alleviation and development, which was an innovative practice of a specific pattern of combination. Eighth, the restoration and reconstruction of poor villages was an important part of the post-disaster restoration and reconstruction after Wenchuan Earthquake, making a positive contribution to achieving the overall goal of the reconstruction.
VI. Poverty Alleviation of Bulang (Mang people and Kemu people) Nationality and Shanyao of Yao Nationality in Yunnan
The number of the Mang and Kemu people living in the 23 natural villages of Yunnan Honghe Haini Yi Prefecture, Jinping Miao, Yao and Dai Prefecture and Mengla County and Jinghong City of Xishuangbanna Dai Prefecture reaches 3972 and they are "Direct Transition Nationalities" that directly transformed from primitive society to the socialist society after the liberation. Having long lived in the primeval forest, also for some historical reasons, the Mang and Kemu people are extremely poor. In January 2008, General Secretary Hu Jintao made the following important instructions: "Yunnan provincial government must put forward support
Column 13: Happy life of Lao Peng, a citizen of Dujiangyan
Peng Jialun, a citizen of Dujiangyan over sixty lived in Fulong Community before the earthquake on May 12. His house was destroyed in the earthquake. After the earthquake, through drawing lots, his family got a three-bedroom apartment of 85 square meters in Yijie District constructed with support of Shanghai and moved into the new house in December 2010. Lao Peng is a culture and sports enthusiast and was active in participating in NGO activities such as Tai Chi performance organized by local elderly sports association. After moving into the new house, he was pleased to find that there are more cultural and sports activity space in the new community and more and more citizens are joining them for Tai Chi performance and Fan Dance. Nowaday, Laopeng feel very happy as he enjoys the rich daily activities.
Source: Sichuan Daily, May 10,2011
measures to help them shake off poverty as soon as possible". Premier Wen Jiabao also made important instructions: "The comrades of poverty alleviation offices must put forward policy measures together with Yunnan provincial government and relevant departments to solve the production and living problems of Mang people and Kumu people". To implement the important instructions of the leaders, in March 2008, LGOP took the lead to establish the coordination group composed of relevant personnel of LGOP, State Ethnic Affairs Commission, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Civil Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Transport, Ministry of Water Resources, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Health, State Administration of Radio, Film and 1W, the State Forestry Administration, Shanghai, China Southern Power Grid and Yunnan Provincial government to give instructions for the poverty alleviation and development of Mang people and Kemu people of Yunnan Province. Meanwhile, to effectively solve the production and living difficulties of Mang people and Kemu people, and help the poor in ethnic minority areas shake off poverty as soon as possible, from 2008 to 2009, the central government arranged financial anti-poverty funds of 20 million Yuan to implement pilot projects for poverty alleviation of Mang people and Kemu people. After the project construction, great changes have taken place to the production and living conditions of Mang people and Kemu people.Over the two years, the government implemented Entire Village Advancement program in all the 23 natural villages concentrated by the Mang people and Kemu people and constructed 324 housing projects for them, with an average household living area of more than 80 square meters. Meanwhile, the government vigorously constructed "five small" water conservancy projects to improve the irrigation of mountain areas; built basic farmland of 5100 mu, two water reservoirs with capacity of 820,000 cubic meters and solved the drinking water problem of local people and livestock. In addition, it accelerated the construction of power grid and built village highroads of 203.9 li and 11 bridges, achieving the goal of universal access to highroads of the Mang and Kurnu villages. Besides, the government has erected 10-KV transmission lines of 27.17 km to solve the electricity problem in the production and life of the masses.
Increase support for the development of featured industries. Leading industries have been initially fostered. In accordance with the requirements of "backbone industry for villages and projects for income growth of households", the government put more efforts to the construction of industry and invested a total of 11.555 million Yuan in the two years to promote the development of featured planting and breeding industries. By the end of 2009, the per capita net income of Mang people and Kemu people reached 1413 Yuan and 1887 Yuan respectively,924 Yuan and 689 Yuan more than that in 2007. The food and clothing problem of the poor among Mang people and Kemu people was basically solved.
Increase efforts on technology and practical skills trainings. Over the two years, the government had organized a total of 187 agricultural technical trainings for 10,900 person-times, and transferred 45 village working team members to help the masses develop production.As a result, the self-accumulation and self-development capacities of the poor have been significantly improved.
Increase efforts on social construction to enable Mang people and Kemu people share the results of reform and opening up. Effectively increase investment in education and implement school building and students' neighborhoods preferential admission policy. By the end of 2009, the school-age children enrollment rate in Kemu neighborhoods reached 99.7%, plus the rural health infrastructure construction, it has solved the problem of difficulty in seeing a doctor. Combining the construction of "Frontier Cultural Corridor", "universal access" to radio and TV program of the villages, the 23 natural villages concentrated by the Mang people and Kemu people have got access to radio and TV program; vigorously increased the intensity of social security and included 1806 poor Mang and Kemu people into the rural minimum living security system to help them participate in the new rural cooperative medical system and illness relief system. Through strengthening the development of education, health, culture and other social undertakings, it has promoted the overall coordinated economic and social development of Mang and Kemu neighborhoods.
Shanyao is a branch of the Yao Nationality and Shanyao people mainly live in the regions with harsh natural conditions and backward infrastructure characterized by the lack of information and economic resources. In these regions, the development of social undertakings seriously lags behind and there are no conditions for mankind to survive and develop, so the masses live in extremely poverty with extremely backward production and lifestyle. The poverty is reflected by "four low" and "five difficulties": a small area of arable land; low income level; low standard of living and low quality of population. Meanwhile, the problem of "five difficulties" is prominent, involving difficulty in drinking water, traveling, housing, electricity and medical service. Since 2010, with strong support of the relevant ministries and Shanghai Municipal government, Shanyao launched the pilot work of poverty reduction. According to the guideline of "moving home, planting trees and developing education" for overall development,through "cross-township ex-situ relocation within the county, including resettlement into the construction of small towns and supporting local development", the government launched six major projects, namely "industrial development, infrastructure construction, housing,food and clothing, improvement of quality, environmental protection and construction and livelihood security", and achieved substantive results in lifting Shanyao people out of poverty and supporting their development. (1) Industrial development projects: As of May 2011, the six towns with Shanyao people had developed tea-oil trees of 4281 mu, walnut trees of 137 mu and sugar cane of 3820 mu; built sheep pens of 1000 square meters and raised 4856 sheep and 4560 pigs; organized 25 labor transfer trainings for 1700 person-times, transferred 1120 labors, sent more than 830 labors to Yachang Farm and other enterprises and organized 25 technology trainings for 2368 person-times, which further broadened the sources of economic revenue of the Shanyao masses. (2) Infrastructure construction projects: Constructed Grade Four gravel roads of 15 kilometers from Yakou of Neiwu to Longmen, village roads of 200 meters in Puba, village roads of 15 kilometers in Pubo and village roads of 2 kilometers in Huami; newly built water pipelines of 125.18 kilometers for man and livestock, built 690 small water cellars and irrigation canals and ditches of 13 kilometers. (3) Housing, food and clothing projects: So far, it has completed the housing construction for 993 households, hardened village roads of 54100 square meters, constructed 120 low-renting houses for residents of small towns and basically completed the construction of basic farmland of 20 mu. (4) Improvement of quality: Completed the construction of teaching buildings and dormitory buildings of 5526 square meters for ten schools with Shanyao children including Jianlongmen School, opened up a boarding class for Shanyao children in the county and recruited 50 Shanyao students, issued subsidies of 391,500 Yuan for poor Shanyao students, built 12 technological and cultural activity rooms and one clinic, renovated one toilet; implemented radio and television coverage works for 1100 Shanyao households of 43 production teams; and officially launched the preparation work for the construction of Xinhua Central School, Shanyao Class of No.1 Middle School of the County, teaching building of Dongpo Town's Central School, teaching building of Naneng Town's Central School, Zhesang Town's Central School and other schools for Shanyao students. (5) Environmental protection and construction projects: Built 248 biogas digesters, returned farmland to forests and closed hillsides of 320 mu to facilitate afforestation in Shanyao Town. (6) Livelihood security projects: Invested one million Yuan to build a Class II nursing home of 670.7 square meters; included 8429 Shanyao people from 1828 households into the rural minimum living security system to achieve full coverage of eligible people; 8,429 people were exempted from payments for participating in the rural cooperative medical system;1,698 Shanyao students were exempted from tuitions and received subsidies for living expenses.Meanwhile, subsidies of 391,500 Yuan were issued for needy Shanyao students.
Charpter VIIIDevelopment Capacity Building of Poverty Alleviation and Development Institutions
For the development of impoverished areas and the poverty reduction of the poor,external support is the condition and their own efforts are the foundation. Since the 16th National Congress of the CPC, the Chinese government has attached great importance to the development capacity building of poverty alleviation and development institutions, given full play to the initiative and creativity of poverty-stricken areas and the objects of poverty reduction, strengthened ideological guidance, deepened the reform and innovation of institutional mechanisms, encouraged self-reliance of the masses of poor areas and actively implemented participatory poverty alleviation to enhance the level of self-management and development capacity of the objects of poverty reduction.
I. Actively Implement Participatory Poverty Alleviation
After the "Outline" was promulgated, the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development clearly pointed out that China will take participatory poverty alleviation and entire village advancement as two basic pro-poor strategies. No matter seen from the poverty reduction scale or the implementation effectiveness, participatory poverty reduction is a major event in Chinas rural development and has a profound impact on Chinas poverty alleviation and rural development.
Combining its concepts and methods with the anti-poverty work, participatory poverty alleviation aims to "make the objects of poverty reduction help themselves" and participate in the design, implementation and evaluation of poverty-relief projects as well as the project facility maintenance. Participatory poverty alleviation pays special attention to the applications of proper methods such as an attitude of equality, reaching a consensus through consultations,being concerned about the capacity building of the aided, making clear the real needs of the target groups, encouraging communities to design and implement projects by themselves and establishing and improving community management mechanisms. The introduction of the concepts and methods of participatory poverty reduction can overcome some of the problems for the traditional approaches to poverty reduction. For example, the traditional poverty alleviation can hardly ensure to really benefit the poor and the masses in some places are unsatisfied with the distribution of poverty alleviation resources and the project's effectiveness.Compared to the traditional way for poverty reduction, participatory poverty alleviation stresses not only government and social support for the poor, but also the self-reliance and self-development of the poor masses. It can be said that participatory poverty alleviation is a concept and method to build the self-development capacity of poor communities and achieve long-term effective poverty reduction and the goal of poverty alleviation through mobilizing and promoting the poor to actively participate in the poverty alleviation and development activities for poverty reduction and development.
In the process of implementing participatory entire village advancement, first of all, the poverty alleviation system pays attention to the decisive role of poor farmers in the project. In the past, the selection of poverty alleviation projects, the use and arrangements of funds,the formulation of the plan, the project implementation and the identification of poverty alleviation achievements were all decided by the government department. At present, the decision-making power for poverty-relief work and the use of funds has been given to the masses and all the beneficiary farmers decide what to do, how to do it and who will do it. It has greatly stimulated the initiative and enthusiasm of poor farmers.
Secondly, introduce and attach importance to democratic supervision. In the past, the poverty-relief project application and approval procedures basically followed the practices of the planned economy era, the whole operation was controlled by the administrative institutions under a closed condition and farmers almost had no right to speak on the project or what project to be launched. Participatory poverty alleviation, however, stresses the transparency of anti-poverty funds and projects and the democratic supervision. In accordance with the provisions of the "Notice on the Establishment and Implementation of Announcement System for Poverty Alleviation Projects (Guo Kai Fa No. [2004] 2)" issued by the State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development, all the financial anti-poverty funds (including work-relief funds, minority development funds and special subsidies for the agricultural development in the "Three West" areas) and anti-poverty discount loans issued by the central government, the poverty-relief funds issued by regional governments as well as the projects implemented with these funds must be publicized. The contents of the publicity include the total amount, sources, nature and use of poverty-relief funds, the distribution principle and plan for the use of the funds, the name, location, construction content, implementation unit,the amount of funds and quality requirements of the anti-poverty projects, etc. For the projects for villages and rural households, advance publicity is required and the government must extensively solicit opinions and make announcement in the project construction site. In some places, the government even announced the key villages for support and the funding plan and arrangements of that year. Some regions established the planning supervision team composed of villagers and poor farmers to conduct supervision on the implementation of poverty-relief projects.
Thirdly, promote the full participation farmers. Participatory poverty reduction emphasizes to promote and encourage farmers to participate in the key links of entire village advancement projects through propaganda, including the investigation on the village, the discussion on development ideas, the planning, implementation, management, supervision, examination and acceptance. Empower the masses. Through guiding the participation of the masses in the whole process, screen development projects, develop poverty alleviation planning and organize the project construction so that the poor farmers can be involved in the whole process of project selection, screening, implementation, management, supervision and evaluation.
The successful implementation of participatory poverty reduction in China achieved very good poverty reduction effect. Participatory poverty alleviation stimulated the inherent impetus to the development of poor communities and poor farmers. Through empowering poor farmers, it has established the dominant position, dignity and self-confidence of the poor,helped the poor masses establish the spirit of ownership and a strong sense of responsibility to lift themselves out of poverty for sustainable development and further carry forward the spirit of self-reliance and hard work. Participatory poverty reduction helped the poor farmers build capacity for sustainable development. It puts more emphasis on taking the process of the design, implementation, management and evaluation of village-level poverty alleviation planning and projects as a process for poor farmers to learn. Through learning by doing, the farmers will enhance their ability. With all the opportunities in the process, participatory poverty alleviation encouraged farmers to deal with the problems of their own communities. In he process of dealing with problems and the implementation and management of anti-poverty project, farmers make decisions based on self-management and thus improve their decision-making ability and management capabilities. In such a way, participatory poverty reduction achieved the essential conversion from "giving a man a fish" to "teaching a man to fish".
Through these efforts, Chinas participatory poverty reduction achieved remarkable results.More and more farmers have understood the projects implemented in their villages. From 2002 to 2010, in the villages where poverty relief projects were implemented, the proportion of the farmers who knew the project launch or fund issuance in their villages increased from 91.4% to 93.8%; the proportion of the farmers selecting projects by themselves in the farmers involved in the project construction rose from 38.1% to 50.1%; and the proportion of the farmers involved in anti-poverty activities increased from 10.7% to 22.6%. The implementation of participatory poverty alleviation activities becomes increasingly open and fair. In 2010, in the villages where poverty-relief projects were launched, the farmers who understood the project contents through public channels accounted for 72.9% of the total,9.9 percentage points higher than that in 2002.
Participatory concept and method was introduced from abroad, but its purpose is similar to Chinas traditional "mass line" and it can guide the better development of ChinaEmpower the masses. Through guiding the pars current social patterns and governance. Participatory poverty alleviation is a new concept to apply participatory concept and method to the cause of Chinas poverty alleviation and is, to a large extent, a concept born in China. The development of participatory poverty alleviation is a process of constant exploration, constant revisal and continuous improvement, a process of constant combination with the reality of China and the tide of political system reform in China, and is a great innovation of Chinas poverty alleviation system
II. Specialized Farmers' Cooperative Organizations
According to the "Law of the People's Republic of China on Specialized Farmers' Cooperatives", Specialized farmers' cooperatives are "mutual-help economic organizations joined voluntarily and managed in a democratic manner by the producers and operators of the same kind of farm products or by the providers or users of services for the same kind of agricultural production and operation".
Over the three decades since reform and opening up, the development of China's new rural cooperative economic organizations has gone through three basic stages. In the first stage (prior to the 1990s), the cooperatives mainly promoted the development of professional technical associations, specialized agricultural production households and specialized villages,laying an important foundation for the development of agricultural products specialized cooperative organizations. In the second stage (early 1990s-late 1990s), specialized cooperatives and professional technical associations both witnessed rapid development. In the third stage (since the 21st century), the innovation pace of various farmers' cooperatives began to accelerate.At the beginning of the 21st century, With Chinas WTO entry, farmers are confronted with the competitive pressure from the domestic and international market and the slow growth of farmers' income became the most important problem of the "three rural" issues. Central government's agricultural policy turned to support the unity of farmers for the development of specialized cooperatives. The "Agricultural Law" launched on July 1,2003 clearly states that the state encourages farmers to set up various kinds of specialized cooperatives on a voluntary basis,and encourages and supports farmers' specialized cooperatives to participate in agricultural industrialization, agricultural product circulation and processing as well as the promotion of agricultural technologies, etc. The central government set up the Central Ftlnds for the development of farmers' specialized cooperatives in 2004 to support the healthy development of farmers' specialized cooperatives. In July 2007, the "Law on Specialized Farmers' Cooperatives" was officially implemented. It not only makes clear the dominant position of farmer cooperatives in the market, but also provides regulations on government policy to support farmers' specialized cooperatives.
Since then, China's rural cooperative undertakings has entered the most active innovation and development stage since the reform and opening up and the development of various farmers' specialized cooperatives showed an uptrend, becoming a new highlight of the system innovation for agricultural operation organizations.
As of the end of 2011, according to statistics, the total number of the farmers' cooperatives registered in administration of industry and commerce according to law in China reached 521700 and 41 million rural households participated in the cooperatives, accounting for 16.4% of the total rural households in China. Seen from the involved industries, despite the short history, farmers' cooperatives are engaged in a wide range of industries, involving the primary, secondary and tertiary industry, including farming, aquaculture, agricultural machinery, forestry, plant protection, technical information, handicraft, "Happy Farm" and biogas service, etc, mainly farming and aquaculture. The cooperatives engaged in these two industries respectively account for 43.3% and 29.7% of the total, reaching 73%. Seen from the services the cooperatives provide, the cooperatives engaged in production and marketing,production service, transportation, marketing and storage services, and processing services respectively account for 52.2%,26.2%,4.4% and 2.5% of the total. The cooperatives involved in production and marketing and that specialized in production and marketing account for 85.3% of the total.14.7% of the cooperatives are engaged in other services. It shows that in a buyer's market, it is the main motivation for farmers to establish specialized cooperatives to smoothly sell all the products they make and achieve value added through processing.
The legislation system for the development of cooperatives has been basically established. In recent years, the "Law on Specialized Farmers' Cooperatives", the "Administrative Regulation on the Registration of Farmers' Professional Cooperatives", the "Model Regulations" and the Financial and Accounting Rules have been successively implemented and the process of local legislation has also been gradually accelerated. Some provinces have successively revised or issued the supportive measures on the "Law on Specialized Farmers' Cooperatives" based on local actual situations, while some other provinces have included the implementation method of the "Law on Specialized Farmers' Cooperatives" in the provincial congress' legislation plan or legislation survey plan. The promulgation and implementation of these supportive regulations further provided a solid legal protection for the development of cooperatives.
At the same time, the policy system to support the development of cooperatives has been initially established. A series of supportive policies and measures on finance, taxation, financial and agriculture-related products as well as industrial support have been successively issued. Almost all provinces' party committees and governments have developed relevant documents to promote the development of cooperatives. Especially some government departments and provincial governments have provided effective support for the development of farmers' cooperatives and allocated funds to support cooperatives to undertake comprehensive agricultural development projects, improve the conditions for agricultural production (such as standardized plantation and standardized cultivation communities) and the infrastructure for the circulation of farm produce (such as refrigeration houses for storage of fruits and vegetables, vehicles for the transportation of farm produce), improve their production conditions and strengthen their marketing service capacity.
The talent team building of cooperatives has been constantly strengthened. The personnel training of cooperatives has been included in the "Outline for the National Planning for Medium and Long-term Development of Personnel (2010-2020)". The Ministry of Agriculture organized the implementation of "Sunshine Project for Management Personnel Training of Cooperatives" and the "Modern Agricultural Talent Support Plan for the Training of Principals of Cooperatives", formulated and issued the regulations on the work of cooperatives' instructors and the regulations on administration of cooperatives' personnel training bases to guide local governments to integrate training resources, optimize training environment, enrich training contents, innovate training methods and effectively increase efforts on personnel training for cooperatives. From 2006 to 2010, various kinds of cooperatives organized personnel trainings for more than 1 million person-times.
The credit cooperative modes of farmers' specialized cooperatives in China are as follows:
(1) Internal "production cooperation + capital cooperation" of farmers' specialized cooperatives
In October 2008, the "Decision on Several Major Issues on Promoting the Reform and Development of Rural Areas" approved by the Third Plenary Session of the 17th Central Committee of the CPC proposed for the first time to "allow farmers' cooperatives with certain conditions to carry out credit cooperation". Nol Document of the Central Government issued in 2009 further proposed to "issue specific measures for farmers' specialized cooperatives to carry out credit cooperation as soon as possible" and "develop specific regulations for finance to support cooperatives as soon as possible". With the expanding of the pilot area for the new rural financial agencies in rural financial market, some regions began to launch pilot projects of rural mutual cooperatives and village-level mutual-funds, aiming to make internal mutual-fund cooperation of farmers' cooperatives and the development of integrated cooperatives as a potential method to solve the financing difficulties of cooperatives.
Column 14: The Model of "Production Cooperation + Capital Cooperation" of Guhe Pig Breeding Cooperatives of Funing County in Yancheng of Jiangsu
Guhe Pig Breeding Cooperatives of Funing County in Yancheng of Jiangsu is a comprehensive specialized cooperatives integrating the operation of Guhe livestock Market, Feedstuff Sales Department and Thoroughbred Sow Breeding Cooperatives. Covering a land area of nearly 30 mu, Guhe Livestock Market is responsible for the sales of all the livestock bred by contracted members and the local town and sells more than 150,000 piglets every year for surrounding areas as an agent, with sales network covering more than 600 counties and cities of 15 provinces (municipalities, autonomous regions). The cooperatives raised 200,000 Yuan of share capital to open the Feedstuff Sales Department. It sells the feedstuff at mill price to reduce the feed cost of its members and farmers.The Thoroughbred Sow Breeding Cooperatives was set up in 2004 by 25 members with 590,000 Yuan,with the cooperatives' pig farm as the base.
In order to solve the capital shortage for its member farmers to buy boars, in July 2007, Guhe Pig Breeding Cooperatives explored the establishment of internal mutual-funds and mutual-fund service department and raised mutual-funds of 1.4 million Yuan from more than 200 members. In accordance with the principle of"only serving its members, absorbing share capital but not savings, allocating dividends but not interests, voluntary and paid mutual services", the mutual-fund service department raised its members' dispersed, idle capital in the form of share capital and regularly issued the capital to its members for pig breeding with interest rate lower than that of local rural cooperative banks at that time. If the funds are still insufficient, the cooperatives will provide loan guarantees for rural financial institutions to issue loans to its members.
Source: Study Case, Bao Zongshun, President of Jiangsu Rural Development Institute
(2) "Production cooperation + warrant cooperation" of farmers' specialized cooperatives
China Banking Regulatory Commission and the Ministry of Agriculture jointly issued the "Opinions on Financial Services for Farmers' Specialized Cooperatives" in March 2009. The "Opinions" proposed to "encourage the development of farmers' cooperatives with security function and provide guarantee for the members to obtain loans through joint guarantee, guarantee funds and the risk margin so as to develop union credit loans to meet the financial needs of the members of farmers' specialized cooperatives". As the members of farmers' professional cooperatives are relatively homogeneous in production and operation, it is convenient for them to know and monitor each other to ensure the symmetry of information and prevent moral hazard. The security cooperation based on the production collaboration,therefore, is similar to the joint guarantee loan mechanism. It makes filll use of local information and the trust between the members. Meanwhile, to the members, the cooperation in the field of production increases the cost of default.
Column 15: The Mode of"production cooperation + security cooperation" of Yuguo Comprehensive Agricultural Development Cooperatives of Suixian County
Sanligang Town of Suizhou in Hubei Province is the largest distributing center of mushrooms in China and the mushrooms in the market of this town account for about 60% of the total in the country every year. Founded in October 2009, Suixian Yuguo Comprehensive Agricultural Development Cooperatives is located in Jixiangsi Village of Sanligang and was jointly initiated by Yuguo Mushroom Industry Co., Ltd and Jixiangsi Village. It has the mushroom srowing cooperatives, loan mutual guarantee cooperatives, a logistic company and a travel service company as a union cooperative. With a legal capital of 4.15 million Yuan, the Cooperatives has now 2369 farmer members.
In order to solve the capital shortage of its members in mushroom production, transport and sales, the Cooperatives, in cooperation with the Agricultural Bank of China, set up the Farmers' Loan Mutua Guarantee Cooperatives in 2009. Its main practice: The members in need of capital voluntarily form a few union guarantee teams (averagely ten people for each team) and each farmer needs to pay 5000 Yuan of security deposit to participate in the cooperative. The Agricultural bank of China issues loans according to the standard of ten times the deposit and farmers can obtain loans of 50,000 Yuan at most. The operating income of the guarantee cooperatives is the guarantee fee and interest income of stock capital. Farmers pay the security deposit to the cooperatives according to the standard of no more than 1% of the loans.40% of the operating income of the guarantee cooperatives is in the account of the compensation guarantee funds, used to repay the overdue loans. Meanwhile, the guarantee cooperatives has set up a guarantee fund account and the share capital of the members is in this account, mainly used to repay the loans when the compensation guarantee fund is insufficient to repay overdue loans. A special fund management account was set up for the remaining 60% of operating income, which is used as the administration fee of the guarantee cooperatives.
Source: Study case, Ma Jiujie, Professor of Renmin University of China
The main innovation of this mode is to combine guarantee cooperatives with the members' joint guarantee mode to form a unique guarantee system and mode. Meanwhile, we must pay attention to the following two problems in the operation. First, the difference in the operating capacity of the cooperatives' members leads to different capital needs, but the premise for the establishment of the joint guarantee team is that the capital needs of the team members do not differ, otherwise, the benefits and risks will be asymmetric and it is difficult to form a joint guarantee team. Second, it can be promoted in the regions with certain industrial support and mature industrial chain. For financial agencies, on the one hand, it is convenient to monitor the operation activities of the loan borrowers to prevent collective strategic default of the joint guarantee team members. On the other hand, the regions with such conditions have mature products and market and strong ability to resist risks.
(3) Embedded agricultural industrial chain financing mode of farmers' specialized cooperatives
With the advance of agricultural industrialization and modernization process, the vertical collaboration in the field of agriculture is becoming more common and it is particularly important how to effectively organize all relevant sectors and industries to form a complete industrial chain to jointly participate in market competition at home and abroad. When taking agricultural production and management process as a whole, we can see that from the supply of agricultural materials (seed, feed, machinery, etc.) to agricultural production, and from the processing of agricultural products (grading, packaging, storage, etc.) to the sales of farm produce, it is an order chain composed of a series of companies and organizations. When agricultural market develops from local areas to nationwide and even to the international market, agricultural competitiveness is reflected by the overall competitiveness of industrial chain and operating system. At present, more and more farmers' professional cooperatives begin to embed into the industrial chain of relevant industries to participate in vertical collaboration as the industrial chain of industrial production and trading has attracted the attention of financial agencies and created industrial chain financing mode. This mode has been gradually applied to agriculture by some financial agencies. For farmers' specialized cooperatives in the industrial chain of agriculture, it is a feasible loan mode to solve external debts.
III. Mutual Funds of Impoverished Villages
Since 2006, in order to effectively alleviate the shortage of development funds for poor farmers, actively explore the establishment of new mechanisms and new models for improving the use and management of financial anti-poverty funds and strengthen the capabilities for self-development and sustainable development of impoverished villages and households, learning from the experience in microfinance, the LGOP and the Ministry of Finance have launched the pilot project of mutual funds for impoverished villages.
Pilot project of mutual funds is a special kind of poverty alleviation designed to alleviate the backwardness of rural finance, shortage of financial products, lack of production capital and the prominent problems restricting agricultural and rural development, especially the poverty reduction of impoverished rural households.
Mutual funds refer to the production development funds established in impoverished villages owned, used, managed and enjoyed by the people for turnover and rolling development.Mutual funds are mainly used for poverty reduction with mutual assistance as the core and cooperation as the direction. The principles for identifying pilot villages: First, the impoverished villages where entire village advancement project is being or has been implemented; Second,the poor villages where the masses are simple and honest and willing to develop with high enthusiasm and the village cadres have strong cohesive force, appealingness and fighting capacity. Third, the impoverished villages with certain potential for industrial development. On the basis of following the above principles, priority is given to the villages with a higher degree of poverty and such impoverished villages are identified through competition with a village as the unit.
Mutual aid organizations are all named as "xx Village Mutual Aid Society". Mutual aid societies are established in administration villages and cannot be set up until the participation rate exceeds 50% and the total number of involved rural households reaches 50. The management agencies and staffs of mutual aid societies are democratically elected and registered in local department of civil affairs. Farmers are free to join and leave the mutual aid organizations. Mutual funds must be paid when a farmer joins the mutual aid society. Mutual aid organizations take households as the unit and one person of each household is permitted to joint it. Meanwhile, mutual aid societies practice the system of "one person, one vote". Mutual funds are operated closely within the mutual aid organizations and loans must be repaid in time for turnover and rolling development and mustn't be privately divided. Members share the benefits and risks together. The principle of giving priority to poverty-stricken households shall be followed and mutual aid organizations may not absorb savings or engage in any other unauthorized financial or operating activities.
The overall objectives of pilot mutual funds: To innovate models of poverty alleviation, effectively alleviate the fund shortage for development of impoverished villages and poor rural households; explore the establishment of an effective way to combine anti-poverty funds with the independent operations of farmers, guide the development of pillar industries, cultivate new farmers' cooperatives and new types of farmers and achieve sustainable development.
The basic principles of pilot mutual funds: Pilot areas must be strictly limited to poor villages. Poor households may be exempted from the participation fee or pay less to participate in the mutual funds but enjoy the same rights as members and will be given priority to obtain financial and technical support. The operation and management must be standardized. Mutual aid societies are established in administration villages and mutual funds may not be issued to other villages and may not absorb savings. Actively and steadily promote the implementation of pilot program and develop a scientific planning for the scale of pilot projects within our reach with risks under control. Give priority to the provinces and counties with high working enthusiasm and a solid foundation that vigorously implemented the projects with standardized operations. Average allocation is not proposed.
"Mutual fund" consists of four parts: First, fiscal anti-poverty funds. The central government provides subsidies of 150,000 Yuan averagely for each pilot area; Second, mutual funds voluntarily paid by villagers; Third, unconditional donations from all circles of society; Fourth, value added of the mutual fund. Among them, the fiscal anti-poverty funds, donations and the value-added are owned by all the villagers of the administrative village; while the mutual fimds paid by villagers are owned by the villagers themselves. The use rights of mutual funds are owned by all the members. The General Assembly of the mutual aid organizations is the highest authority for the management of mutual funds. The council is responsible for day-to-day operation and management of the mutual funds while the Board of Supervisors is responsible for the supervision of the operation and management of mutual funds. As of 2011, pilot projects of mutual funds had been launched in 16300 villages of 1141 counties nationwide and the mutual fimds amounted to 3.306 billion Yuan.
Through the implementation of the pilot project and the establishment of mutual aid organizations in poor villages to promote self-development of poor rural households and strengthen the targeting of poverty reduction, it has effectively alleviated the fund shortage of poor farmers,innovated the mechanism for the use and management of anti-poverty funds, improved the degree
of organization and self-development capacity of poor households and promoted the grassroots democracy construction and tile changes in the working style of government.
IV.Mircrofinace
Microfinance itself is a credit lending model. As it has successively addressed the problem of providing effective credit services for poor famers that was not solved by formal financial institutions for a long time and achieved the sustainable development of credit agencies themselves at the same time, microfinance has been regarded as an effective way for poverty alleviation by many development aid agencies and the governments of developing countries.Chinas microfinance was initially introduced by the United Nations aid agencies in the 1980s to support women's development and promote employment and poverty alleviation.
At the early stage of development, microfinance in China was operated in the form of project or through microfinance organizations and the funding sources included international or domestic donations or soft loans. International loans were mainly used in domestic projects, operated by non-government organizations, qhe loans were mainly used to improve the status of women, increase employment opportunities, improve the conditions for health care and childbearing and achieve financial inclusion. In 2000, domestic capital for microfinance began to increase and the loan objects were expanded to low-income people, including non-poor farmers. Apart from the poverty reduction effect, it also contributed a lot to the improvement of the livelihood and quality of life of rural households, the improvement of rural communities and the achievement of financial inclusion and social justice.
In addition to the government, non-government organizations (NGOs) played an important role in the microfinance. According to the statistics of Microfinance Alliance Annual Report 2010,44 NGOs organized relevant microfinance agencies and rural mutual aid societies (members) to issue loans for a total of 75575 clients, averagely 1717 for each agency.
Since the introduction of the financial poverty alleviation model - mirocredit from Bangladesh in 1993, microfinance has become an important supplement to formal finance in rural areas and made important contributions to solving the financial needs of disadvantaged groups. The role of microcredit is mainly reflected in the following three aspects:
First, microcredit helps poor farmers to get credit loans and the opportunity for technical trainings. "Through its special institutional arrangements, microfinance may increase opportunities for poor households to get loans and provide technical training services for the users while providing credit service. The funds provided by microcredit can be used to promote the development of micro-enterprises of industry and commerce and play an important role in stabilizing non-agricultural employment opportunities. Microfinance has a positive effect on reducing the natural and market risks of poor households. Through providing the users with financial and technical support, it can increase the sources of income of poor households and,to some extent, change the grain production-based production structure and income structure of the poor. Some microfinance projects provide loans for the users in case of disasters to reduce risks, which also alleviated, to some extent, the predicament of poor households in obtaining loans when they are hit by natural and man-made disasters. Microfinance is widely considered by the international community as an important way to empower women. In the design and implementation process, microfinance in China takes it as an important principle to target at poverty-stricken women and many microcredit programs dearly put forward the policy of giving priority to women. Microfinance has played a positive role in increasing employment opportunities for women and the opportunities for women to contact the world outside the home.
Second, microcredit promotes the improvement of the fnancial pro-poor policies. First,explored an approach for anti-poverty funds and projects to reach rural households; Second,increased opportunities for the poor to select projects; Third, make all circles of society pay more attention to the repayment of loans; Fourth, strengthened the organization and management of poverty alleviation work to some extent.
Third, microcredit promotes the development of rural cooperatives. In impoverished regions without poor organizational resources, the grassroots organization for mutual supervision and risk-sharing of the users set up by microfinance project with credit service as the core is undoubtedly another important contribution made by microfinance to the poor in addition to the improvement of poverty situation to obtain financial service opportunities. So far, many central and western provinces and autonomous regions have established grassroots organizations in poor areas to support the operation of microfinance, such as poverty alleviation society, service society, rural development association and so on. These grassroots organizations directly provide services for poor households and allow the poor to participate in the management. While supporting microcredit financial services and technical services, these organizations developed in microfinance may also have an important effect on the cooperation and cohesion between poor people and the formulation and implementation of community development plans.
Charpter IX The Sitution and tasks of Poverty Alleviation and Development in China
The deepening of reform and opening up and socialist modernization provides more favorable conditions for the poverty alleviation and development in the new era. However, we must be aware that China is still and will be in the primary stage of socialism for a long time,the overall level of economic and social development is not high, the problem of unbalanced regional development is prominent, the deep-rooted structural imbalance restricting the development of impoverished regions still exists and the task of poverty alleviation and development is still very arduous.
I. The Overall Development of Poor Areas Lags Behind
The level of economic development in the key counties is rather low. In 2010, the per capita GDP of the country's 592 key counties was 11,170 Yuan, per capita net income of farmers was 3,273 Yuan and rural per capita living expenditure was 2662 Yuan, respectively accounting for only 37%,55% and 61% of the national average; the urbanization rate of the ten western provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities except Tibet and Xinjiang was only 40.92%, roughly equivalent to the national average in 2003. The urbanization rate of the key counties was lower than that of the western regions, with a great gap with the national average. According to the latest statistics, in 2011, the per capita net income of farmers in 11 contiguous poor areas was 4,191 Yuan and per capita living expenditure was 3662 Yuan,respectively 60.1% and 70.1% of the national average in rural areas. The rural Engel coefficient of the contiguous poor areas was 16.8%,6.4 percentage points higher than the national average in rural areas.
The proportion of primary industry in the key counties is fairly high, roughly equivalent to the level of domestic cities and counties in 2003. The proportion of the labors engaged in primary industry is fairly high, roughly equivalent to the national level in 2000. Seen from the structure of farmers' income, in 2010, the proportion of operating income of rural families in the key counties was 5.8 percentage points higher than national average in rural areas and the proportion of wage income was 5.4 percentage points lower. In 2010, the per capita wage income of rural areas was 2431 Yuan,370 Yuan more than that of the previous year, tip 17.9%, and wage income contributed 48.3% to the income growth of rural residents that year. In poor areas, the per capita wage income was 1169 Yuan,157 Yuan more and up 15.6%, contributing 36.5% to the income growth, and the main indicators were below the national average.
The level of public services in rural areas of the key counties is rather low. In terms of infrastructure, after years of efforts, by the end of 2010, the level of "four access" (access to roads, electricity, telephone line and TV program) in the administrative villages of the key counties was relatively close to the national average in rural areas. In other aspects, however, there are still obvious gaps: The rural per capita housing area was 9.2 square meters smaller than the national average, the proportion of the farmers drinking tap water and deep well water was 17.1 percentage points lower than national average and the proportion of the users of aqua privies and flush toilets was 5.4 percentage points lower.
II. A Large Number of Objects of Poverty Reduction
Due to the substantial increase in the poverty line, by the end of2011, the number of the objects of poverty reduction reached 122 million, accounting for 12.7% of the rural people.With the increasing of the objects of poverty reduction, the distribution of the poor also shows new features.
Significant changes have taken place to the distribution of the objects of poverty reduction in the eastern, central and western regions. In 2010, based on the original poverty line, there were a total of 26.88 million poverty-stricken people in rural areas, of which 17.51 million lived in the western regions,8.13 million in the central areas and 1.24 million in the east, respectively accountingfor 65.14%,30.25% and 4.61% of the total. In 2011, based on the new poverty line, the number of the objects of rural poverty reduction was 63.45 million in the west,42.38 million in the central areas and 16.55 million in the east, respectively accounting for 51.9%,34.6% and 13.5% of the total. Although more than half of the objects of rural poverty reduction lived in the western regions. Compared to the original standard, the proportion of the poor in western regions dropped fell by 13 percentage points. It indicates that although most of the poor whose food and clothing problem has just been solved are concentrated in the middle and western regions, the objects of poverty reduction who still lack conditions for development after the food and clothing problem has been steadily solved are widely distributed in the country. It brings some difficulties to the targeting of poverty alleviation and development.
III. A Huge Development Gap between Urban and Rural Areas
Uneven development is a major problem encountered in the process of transformation of China's development. Different institutions have calculated China's Gini coefficient to reflect the income gap and all believed the Gini coefficient for urban and rural areas is over 0.4. Not only the development gap between urban and rural areas is constantly widening, the problem in poverty-stricken areas is also very serious. In the impoverished areas, the prominent problem is that in the places rich in resources, the counties are wealthy, such as Yan'an, Yulin, Ordos and Baise, and rapid progress has been made in urban construction, but the development of remote villages lags behind. The total fiscal revenue of Luliang City in Shanxi Province ranks only second to Taiyuan in the province, but the per capita net income of farmers is the province's penultimate.
In recent years, the gap between disposable income of urban residents and rural per capita net income has been maintained at 3.2 times and the absolute value gap was more than 13,000 Yuan in 2011. Within the rural residents, based on per capita net income quintile, the per capita net income of rural residents of the lowest-income group in 2010 was 1,870 Yuan,with an average annual increase of 8.8% in the past decade; that of the highest-income group,however, reached 14,050 Yuan, with an average annual increase of 10.5% in the past decade."The difference between the two expanded to 7.5 times in 2010 from 6.5 times in 2000. From 2002 to 2011, except 2006 and 2010, the Gini coefficient of the per capita net income of rural residents showed an upward trend, reaching 0.3897. Even in the relatively underdeveloped central and western rural areas, the problem of imbalance is also very prominent. The rapid growth of fiscal revenue of some places covered up the low growth of farmers' income; the development of some counties and new rural construction demonstration villages covered up the relative poverty and backwardness of many rural areas; and the typical households and wealthy fanlilies that developed well covered up the overall backwardness of poor rural areas.
IV. Poverty-returning Pressure on Objects of Poverty Reduction
According to the poverty monitoring data of the National Bureau of Statistics, the short-term poor account for two-thirds of the announced total poor and people in long-term poverty account for only one-third. In other words, the poor who returned to poverty that year account for two-thirds of the total poor. "The factors for poverty-returning are complex. The traditional factors for poverty-returning mainly include natural disasters and family tragedies. With the development of market economy, however, the problem of poverty-returning due to the macroeconomic conditions for the development has become increasingly prominent.
Natural disaster is still the most important factor for poverty-returning. The incidence of serious natural disasters of poor villages is five times that of other regions. With fragile ecological environment, poor infrastructure and weak fiscal capacity, poor areas can hardly prevent and fight natural adversities and poverty-stricken families seem to be so helpless in the face of disasters. The poverty alleviation industries cultivated for years are often destroyed on one day in case of a disaster.
Families' individual factors can also lead to poverty-returning. The new rural cooperative medical system has, to some extent, alleviated the difficulties of farmers in seeing a doctor,but major illness, serious illness and disabilities are still important reasons for rural families to return poverty. With the improvement of the level of education and the rising tuition for non-compulsory education, the phenomenon of "falling into poverty due to education" is still very prominent in rural areas.
Macroeconomic fluctuation has become an increasingly prominent impact on poverty reduction. From 2004 to 2007, with the implementation of the central government's policies to support agriculture and rural areas and enrich the farmers, the annual decrease in the number of poverty-stricken people reached 10 million. After 2008 global financial crisis, however, this figure was reduced to 3 million, the same as that in 2003. In 2009, through hard work, this figure rose to 4.1 million. In 2010, the national economic situation was better and the decrease in the number of poverty-stricken people soared to 9.09 million, which directly reflects the impact of economic fluctuations on the effectiveness of poverty reduction.
V. Difficulties in Development of Contiguous Poor Areas
Contiguous poor areas are mainly in the western regions. Seen from the location and social characteristics, they are mainly in old revolutionary base areas, minority areas and border areas. Seen from the natural geography, there are five kinds of contiguous poor areas:Characterized by pneumatorexis and hydropenia, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is prone to disasters;in desertified areas, water shortage is a serious problem; loess plateau has the same problem of aridity; the main problems in stony desertified areas are the lack of soil and leakage of water; in mountainous areas, the problera of soil erosion is serious.
The 11 contiguous poor areas identified in 2011 and Tibet, the Tibetan areas of four provinces and the three prefectures in South Xinjiang covered a total of 680 counties, where the level of economic and social development is far lower than the national average and even lower than the western average. Based on the average figure from 2007 to 2009, the per capita GDP of these counties was 6,761 Yuan, the per capita local general budget revenue was 272 Yuan and the per capita net income of farmers was 2,677 Yuan, respectively equivalent to 49%,44% and 73% of the western average, much lower than the national average.521 of the 600 counties ranked lowest in the country are in the contiguous poor areas, accounting for 86.8%. In 20ll, there were 55.64 million objects of poverty reduction in the 11 contiguous poor areas, accounting for 45.5% of the total in the country, but the land area of these regions only account for 14.5% of the total. The incidence of poverty here was 28.4%,15.7 percentage points higher than the national average, qhe main battlefield of poverty" alleviation has almost covered most of the regions in a relatively deep degree of poverty and the masses in deep poverty in the country. These areas generally have a weak economic foundation, poor production and living conditions, low level of industrial development and poor infrastructure and public services. In individual area, even the food, clothing, housing and road problem of the masses has not been fundamentally solved and the farmers have to live on government relief and social assistance. The task of poverty alleviation and development is extremely arduous.
Charpter X China’s Strategic System for Poverty Alleviation and Development in the New Era
2011 is an important year in the history of Chinas poverty alleviation and development.In this year, the central government promulgated and implemented the "New Outline", held a central anti-poverty work conference, significantly raised the national poverty line, started the implementation of the planning for key problem tackling for the poverty alleviation and development of contiguous poor areas and painted the blueprint for Chinas poverty alleviation in the new era.
From 2011 to 2020, under the guidance of socialism with Chinese characteristics, Deng Xiaoping theory, the important thought of"Three Representatives" and the Scientific Outlook on Development, the government will raise the poverty line, intensify support, make the contiguous poor areas with special difficulties the key target areas, and make quicker access to food and clothing and help people shake off poverty faster the top priority. The government will continue to play a leading role in striking a balanced development, transforming economic development pattern, improving comprehensive quality of the people, achieving an equal distribution of basic public services, tackling acute problems that restrict development, and striving for a better and faster development.
We will continue to adhere to the policy of development-oriented poverty reduction, achieve the effective linkage between development-oriented poverty reduction and the subsistence allowance system, make development-oriented poverty reduction program the main channel for shaking off poverty, encourage and aid able-bodied needy people to shake off poverty through their own efforts; make social security network the basic means to ensure subsistence and improve social security network gradually.
I. The Goal and Key Tasks of China's Poverty Alleviation and Development in the New Era
The overall objective to deepen the poverty alleviation and development by 2020:Adequate food and closing, compulsory education, basic medical care and housing will be available to poor population; per capita net income growth rate of poor peasants will be higher than national average, leading indicators of basic public services will be close to the nationalm average, and the widening development gap will be bridged overtime. Specifically, breakthrough will be made in the following five aspects:
First, significant improvement in the production conditions. The basic farmland,irrigation facilities and other infrastructure in poverty-stricken areas will be improved significantly, basic food grain per capita will be guaranteed, featured projects to increase the income of farmers will be launched, featured competitive industries will witness rapid development and featured backbone industry system will be basically established.
Second, significant improvement in the living conditions. Further enhance the degree of rural drinking water safety and the popularizing rate of tap water in poor areas,provide a comprehensive solution to the electricity problem of the administrative villages and people without electricity; build asphalt (cement) roads for administrative villages with certain conditions and provide regular bus for all villages; and expand the scale of renovation of dilapidated houses in rural areas to significantly improve the living conditions of the masses.
Third, Rapid development of social undertakings. Make pre-school education universal in poor areas, further enhance the level of compulsory education, popularize high school education; basically improve the county, town and village-level medical service network,significantly enhance the medical service capacity and level of county hospitals, make the participation rate of the new rural cooperative medical system maintain at 90%, achieve more equal access to public health and basic medical services for the masses in poor areas more equal,establish and improve radio and television public service system, comprehensively achieve access to broadcasting and TV program for all villages, provide Broad Band service for all natural villages, build libraries and cultural centers for each key county, comprehensive cultural stations for all towns and literate activity room for all the administrative villages.
Fourth, significant enhancement of the level of social security. Further improve the rural minimum living security system, the "five guarantee" system and the temporary assistance system, achieve full coverage of the new rural social pension insurance system and further enhance the level of social security and services in rural areas.
Fifth, significant improve in the ecological environment. The ecological civilization construction will be strengthened and the forest coverage ratio increase by 3.5% over 2010. We'll gradually achieve balanced population development to promote harmony between man and nature.
II. Overall Requirements of Poverty Alleviation and Development
First, adhere to government leadership and hierarchical accountability. This is a valuable experience for Chinas poverty alleviation and development and must be adhered to for a long time. We will adhere to the poverty alleviation and development management system under the coordination of the central government with provincial government taking the overall responsibility and county government responsible for the implementation, implement poverty alleviation and development goal accountability and appraisal system, implement the system for party and government leaders to take the overall responsibility and establish the working mechanisms with contiguous poor areas the core and specific work done for villages and poverty reduction for households. We'll include poverty alleviation and development in the economic and social development strategy and overall planning to ensure the steady growth of funds for poverty alleviation and development and give full play to the leading role of the government in poverty alleviation and development. We'll continue to improve the mechanism for the assessment of the poverty alleviation and development work of party and government leaders, relevant department and the key counties, strengthen the supervision, assessment and evaluation on the anti-poverty work, strengthen the management of the use of anti-poverty funds and timely understand the implementation situation of the poverty alleviation and development planning, the implementation situation of the relevant measures, the use of anti-poverty funds and the progress of the work.
Second, highlight the priority and give specific guidance. China is a country with a vast territory and the situations of various regions are quite different. Adhering to combining the deployments of the central government with the actual situation of different regions, we'll strive to promote the poverty alleviation and development based on actual situation. The central government will increase support for poverty alleviation and development, mainly for the development of old revolutionary base areas, ethnic minority areas, border areas and especially contiguous poor areas with special difficulties. "lhe poverty reduction in the central and western regions will focus on consolidating the achievements in solving food and clothing problem and accelerating the pace of shaking off poverty in order to solve the major bottleneck restricting the development. Eastern regions where conditions permit will enhance the level of poverty alleviation and development and explore an effective way to reduce relative poverty and achieve common prosperity. To the poor who fall into poverty for different reasons, we'll adopt more targeted measures to support them.
Third, insist on the participation of the whole society to jointly promote the anti-poverty work. Poverty alleviation and development is the common responsibility of the whole party and society. We will continue to vigorously carry forward the fine tradition of the Chinese nation in helping the poor to form a strong joint force for poverty alleviation and development through joint efforts of the party and society. Various departments and regions will perform their duties and make close cooperation with each other according to the requirements of the "New Outline", make it part of their work to support the development of impoverished areas and actively complete their task for poverty alleviation and development. We'll continue to give full play to the important role of social forces in poverty alleviation and development and extensively mobilize all circles of society to participate in poverty alleviation and development.
Fourth, insist on respecting the dominant position of the objects of poverty reduction to stimulate the inherent vitality of the poverty-stricken areas. Based on local conditions, we'll further promote the reform and innovation, expand the opening up and accelerate the construction of the systems and mechanisms conductive to scientific development and poverty reduction. We'll continue to combine poverty alleviation and development with the urbanization and building a new socialist countryside and combine the anti-poverty work with ecological construction and environmental protection to achieve sustainable development. We'll continue to vigorously carry forward the fine tradition of self-reliance and hard work,stimulate the enthusiasm, initiative and creativity of the cadres and masses of poverty-stricken areas, respect the dominant position of objects of poverty reduction and encourage them to be independent. We'll encourage and send excellent young cadres, veterans and college graduates with good thinking, style and strong ability as well as the willingness to serve the masses to poor villages to help build poverty reduction teams, give instruction in development and lead the masses to develop economy and shake off poverty.
Fifth, strengthen international exchanges and cooperation in the field of poverty alleviation and development. Since the reform and opening up, China has attached great importance to the use of foreign capital in poverty alleviation and learning from the experience of foreign countries in poverty alleviation, implemented many anti-poverty projects or activities in various forms joint with the international community and achieved good results. We will continue to strengthen international exchanges and cooperation in poverty alleviation and development, make innovations to the mechanisms and broaden the channels to carry out cooperation in poverty reduction projects through going out and bringing in. We'll actively present our achievements and experience in poverty alleviation and development to the international community and strive to make new and greater contributions to the cause of global poverty reduction.
III. Range of Objects of Poverty Alleviation and Development
Able-bodied rural residents whose incomes are below the poverty line are objects of poverty reduction. The government will gradually establish and improve the mechanism to identify the objects of poverty reduction, improve the information management system for the use of poor farmers and implement a dynamic management to lay a good foundation for the protection of the objects of poverty reduction.
Based on the conditions and characteristics of the distribution of Chinas rural poverty alleviation objects, the priority of poverty reduction should be given to the contiguous poor areas concentrated with objects of poverty reduction. The government beill channel more resources to those identified regions, step up trans-provisional guidance and coordination,pool strengths and launch projects in turn. Provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government should be responsible for helping contiguous poor areas with special difficulties. Guided by the central government, local governments should design and implement the plan of county-based poverty reduction projects. Departments of the State Council and local governments at all levels should facilitate better coordination, carry out a series of welfare projects covering education, health, culture, employment and social security to improve the production and living conditions, cultivate and strengthen specialty and competitive industries, expedite the development of important regional infrastructure, enhance ecological and environmental protection, tackle bottlenecks that restrain the development,promote the equalization of basic public services, and put an end to the backwardness of poor areas. Provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government also enjoy the right to give more support to contiguous poor areas with special difficulties identified by themselves. At present, in accordance with the basic idea for regional development to promote poverty alleviation and development and anti-poverty work to promote regional development, the government is developing and implementing the planning for key problem tackling for the poverty alleviation and development of contiguous poor areas and various department have all issued relevant policies.
We'll continue to do a good job of poverty alleviation in the key counties and poor villages except the contiguous poverty-stricken areas. The support policies for original key counties will maintain unchanged. Various (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government) will develop policies and adopt relevant measures to make adjustment based on actual situations so as to gradually reduce the number of key counties. The government will not reduce efforts on supporting the provinces that reduced the number of key counties.
IV. Consolidate and Develop the Large-scale Poverty Alleviation Pattern Integrating Special Poverty Alleviation, Industrial Poverty Alleviation and Social Poverty Alleviation
After years of exploration, China has formed a large-scale poverty alleviation pattern integrating special poverty alleviation, industrial poverty alleviation and social poverty alleviation and effectively mobilized all circles of society to participate in poverty alleviation and development. We'll continue to consolidate and improve this pattern in the practice, further position these three kinds of poverty alleviation to make them support and complement each other based on a rational division of labor.
In the poverty alleviation, the provinces shall assume overall responsibility while the counties shall formulate concrete measures for implementation in the villages and ensure the poverty reduction of specific households. The government will perform its function to protect the poorest regions and people, focus on developing anti-poverty industries, enhancing the development capabilities of the poor and improving the basic production and living conditions of impoverished areas, and organize the implementation of poverty-relief relocation, entire village advancement, work-relief work, industrial poverty alleviation, employment promotion, pilot poverty-relief projects and the construction of old revolutionary base areas, etc.
Based on the business functions of various sectors, the industrial poverty alleviation will play its role in helping the poor, take the improvement of development environment and conditions of impoverished regions as an important content of the industrial development planning, give priority to impoverished regions in the allocation of funds and projects, support the development of featured industries, carry out poverty alleviation by science and technology,improve the infrastructure, develop education and cultural industry, improve the public health and the management of population services, improve social security systems and attach importance to energy and ecological environmental protection to complete the anti-poverty task assigned by the state.
Social poverty alleviation will highlight the synergy function, strengthen fixed-point poverty reduction, promote East-West cooperation in poverty reduction, give play to the role of the army and armed police forces and mobilize businesses and all circles of society to participate in poverty reduction. Relevant departments and units directly under the central government, people's organizations, the public institutions managed according to the Civil Servant Law,large-scale state-owned backbone enterprises, state-owned holing financial institutions, national key scientific research institutions as well as the military and armed police forces should actively participate in flxed-point poverty alleviation and bear the corresponding task of flxed-point Poverty reduction. We'll continue to support the democratic parties and All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce to participate in poverty alleviation work, actively encourage,guide, support and help all kinds of non-public enterprises and social organizations to undertake poverty alleviation task. The government will encourage and guide enterprises, social organizations and individuals to be involved in poverty alleviation and development through a variety of ways and actively advocate volunteer action of poverty reduction.
V. Continue to Improve the Policy System for Poverty Alleviation and Development
The policy is an important guarantee for poverty-stricken areas to accelerate development and for the poor to shake off poverty. We'll further improve the taxation, investment,financial, industrial, land, ecological, and human resources policies and measures to support the development of poor areas so as to form the pro-poor strategy and policy system for impoverished regions and the poor to accelerate development.
The government will gradually increase investment of central and local governments in poverty alleviation, increase the central and provincial government's general transfer payment for poverty-stricken areas and increase efforts for central lottery funds to support the cause of poverty alleviation and development. The increased anti-poverty funds of the central government will be used to support the development of contiguous poor areas. The government will increase investment in the construction of infrastructure, ecological environment and people's livelihood projects in poor areas.
We'll strengthen the capacity building of the financial services system in poverty-stricken areas, achieve full coverage of financial services in the towns of poor areas as soon as possible,encourage and support the county-level banks and financial agencies in poor areas to use the new loanable funds for local development, continue to improve the national discount loans policy for poverty alleviation, encourage the issuance of micro-credit loans and strive to meet the capital needs of the poor for the development of production.
In the allocation of large-scale national projects, key projects and new industries, the government will give priority to eligible impoverished regions and guide labor-intensive industries to transfer to impoverished areas. In accordance with the provisions of relevant system on the protection of farmland and the management of rural land use, in the allocation of new construction land targets, priority will be given to housing construction of the relocation projects in poor areas. The government will make rational arrangements of the construction land for small towns and industrial zones of poor areas.
The government will develop relevant policies to encourage colleges, research institutes and medical agencies to organize personnel trainings for impoverished regions, guide college graduates to work and launch businesses in poverty-stricken areas, develop relevant policies to encourage the work of cadres in poor areas, give priority to various technicians in arranging positions and titles and be concerned about the sending cadres for fixed-point poverty alleviation and East-West cooperation in poverty alleviation to give full play to the important role of various kinds of talents in poverty alleviation and development.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
China is a developing country with a population of over 1.3 billion and the difficulty for it to conduct poverty alleviation and development is rare in the world.China has made arduous efforts to address the problem of poverty and made significant progress.
Looking to the future, the Chinese government will adhere to the scientific concept of development, put poverty alleviation and development on a more prominent position, comprehensively implement the "Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development in China's Rural Areas (2011-2020)", take it as the new policy goal to consolidate its achievements in solving food and clothing problem,accelerate poverty reduction, improve the ecological environment, enhance the development ability and vigorously promote the in-depth development of the cause of poverty alleviation and development.
Poverty reduction is a common cause of human society and China's poverty alleviation and development is an important part of the global poverty reduction. As a responsible country, China will continue to actively participate in the international poverty reduction, share advanced poverty reduction ideas and experience and deepen the exchanges and cooperation in the field of poverty alleviation and development. China is willing to make unremitting efforts jointly with the international community to create a beautiful world without poverty for common prosperity.
REFERENCES
"Seven-Year Priority Poverty Alleviation Program (1994-2000)"
"Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of China's Rural Areas (2001-2010)"
"Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of China's Rural Areas (2011-2020)"
"New Progress in China's Rural Poverty Alleviation and Development" (issued in November 2011)
"Outline for Poverty Alleviation and Development of China's Rural Areas (2011-2020) - Cadre Counseling Reading"
"Yearbook of China Poverty Alleviation and Development (2010)"
"Yearbook of China Poverty Alleviation and Development (2011 )"
"Selections of Research Reports on Poverty Alleviation Cases (2011)"

扫描下载手机客户端
地址:北京朝阳区太阳宫北街1号 邮编100028 电话:+86-10-84419655 传真:+86-10-84419658(电子地图)
版权所有©中国国际扶贫中心 未经许可不得复制 京ICP备2020039194号-2